Anatomically realistic 3D brain model depicting localized activity in real time. Each color represents the source of bioelectrical activity and connectivity in a different frequency band (theta, alpha, beta, gamma); gold lines represent anatomical white matter fiber tracts. The supposed transfer of information between brain regions is visualized as pulses of light passing along fiber tracts connecting these regions
Bioelectric activity of the brain
(BEA) is the electrical activity of neurons associated with their excitation, i.e. with a shift in membrane potential.
The bioelectric activity of the brain is based on transmembrane ionic currents, which give rise to the phenomena of action potential and impulse activity of neurons. In this way, neural transmission of signals is carried out in the form of short electrical impulses, each of which represents the main information unit of the brain (quantum of information).12
Mechanism
The bioelectrical activity of the brain is explained by the physiology of the nervous tissue. Each neuron is covered by a membrane. Protein pumps built into the membrane create a difference in electrical potentials inside and outside the cell by pumping charged ions of sodium, potassium, chlorine, etc.
The excitation of a neuron is associated with the opening of ion channels and the passage of ions through the membrane, which leads to a change in voltage, which is recorded by various methods in the form of bioelectrical activity.
An individual neuron is in a continuous process of bioelectrogenesis. Excitation of a nerve cell can occur when it is irritated, i.e. when an impulse arrives from other neurons, and in some cases spontaneously. There are no other sources of the bioelectric field, except neurons, in the brain.
➥ Main article: Bioelectric potentials
Vertical integration of spatial scales from the molecular level (nanometer scale) to the entire brain (centimeter scale)
Levels of brain organization
Conventionally, there are three levels of brain organization at which different forms of bioelectrical activity can be studied: microlevel (activity of one neuron), mesolevel (activity of a local group of neurons) and macrolevel (activity of different areas of the brain).
➥ In more detail: Functional systems, structure and organization of the brain
Microscale is the lowest level of brain organization, reflecting the activity of single neurons due to synaptic and molecular mechanisms.
Mesoscale (English mesoscale) is a level located between the micro and macro levels, at which interactions between large neural ensembles occur.
Macroscale - used to define brain regions and large-scale connections between them.
Methods for recording bioelectrical activity of the brain
Registration of BEA at different levels of organization
(A) Scalp electrode (green), multicontact macroelectrode (red) and microelectrode (blue) (resolution: volume
The study of bioelectrical activity is carried out using electrophysiological methods based on recording fluctuations in the potential difference between two points in the medium, for example, between two electrodes located on the scalp.
Electroencephalography (EEG, English electroencephalography, EEG) is a non-invasive method that allows you to record the bioelectrical activity of the brain from the surface of the scalp.
➥ Main article: Electroencephalography
Magnetoencephalography (MEG, English magnetoencephalography, MEG) is a method based on recording a magnetic field that is formed due to the electrical activity of neurons.
Electrocorticography (ECoG, English electrocorticography
, ECoG) is an invasive method of recording bioelectrical activity using electrodes located on the surface of the cerebral cortex.
➥ Main article: Electrocorticography
Microelectrode methods are a set of methods that use microelectrodes for intra- or extracellular recording of biopotentials. These include recording the activity of a single neuron, multi-unit activity, local field potential (LFP), as well as patch clamp and dynamic clamp methods.
➥
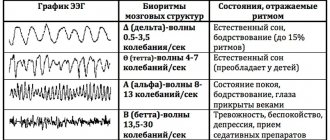
What are the rhythms?
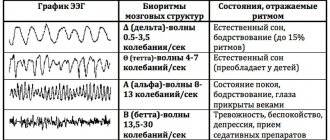
The rhythms generated by the brain differ into five types depending on the amplitude and frequency of vibrations:
- The alpha rhythm is recorded in 95% of healthy patients at the moment of relaxation, when they close their eyes. Best expressed in the occipital regions. α-wave frequency 8-12 Hz. With visual stimuli, there is a deficiency of this radiation. At the same time, in people with congenital blindness or optic nerve atrophy, the α rhythm is absent.
- Beta rhythms are the fastest brain oscillations in the range of 12-40 Hz. They are associated with the processes of learning and concentration. Therefore, they are formed in a child during the development of logical thinking. Normally, this process ends by age five. Beta waves are generated naturally when you are awake. Under stress, their level increases, but a deficiency, on the contrary, is associated with absent-mindedness syndrome, depression and emotional disorders. Without β-activity, no meaningful human activity is possible.
- The gamma rhythm is clearly visible when solving complex problems. These are the highest frequency rhythms generated during an active thought process. Completely disappears in the deep sleep phase.
- The delta rhythm is characteristic of the recovery period and natural sleep. These are the slowest waves. They are formed in the prenatal period. Asynchronous delta waves appear during coma or drug intoxication.
- Theta activity manifests itself in the fetus already at 2-3 months and predominates in children under three years of age. They represent patterns of electrical activity in the range of 4-8 Hz. Normally, theta waves of an adult appear in the twilight state, during the transition from sleep to wakefulness. A significant number of them can be observed in a confused state, with mental disorders. A large amount of θ rhythm can signal a state of chronic stress.
How to “accelerate” your brain for children and adults
The human brain is one of the most complex and poorly understood systems, all of whose capabilities we do not yet know. However, over the years of research, enough information has accumulated on how to activate and improve brain function. Today we will talk about how to develop the intelligence of children and adults, and consider various ways to activate brain activity.
A little theory
The human brain is an organ of the central nervous system and consists of many brain cells and neurons (about 100 million of both). In size it can be compared to a medium-sized head of cauliflower; the brain weighs 1-2 kg (1020-1970 grams). It is worth noting that mental abilities are not related to brain size. Thus, the largest and heaviest brain (2850 grams) was found in a person suffering from mental retardation.
The brain consists of 4 main sections, each of which has its own functions:
- Medulla. Located in the back of the skull, it is a kind of transition from the brain to the spinal cord. The main function of this department is reflex. Thanks to the medulla oblongata, reflex actions such as coughing, sneezing, etc. are carried out, breathing processes and cardiac activity are regulated. The medulla oblongata connects the spinal cord with the overlying parts of the brain - it conducts signals from one to another.
- Rhomboid (hind) brain. Consists of the pons and cerebellum, located in the back of the skull near the medulla oblongata under the hemispheres. Responsible for coordination of movements, maintaining body position in space and balance, regulation of muscle tone, and the implementation of a number of reflexes associated with the vestibular apparatus and muscles.
- Midbrain. Located exactly in the middle of the skull. With its help, it is possible to correctly orient a person in space, maintain body posture and regulate muscle tone, and primary processing of data from the senses (vision and hearing).
- Forebrain. In turn, it is divided into: Diencephalon. Located above the middle, consists of the thalamus, epithalamus, hypothalamus. This is where information comes from all senses, which is processed and selected for further transmission to the cerebral cortex (the most important and significant information is selected). This department is also responsible for the emergence and regulation of emotions, for ensuring the activity of all organs and systems of the body, for ensuring the constancy of the internal environment, and metabolism. The centers of pleasure/displeasure, thirst/satiation, fear, etc. are located here.
- Finite brain. Represented by the cerebral cortex. It is here that the most complex processes are carried out: conscious behavior, thinking, development of intelligence, final processing, analysis and evaluation of information from the senses, coordination of all activities of the body, etc.
It turns out that the leading part of the brain is the telencephalon or cerebral cortex. This is where the main efforts should be directed to activate the brain. At the same time, it is worth remembering that only the coordinated work of all parts can ensure the functioning of mental activity at the highest level.
"Feeding" for the brain
Our brain needs nutrients and vitamins no less than other organs. They are especially necessary for children, because... they experience active growth, as well as people engaged in intense mental work. Regular fruits and special vitamin complexes can be “feeding” for the brain.
Say "Yes!" physical activity and fresh air
Brain function will be much better if a person is engaged in physical activity and spends enough time in the fresh air. Children and adults who encounter difficulties at work (for example, when doing homework or writing a report) are advised to take a short break, ventilate the room well, or go for a walk, and do a simple warm-up (bends, turns, squats, etc.). Tilts, turns and rotations of the head are especially useful.
Exercise is a great way to activate your brain. Photo source
Musical pause
Research by French psychologist Francis Rocher has shown that listening to music can increase brain activity. However, not all pieces of music are suitable, but only those that are distinguished by harmony, smoothness, and the absence of excessive volume and noise. The works of Mozart are ideal, with the help of which Roscher conducted his research.
About the benefits of “new products”
The process of cognition helps to keep the brain in good shape and constantly activate its work. It would seem, why then do schoolchildren need any more exercises, since they already visit an educational institution every day and learn something new? However, school activities may not always help activate the brain. This may be due to the ease/complexity of the material being studied or lack of interest. Therefore, it is equally important to pay attention to the child’s development outside of school: buy educational books/games/films, go to exhibitions and theaters, explain the principles of operation of various instruments and devices, etc. This advice is also good for adults: if you want to increase mental activity, surround yourself with new unusual things that require study, strive to obtain new information.
Orientation in space
Orientation in unfamiliar (unfamiliar) places stimulates brain function well. To do this, it is important to teach the child how to use a compass, determine the parts of the world, navigate by the sun, etc. Parents can teach the student these basics on their own or enroll him in a special section.
If you don’t have the opportunity/desire to go on a hike, you can train your orientation skills in familiar conditions (for example, in an apartment, in a country house, in a yard), but with your eyes closed.
Training of cognitive processes
Photo source
Attention, memory, thinking and speech are the main cognitive processes that are provided by the cerebral cortex. Training these processes can significantly increase brain activity. Depending on the specific process, we can distinguish:
- Memory training. To do this, you can use memorizing poems, retelling the text (immediately after reading and after a certain time has passed), long-term observation of something, and then reproducing what you saw on paper in the form of an image, and various memory games.
- Attention training. Various attentiveness tasks will help with this: searching for differences between pictures, finding and crossing out a particular letter in a set of letters, studying dual images, tracking something with subsequent detailed reproduction, etc.
- Thinking training. This can include solving crosswords, puzzles, math and logic problems, analyzing text, thinking about a specific topic, etc.
- Speech training. Exercises with tongue twisters and sentences with a predominance of a certain letter (The Greek rode across the river...), retellings and reading poems out loud in front of a mirror, learning text by role, etc. are ideal.
Stimulating communication
To improve a child’s intellectual activity and activate his brain, it is necessary to provide him with communication with smart people. These could be older friends, peers who are interested in something and purposefully study this subject (for example, astronomy), adults engaged in intellectual work. Communication with interesting people, whose knowledge and capabilities exceed the knowledge and capabilities of the student, will make him strive to improve his mental activity and will keep him in constant good shape. The main condition here will be the child’s interest in these people.
Thinking + Action
To activate the brain, it is important to constantly think and translate these thoughts into action. These two processes are closely interconnected and stimulate each other: this is how action is born from thought, and in the process of action new thoughts and “insights” can arise. Therefore it is important:
- Encourage your child to create different ideas. Invite the student to come up with a new game, an unusual way to solve a problem, develop an event plan, etc. A good option is to solve practical problems that are interesting to the child: developing a new school education system, ways to combat unemployment, creating a company that produces computer games, etc.
- Bring these ideas to life. After the student has come up with an idea, try to bring it to life with him, even if it seems impossible. In the process of action, the child can change the plan of action, make adjustments, and refine something. Help the student with this if necessary.
- Discuss ideas and their implementation. Together with your child, evaluate the idea, note its pros and cons, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of the chosen method of action.
Photo source
The brain is one of the most complex organs, but the quality of its work can be improved. In order for him to always be in good shape and work actively, it is necessary to receive nutrients, not neglect physical activity and constantly stimulate brain activity by solving all kinds of problems and learning something new.
Header image source
Did you like the article? Share with your friends:
Wise owl June 19, 2015
Therapeutic effect
Brain wave therapy continues to be studied. According to already available data:
- Alpha rhythms help reduce anxiety, tension and restlessness, and improve memory. It accelerates blood supply to the brain structures, increasing the saturation of the body with oxygen and beneficial microelements. Facilitates the recovery period after illness. Reduces the negative impact of traumatic situations. Determines the release of the neurotransmitter serotonin, increasing its level in the body.
- Beta stimulation helps improve learning, communication skills and perseverance in patients. In addition, such exposure helps reduce fatigue.
- The effect of gamma rhythms has proven itself to be effective in enhancing the speed of information processing and stimulating short-term memory. These frequencies have also been found to have a beneficial effect on the brain in chronic migraine. In approximately half of the subjects, the frequency and intensity of attacks decreases.
- Stimulation of the δ rhythm helps reduce stress levels and relieve attacks of chronic pain, including cephalgia.
- Exposure to θ waves can enhance creativity, improve memory, control over the emotional sphere, and enhance intuition. It helps reduce anxiety and stress, strengthen the immune system, and enhance long-term memory, since the rhythm of theta waves is characteristic of the hippocampus, the part of the brain responsible for storing information and memories.
A way to increase brain activity by changing your mindset
There are special techniques and exercises that can be used to increase brain activity and its capabilities. However, in order for mental activity to be consistently high, you need to apply these principles not from time to time, but systematically, linking them with your lifestyle.
Changing habits
Changing familiar locations, changing familiar surroundings, or introducing something new into everyday processes can increase neuroplasticity—the ability of the brain to create new neural networks and connect them with previously formed ones into a single system. This allows the brain to “look” at any problem in a new way, connecting previously unused systems to the solution.
To increase the number of connections, it is recommended to change established routes, try new food in new cafes and restaurants, get up on the other foot, brush your teeth alternately with your right and left hand, and make other changes to your usual life.
Neuroplasticity is a multi-level manifestation of the brain’s ability to restore functions, which is observed both at the cellular level and on the scale of the entire brain, where “roles” and departments responsible for processes are reassigned. In particular, this property of the brain is actively used in the development of memory and learning.
wandering mind
When working on one problem, if the solution algorithm is obvious, it is advisable to focus on it. But if the solution is not obvious or if in the process of intellectual activity a multitasking effect has arisen that stops the process, it is recommended to be distracted and allow your mind to wander. This allows the brain not only to rest, but also to be able to “search” for a solution in those neural networks that, with a narrow focus, ended up on the periphery.
Physical activity
Intellectuals often consider physical activity a waste of time. But the results of various experiments showed a direct relationship between intellectual capabilities and regular varied physical activity.
So, on average, 10% higher intelligence scores were recorded in those children and adults who engaged in physical education several times a week - at least taking long walks. Dancing as a way to improve brain activity has shown good results in the fight against dementia.
This is partly due to the inevitable connection during training of various parts and areas of the brain, with changes in rhythms, and the formation of the skill of quick decision-making. Partially - with improved blood circulation during physical activity.
Alpha wave stimulation
There are several ways to stimulate the body’s wave activity:
- Breathing exercises that allow you to maintain deep breathing saturate the brain cells with oxygen. Systematic breathing exercises promote the generation of alpha waves.
- Listening to stereo sounds with alpha waves is a technique accessible to everyone.
- Yoga and meditation are powerful activators of the α rhythm.
- Hot baths can help you relax and switch to alpha wave production mode.
Features of the study
For a more accurate result, doctors may order an EEG study with sleep deprivation. For this, the patient is asked to stay awake for 24 hours to identify pathologies in the brain. During recording, additional stress may be applied in the form of light stimulation or further sleep deprivation.
EEG video monitoring is used to identify problems related to neurology. This is a long-term study that captures synchronous video recordings and recordings of brain activity under various loads. The patient may be forced to move or experience various emotions or behaviors. Often used to detect epilepsy or sleepwalking. This technique is used for auditory hallucinations, panic attacks, and frequent fainting.
EEG is a painless procedure that does not harm the body. This is a quick way to identify or understand the features of the brain. It is carried out only after the appointment of the attending physician and has no side effects.
Pathological deviations
Disturbances in brain wave activity are observed when:
- Oligophrenia. With it, the total activity of alpha rhythms is abnormally increased.
- Epilepsy, which causes disturbances in the frequency and amplitude of wave activity. This is associated with the development of direct or interhemispheric asymmetry in the hemispheres of the brain.
- Hypertension, weakening the frequency of alpha rhythms and increasing beta activity. Circulatory and cardiovascular system disorders always affect brain wave activity. A similar picture can be observed with beta-lactamase activity of bacteria.
- Paranoid schizophrenia, in which the brain generates an increased number of beta rhythms.
- Cysts and inflammatory processes of the corpus callosum. They cause severe asymmetry between the hemispheres, reaching 30%.
- The pathological picture can occur with traumatic brain injuries, congenital or acquired dementia, and delayed psychomotor development in children.
To evaluate alpha rhythms, it is necessary to undergo an EEG from time to time. You can find out the addresses of clinics that perform this diagnostic procedure on the website.
What does electroencephalography of the brain show?
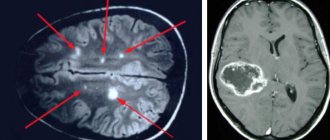
The electroencephalogram, as a research method, has historically been used in many clinical situations. Based on the difference in the received signals and the prevailing brain rhythms, focal brain formations were determined. Also, some neurotic conditions, cerebral palsy and other developmental defects have their own characteristics that appear on the EEG. However, in modern medicine, neurology remains a small niche of indications. EEG is used to diagnose epilepsy; also, much less frequently, EEG is indicated for the diagnosis of rare diseases, for example, spongiomorphic encephalopathies (in particular, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease). The study can also serve as a method for assessing the effectiveness of anticonvulsant therapy.
EEG shows the organization and prevalence of brain rhythms and allows one to detect pathological rhythms and phenomena. The presence of pathological elements, differences in rhythms and their disorganization in different leads may indicate dysfunction of various parts of the brain. Also, epileptiform phenomena make it possible to diagnose epilepsy. A diagnosis is considered absolutely reliable if, during the recording of the study, an epileptic attack was recorded, which has its own characteristic features on film.
Disadvantages of the method
Excessive wave stimulation can cause negative reactions in the body. So, with an excess of alpha activity, a decrease in concentration develops, the formation of attention deficit, depression, and a decrease in visual clarity. A person begins to need daytime sleep and gets tired faster. In addition, under the influence of alpha waves, suggestibility increases.
The downside of beta wave stimulation is increased anxiety, overexcitement and the development of obsessive-compulsive disorder. There are signs of stress and paranoia. Also, under the influence of such stimulation, muscle tension increases and insomnia occurs. The effect on the cerebellar amygdala and hypothalamus provokes an increase in blood pressure.
When exposed to theta waves, you can develop concentration disorders, depression, hyperactivity, or, conversely, apathy. Under the influence of such stimulation, drowsiness, indifference to life, and increased suggestibility occur.
Therefore, before resorting to any methods of stimulating brain wave activity, it is better to consult with specialists.
Features of the study
EEG helps record brain activity using metal electrodes. With their help, brain vibrations are captured, recorded and displayed on the monitor. The result can also be transferred to paper for further study. The resulting image in the form of waves is a graphic duplication of the brain in real time. The patient, while in a special room, receives the necessary stimulation using sound, light or sedatives. The entire procedure takes from 30 minutes to 2 hours and is carried out only during daylight hours.