EEG (electroencephalography) of the brain is a highly informative method for diagnosing the state of the central nervous system, based on recording the bioelectric potentials of the cerebral cortex during its life. The results of the study are recorded on paper tape or displayed on a computer monitor. Neurophysiologists at the Yusupov Hospital interpret the EEG results of the brain in adults using a computer program.
The patient receives a conclusion on the second day. If the results of EEG decoding are interpreted ambiguously, they are discussed at a meeting of the expert council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category. Leading neurologists and neurophysiologists collectively make decisions regarding the diagnosis and further tactics of patient management. The results of an EEG of the brain performed at the Yusupov Hospital are always accurate, since the study is carried out using the latest European and American equipment, and the decoding is done by candidates of medical sciences who have been trained in the best domestic and foreign diagnostic centers.
Normal EEG in adults
Decoding the EEG results consists of three sections:
- description of leading types of activity and graphic elements;
- conclusion after description with interpreted pathophysiological materials;
- correlation of the indicators of the first two parts with the clinical picture of the disease.
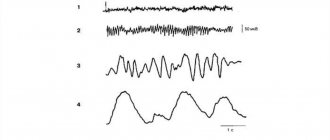
The main descriptive term in EEG is "activity". He evaluates any order of waves. The main types of activity that are recorded during the study and subsequently subjected to decoding, as well as further study, are the frequency, amplitude and phase of the waves. Frequency is measured by the number of wave oscillations per second. It is expressed in units of measurement - hertz (Hz). In the description, the neurophysiologist indicates the average frequency of the activity being studied.
Amplitude is the range of wave oscillations of the electrical potential. It is measured by the distance between the peaks of waves in opposite phases, expressed in microvolts (µV). A calibration signal is used to measure the amplitude. When interpreting the results, neurophysiologists interpret the most common values, completely excluding the rare ones.
The phase evaluates the current state of the process and determines its vector changes. Using an electroencephalogram, functional diagnostic doctors evaluate certain phenomena and evaluate the phases they contain. Oscillations are monophasic, biphasic and polyphasic.
Alpha waves
This type corresponds to a wave oscillation frequency in the range of 7-14 units per second. Alpha waves are a kind of transitional state when brain function is rebuilt between beta and theta waves. Calm playing of the piano is the closest analogue of rhythm.
A person’s sensations during the emission of alpha waves are characterized by relaxation of the brain. He may experience the same feelings as during meditation. Many describe alpha rhythms as a state as if the consciousness has fallen into a light sleep and is having dreams, while in practice people experience a decrease in concentration and are distracted from the entire world around them. Such waves are responsible for dreams and general ability to fantasize. Therefore, those who have not developed this range properly have poor memory and often experience gray dreams that they cannot remember.
Studies have shown that the initial level of alpha wave production is higher in extroverts.
It is generally accepted that the generation of waves of this frequency occurs with the help of white matter, which connects the elements of the brain with each other. With the dominance of the alpha rhythm, people are able to more effectively perform all tasks, remember new information, learn to carry out certain tasks, and cope with heavy physical activity. Also, at such moments, creativity increases, and in parallel with this, a positive outlook on things appears, and the world literally turns into bright colors before our eyes.
A special exercise allows you to develop alpha rhythms, as well as cause their influx. To do this, you need to sit in a comfortable position, relax your muscles, and breathe calmly and deeply. Additionally, you can imagine pleasant pictures that promote relaxation. For example, sunrise, a pleasant wind, nature against a backdrop of complete calm. Regular training will lead to increased self-control, abstract thinking, concentration, productivity, and improved sleep. If you want to reduce wave activity, then you just need to start thinking about something complex or, for example, solving unusual mathematical examples.
Albert Einstein spent most of his time in a state where alpha waves dominated his brain.
Electrical rhythms of the brain
The concept of “rhythm” in the EEG is considered to be a type of electrical activity that relates to a certain state of the brain and is coordinated by appropriate mechanisms. When deciphering indicators of the EEG rhythm of the brain, neurophysiologists take into account its frequency corresponding to the state of the brain region, amplitude and characteristic changes during functional changes in activity.
The characteristics of brain rhythms depend on whether the patient is asleep or awake. Brain activity recorded on the EEG in an adult has several types of rhythms, which are characterized by certain indicators and the state of the body.
On the EEG, the alpha rhythm is characterized by a frequency of 8 to 14 Hz. It is present in most healthy individuals. The highest amplitude values are observed in the resting state of the subject, who is in a dark room with his eyes closed. The alpha rhythm is best determined in the occipital region. It can be fragmentarily blocked or completely subside during visual attention or mental activity.
The wave frequency of the beta rhythm on the EEG fluctuates in the range of 13–30 Hz. Its main changes are observed when the subject is active. Pronounced fluctuations are detected in the frontal lobes under the obligatory condition of active activity (mental or emotional arousal).
The gamma rhythm has an oscillation range from 30 to 180 Hz. It is characterized by a rather reduced amplitude - less than 10 μV. Exceeding the amplitude limit of 15 μV is considered a pathology that causes a decrease in intellectual abilities. Rhythm is determined when solving situations and tasks that require increased concentration and attention.
The kappa rhythm is characterized by an interval of 8–12 Hz. It is observed in the temporal part of the brain during mental activity by suppressing alpha waves in other areas. The lambda rhythm has a range of 4–5 Hz. It is triggered in the occipital region when it is necessary to make visual decisions (searching for an object with open eyes). The vibrations disappear completely after concentrating your gaze on one point. The mu rhythm has an interval of 8–13 Hz. It starts in the back of the brain and is best observed in a calm state. Suppressed when any activity is started.
A separate category of types of rhythms that manifest themselves in sleep conditions or in pathological conditions includes 3 types of this indicator:
- The delta rhythm is determined in comatose patients and in the deep sleep phase, and is recorded when recording signals from areas of the cerebral cortex located on the border with areas affected by malignant neoplasms;
- the theta rhythm has a frequency range of 4–8 Hz, manifests itself during sleep, is responsible for the high-quality assimilation of information, and underlies self-learning;
- The sigma rhythm has a frequency of 10–16 Hz, is considered one of the noticeable and main oscillations of the spontaneous electroencephalogram, and occurs during natural sleep at its initial stage.
Based on the results obtained from recording the EEG, an indicator is determined that characterizes a complete all-encompassing assessment of the waves - the bioelectrical activity of the brain. A functional diagnostics doctor checks EEG parameters - frequency, rhythm and the presence of sharp flashes that provoke characteristic manifestations. On these grounds, the neurophysiologist makes a final conclusion.
The nature of rhythms and connections with brain functions
New discoveries in the field of electroencephalography (EEG) made over the past several decades have significantly changed the classical concepts on which the training of psychiatrists and neurologists in medical schools was based. According to classical concepts, information processing in the human brain is realized through the impulse (spike) activity of individual neurons. Oscillatory electrical activity (eg, EEG rhythms) was, at worst, rejected and ignored, and at best, considered background activity. An example is the book Principles of neuroscience, edited by E. Kandel, J. Schwartz and T. Jessel, which is considered the “bible” of scientists involved in the study of brain activity. The chapter on EEG electrical oscillations was missing from the fourth edition, and John Martin's chapter, “Collective Electrical Activity of Neurons: The Electroencephalogram and the Mechanisms of Epilepsy,” presented in the third edition, was discarded.
Over the past few years the situation has been slowly changing. We are now experiencing an EEG renaissance, driven by new methods for assessing human EEG and new experimental findings in animal studies that have allowed electrophysiologists to discover that changes in EEG oscillatory patterns play a critical role in maintaining brain function and can therefore be used to a powerful tool for diagnosing brain dysfunctions.
From a general point of view, oscillations are present in all physical and biological systems that strive to achieve equilibrium. In almost all cases, oscillations occur when a system is driven by two opposing processes: one that takes the system out of equilibrium and one that brings it back to equilibrium. In this respect, EEG fluctuations are no different from those in other biological systems. In the case of any observed EEG rhythm (such as alpha, beta or theta), we can always detect the factor that throws the neuron or neural network out of balance and the cause that brings it back.
However, oscillations can not only be a reflection of the action of two opposing forces in neural networks, but hypothetically can also serve as a source of a unifying principle in the organization of neural networks. For example, changes in the total local electrical potential created by neurons that generate a given rhythm can involve other neurons in this process that are not directly involved in rhythm generation. This entrainment synchronizes the activity of all neurons in the neural network with the rhythm generators. Despite attempts to prove this assumption, we still do not know whether it is correct or not.
Decoding EEG indicators in an adult
In order to decipher the EEG and provide accurate results, without missing any of the smallest manifestations in the recording, neurophysiologists take into account all the important points that may affect the indicators being studied, such as:
- patient's age;
- the presence of certain diseases;
- possible contraindications.
After collecting all the EEG data and processing it, the functional diagnostics doctor conducts an analysis and generates a final conclusion, which he provides for making a further decision on the choice of therapy method. Any disturbance in activity may be a sign of diseases caused by certain factors.
EEG disorders are considered:
- constant fixation of the alpha rhythm in the frontal lobe;
- constant violation of wave sinusoidality;
- presence of frequency dispersion;
- exceeding the difference between the hemispheres by up to 35%;
- amplitude below 25 μV and above 95 μV.
The presence of violations of this indicator indicates possible asymmetry of the hemispheres. This may be the result of malignant neoplasms or cerebral circulatory disorders (ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke). A high frequency indicates traumatic brain injury or brain damage.
If a high amplitude of the delta rhythm is detected, the neurophysiologist can assume the presence of a space-occupying tumor in the brain. Inflated values of the theta and delta rhythm, which are recorded in the occipital region, indicate impaired circulatory function, inhibition and a delay in the development of the child.
Beta waves
Another type is beta brain waves. They are recorded in the range from 14 to 30 vibrations per second. Such fast waves are normal and are activated when a person is involved in the world around him. They are also actively emitted when excited, stressed or anxious. In order for them to begin to dominate, it is enough to start a conversation with any person. All the attention of people with dominant beta waves is directed to the environment.
Beta activity in the human brain is associated with increased blood pressure and a sharp increase in metabolism. Its rhythm is similar to drumming. If the brain rarely functions in the beta rhythm, then the person will experience frequent depression, lack of normal concentration, and very poor memory.
The dominance of such waves is considered a state close to stress, regardless of the nature of a person’s emotions.
You can develop beta rhythms through normal active life. Any communication, physical activity, manifestation of a social position, stress, fears - all this contributes to their increase. You can reduce their activity by simply relaxing and giving up negative thoughts.
There are three types of beta waves. They are separated for a more accurate characterization of several intervals, because The frequency range is quite large, and the sensations may be different. The following types are distinguished:
- Low (13-16 hertz). When the activity of brain neurons begins to emit impulses at this pace, weak involvement in the world around us begins to appear. This activates the left hemisphere of the brain. The person loses the feeling of relaxation, but there is still no excitement. With regular training of this frequency, the skill of managing concentration and attention will appear.
- Medium (16-18 hertz). At such frequencies, the right hemisphere of the brain is connected to work. An awareness of one’s “I” and surrounding things appears. People start to feel a little excited and involved in the world. When performing training, intellectual abilities and concentration will develop.
- High (18-30 hertz). Such waves are compared to driving fast in a sports car. The sensations are similar to those when a lot of adrenaline is released. Strong excitement and interest in the world around us and everything that happens appears.
The work of the brain in such a rhythm causes two sensations. On the one hand, a person is active and shows interest in the world around him. On the other hand, he is under a lot of stress.
Decoding the EEG of the brain in children
EEG in children has its own peculiarities. An EEG recording of a premature baby born at 25–28 weeks of gestation looks like a curve in the form of slow flashes of delta and theta rhythms, which are periodically combined with sharp wave peaks of 3–15 seconds in length with a decrease in amplitude to 25 μV. In full-term newborns, these values are divided into 3 types of indicators:
- when awake (with a periodic frequency of 5 Hz and an amplitude of 55–60 Hz);
- in the active phase of sleep (with a stable frequency of 5–7 Hz and a fast, low amplitude);
- during restful sleep with flashes of delta oscillations at high amplitude.
Over the course of 3-6 months of a baby’s life, the number of theta oscillations is constantly growing. The delta rhythm is characterized by a decline. From 7 months to one year, alpha waves are formed in the child, and delta and theta gradually fade away. Over the next 8 years, the slow waves on the EEG are constantly replaced by fast alpha and beta oscillations. Until the age of 15, alpha waves predominate. By the age of 18, the formation of the biological activity of the brain is completed.
In order to undergo an examination and decipher the EEG results, call the Yusupov Hospital. The contact center is open every day around the clock. Neurophysiologists analyze the EEG over time and compare the results of the study with the normal EEG.
Schumann resonance.
This resonance is the electromagnetic frequency of the Earth, which has long been equal to 7.8 Hz, which coincides with the Alpha rhythm of the human brain. The analogue is an orchestra, the instruments of which merge into one quiet sound and an organ plays in the background.
The Schumann frequency is growing and today is 14 -15 Hz, corresponding to Beta - the rhythm of the brain, conscious activity. Because of this, most people experience dizziness, the brain is forced to work at ever-increasing frequencies.
With a further increase in frequency, the brain will reach 30 Hz or more, little studied
Gamma is the brain rhythm responsible for inspiration and creativity.
At this level, reason and reason are almost powerless; other mechanisms of perception and action operate here. It's like a superstructure over human consciousness. The frequency of brain vibration is 50 Hz, Zen - Buddhists call enlightenment. By increasing its frequency, the Earth thereby forces our brain to come out of hibernation and work more consciously. Every person intuitively has the ability to adjust their brain rhythm to the desired wavelength range. Or he does it consciously, knowing the adjustment mechanism.
Gamma waves
The last type is gamma brain waves. They are characterized by an extremely high frequency from 30 to 120 hertz. Such fluctuations in the brain are called enlightenment. A person’s mind and reason are completely turned off, transferring control over perception to other mechanisms located in the depths of the unconscious. Gamma rhythms are responsible for inspiration and creativity.
This high-frequency wave rhythm appears during learning or processing complex information. However, then it is in the region of 30-40 pulses per second. But at the same time, the production of beta-endorphins, which work together with the brain, is stimulated. They activate the processes of awareness and perception of the surrounding world.
The high frequency of the gamma rhythm allows you to recall any information much faster. Special studies were conducted when a group of students listening to gamma rhythms daily, after 2 weeks, gave a much more positive test result compared to the second group, whose participants lived in their usual way.
Gamma stimulation helps reduce the frequency and intensity of migraine attacks.
People can benefit from gamma rhythm training. After the first hours of working on yourself, your brain waves will give you a feeling of happiness, make you change your view of reality and improve the quality of brain activity. In more detail, this is what awaits such a person:
- Heightened senses. Efficiency of using smell, vision, taste. It will be possible to simultaneously process many feelings at once.
- Increased compassion. This will at the same time allow for an even greater increase in gamma activity.
- Improved brain function. Intelligence, attention, learning ability increase, memory is strengthened, information is processed faster.
- Perception expands. A different view of the world, the arrangement of social life, and one’s “I” appears.
- Positive thinking develops. The appearance of any depressive conditions is eliminated, and the outlook on the world becomes positive.
The negative characteristics of such a rhythm include an increasing feeling of anxiety and the unpreparedness of many people for changes in their perception of the world.
You can achieve the development of gamma waves in the human brain with the help of good sound sleep, regular meditation or yoga, special stimulants, and hypnosis.
Delta waves
The delta waves of the human brain are recorded at the lowest frequency. They can operate in a rhythm from 0.1 to 4 hertz. When neurons begin to emit such waves, people are in a state of trance or dreamless sleep. The rhythm can be compared to a light symphony
This type of waves is associated with a person’s involvement in some process when everything else does not interest him. It is believed that every child under one year of age constantly experiences a predominance of delta waves in the head. They help to navigate in space and time, make one anticipate various dangers, increase intuition, and develop instincts. As a rule, the presence of developed delta waves is observed in people engaged in research into human psychology and feelings, i.e. from psychotherapists.
If you notice the work of such waves, they will immediately complete their activity.
This is the type of waves that allows you to establish a connection with the unconscious. To do this, you will need to overestimate the degree of their activity. When activated, a person’s consciousness turns off and is distracted from the outside world, and with good training, one will be able to independently and consciously enter a state of trance. However, even with weak delta waves, a person may have problems concentrating on any task. To do this, you will need to weaken their effect by showing maximum activity.
Some people have a large amplitude of delta waves. They have very developed intuition. They can literally think a minute or second before an event that it will happen. This often happens to them, for example, before meeting an acquaintance or shortly before receiving a call on their mobile phone. They can also sense other people. This manifests itself both emotionally and physically. An excess of waves leads to problems. They manifest themselves psychologically. Waves of excessive brain activity of this frequency lead to the fact that a person receives too much information at an unconscious level. Also, people often feel guilty for someone else’s pain, which they suddenly begin to feel.
Clairvoyants and healers actively use the power of delta waves when receiving the necessary information.
Causes of alpha rhythm disturbance
In addition, changes in brain activity indicators may be accompanied by the following pathologies:
- essential hypertension, epilepsy, including that developed due to drug use (in such situations, direct asymmetry of frequency and amplitude in the left and right hemispheres of the brain is diagnosed);
- hypertension (manifested by a decrease in rhythm frequency);
- oligophrenia (accompanied by increased activity of α-waves);
- tumors of various origins, cysts, pathologies of the corpus callosum (characterized by asymmetry between the cerebral hemispheres, reaching 30%);
- deterioration of blood circulation.