What it is?
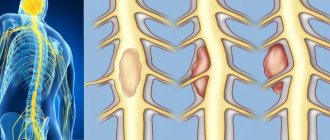
Myelitis refers to all inflammatory processes of the spinal cord affecting the gray and white matter , or any spinal inflammation. They can be primary and secondary; the causes of primary processes, which are viral in nature, largely remain a mystery.
Myelitis is an inflammation of the inner and outer parts of the spinal cord
Secondary myelitis can manifest itself as complications of many diseases - measles, scarlet fever, typhoid fever, influenza, HIV infection, tuberculosis, syphilis and others.
The severity of the symptoms of the disease varies and depends on the form and its prevalence, but in any case it is severe, difficult to cure, and is fraught with serious complications. Sources of infection and the poisons (toxins) they release, entering the spinal cord through the lymphatic and circulatory system, lead to inflammatory and dystrophic abnormalities in it. Viral myelitis affects the spinal membranes, roots and nerve endings.
Picture of the course of the disease
Factors causing the disease lead to swelling of the spinal cord . Its beginning is considered to be the moment when the pathological process is launched, the next stage of which is the appearance of blood clots in the vessels due to circulatory disorders. And this leads to worsening swelling, i.e. the neurological process proceeds in an unbreakable circle.
Partial or (in some areas) even complete circulatory disorder provokes maceration (softening) and death (necrosis) of tissue . During the process of rehabilitation after an illness, areas of necrosis grow with connective tissue, i.e. transform into scars.
Scar tissue is unable to function, which causes pathological abnormalities (some or many) to become permanent. The spinal substance remains swollen, replete with infiltrates and hemorrhages, loses elasticity, and the “butterfly” retains its vague outline.
Classification
In most cases, the exact cause of myelitis is not known, but the factors that provoke it have been identified.
Diseases are classified according to etiology or cause of occurrence into four types:
- Infectious . This is the most common form, because observed in almost half of patients. It is divided into primary, when the infection initially entered the spinal cord, and secondary. In this case, inflammation of the spinal cord is a complication of another disease. Infectious myelitis is most often of a viral nature, sometimes it is provoked by a meningococcal infection. Secondary infection is often observed with osteomyelitis of the spine or due to infection through the blood when the whole body is affected. In addition to general intoxication, in these cases symptoms of a specific viral or bacterial disease also appear. For example, with measles it is a cough and a characteristic rash.
- Intoxication myelitis in many cases is a consequence of acute or chronic poisoning (harmful production) with salts of heavy metals, solvents, and alcohols.
- Traumatic – due to spinal injury. This includes mechanical damage or compression of the spinal cord with disruption of its functions, and possible penetration of infection into the spinal canal through an open wound.
- Neuroallergic (autonomic) . It is caused by systemic diseases, for example, in multiple sclerosis, myelitis is one of the signs of the disease. It also manifests itself in the early stages of the appearance of cancerous tumors.
| Based on the location of the source of inflammation in a particular spinal region, myelitis is divided into: | By degree of distribution: |
|
|
Myelitis can be classified depending on which part of the brain is inflamed
Prevalence
This disease, fortunately, is not considered common, because... occurs in 5 people out of a million .
Why does myelitis occur?
The brain is responsible for all processes in our body. Information from various organs is sent to brain cells, where it is analyzed and then transmitted along nerve fibers to various organs of our body. The cause of myelitis (like most other diseases) is a combination of various factors.
Under the influence of these factors, neural connections are disrupted, and therefore certain parts of the brain begin to work poorly. In other words, the brain stops giving the “correct” orders for the smooth functioning of your neural system, which leads to myelitis, and then to more serious consequences.
Risk factors, causes
In addition to the etiology of the disease already listed, there is also a risk of damage to the spinal cord for the following reasons:
- allergy to the vaccine during vaccination;
- as a consequence of treatment of a malignant tumor with radiation.
- A disruption of the immune system, when the tissues of the spinal cord are not perceived as “our own”, and protection against them is activated with the production of antibodies.
There are no patterns in the risk of getting it based on gender and age. But some sources believe that teenagers 10-20 years old and older people are more often susceptible to myelitis.
Consequences
Did you know that...
Next fact
If the course of the disease is unfavorable, the following complications of the disease are possible::
- Bedsores - due to deterioration of skin nutrition in long-term bedridden patients.
- Contractures are a disorder of joint mobility in paralyzed limbs.
- Inability to restore the functions of organs and systems due to scar changes in the spinal canal: paralysis, incontinence.
The consequences of the disease depend on the severity of its course, the localization of foci and the degree of their spread . So, if after 3 months there is no improvement, then the patient faces disability or even death. The most dangerous for the patient’s life is the localization of inflammation in the cervical spinal cord, and if other parts of it are affected, this can lead to paralysis of the limbs.
Video: “How the spinal cord works”
Symptoms of myelitis
Among the signs of this neurological disorder, the first to appear are symptoms characteristic of any inflammation in the body. This is body temperature, often rising to 39-40 degrees or more. At the same time, aching bones, chills, a feeling of fatigue and general malaise, which are common for high temperatures, may occur. In this regard, the first signs of myelitis are often mistaken for typical cold symptoms.
Neurological disorders become noticeable later, when the lesion manifests itself as pain at the site of inflammation. Transverse myelitis causes especially severe pain. Discomfortable sensations spread not only to the back area, but also to the limbs, radiating to the internal organs.
The set of signs of myelitis depends on its stage and place of development. For example, symptoms such as loss of sensitivity, severe numbness and paresis of the legs are observed in cases where the disease affects the lumbar region. These conditions are accompanied by the absence of reflexes and impaired functioning of the internal organs of the small pelvis.
If myelitis is localized in the cervical region, then its main symptom is difficulty breathing, speech impairment, pain during swallowing. General malaise, dizziness and weakness also appear.
Myelitis of the thoracic spine is expressed by stiffness of movements and the presence of pathological reflexes. In this case, disturbances in the functioning of certain organs may occur.
If such symptoms are detected, it is important to immediately seek professional help, since prolonged inactivity aggravates the problem as a result of the rapid development of the disease. The stronger the tissue damage, the more difficult it is to return the spinal cord to its previous state, since its structure may change irreversibly. This threatens the loss of ability to work and the ability to move fully.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
The symptoms of myelitis change at different stages of the disease. The primary manifestations of its infectious form are similar to other infectious diseases. This is a sharp increase in temperature to high numbers, chills, weakness.
Then they become more specific:
- Back pain , which is often not local in nature, but spreads to other parts of the body. This occurs due to the involvement of the spinal cord roots in the inflammatory process, as in radiculitis. This symptom quickly becomes acute.
Pay attention to the symptoms of myelitis. If the cervical part of the spinal cord is damaged, this is paresis (muscle weakening), and if the phrenic nerve is damaged, there is a risk of respiratory arrest. Inflammation of the upper part of the cervical spine is especially dangerous, threatening disorders of the medulla oblongata. And localization of the process in the lower part of the cervical region is dangerous due to persistent motor dysfunctions.- Damage to the thoracic part of the spinal cord, which is more common than other types, is characterized by spastic paralysis of the legs with muscle hypertonicity and cramps.
- Damage to the lumbosacral portion of the spinal cord is characterized by paresis in the legs and dysfunction of the pelvic muscles (incontinence). Muscles deprived of normal nutrition and regulation (due to nerve damage) gradually atrophy.
- Sensitivity disorders below the site of inflammation . This is a complete absence of pain, insensitivity to touch, cold, etc.
Diagnosis often relies on data from various spinal punctures (spinal fluid analysis). MRI of the spine and myelography are also used. These methods, together with symptoms and history, in most cases are sufficient to determine an accurate diagnosis.
Find out more about other spinal infections:
- To learn about spinal spondylodiscitis, follow this link
- Symptoms and treatment of spinal epidural abscess of the spine
- What is spinal discitis and what is the clinical picture of the disease, is described in the following article
- You can learn more about the diagnosis and treatment of Pott's disease on the page
- You can find out whether spinal tuberculosis is contagious or not here
Treatment
Treatment of this dangerous disease is carried out only in a hospital setting , it is long-term and complex, including drug therapy, physical therapy, careful care to prevent bedsores, massage and exercise therapy. Read more about some of these methods.
Drugs
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed for infectious inflammation of the spinal cord. In conservative treatment, antibacterial drugs are used to combat infection or septic complications . For this, Prednisolone is used, the course of treatment of which is 2-6 weeks, broad-spectrum antibiotics in large doses and sulfonamides.
They include desensitizing agents (Tavegil, Suprastin), vasodilators (Eufilin, Papaverine), hypocoagulants (Curantil, Heparin), antioxidants and vitamins C, group B, melliktin - to restore motor functions, reduce muscle tone in case of paralysis.
And if urination is impaired, they practice frequent catheterization , rinsing the bladder with manganese, boric acid, and prescribe diuretics and antimicrobial agents (Furagin, Furazolidone).
Bedsores are washed with peroxide, the pus is swabbed with sodium chloride, bandages with Vishnevsky ointment, syntomycin emulsion, sea buckthorn oil are applied to them, they are quartzed, and healing is accelerated by rinsing with insulin. To treat cystitis, chloramphenicol and biomycin are used.
Surgery
In the acute form of transverse myelitis with aggravating symptoms, treatment is only surgical. This method is also necessary for purulent or septic lesions located adjacent to the spinal cord .
Exercise therapy, massage
Passive exercise therapy classes are carried out from the second day of the disease.
Physical therapy exercises at different stages of the disease:
- In the first period they are done lying on the back, stomach or side, and possibly on all fours at a slow pace. ¾ of the complex consists of general strengthening and breathing exercises, and the rest is special. On days 10-15 they are supplemented with training of the buttocks, perineal and posterior muscles.
Exercise therapy for myelitis should be performed carefully and only under the supervision of a specialist. Then, lying on your stomach, train the muscles of the back and shoulder girdle 20-30 times. If the lower back and chest are affected, by the end of the month the patient should learn to roll over onto his stomach, then move in bed with the help of his hands, and within 2 months get on all fours (first with help). - In the second period, training of coordination, balance, stability while sitting and standing, maintaining posture in a calm state and when moving, predominates. This also includes exercises with a ball, a stick, against a wall, or on a walker. They are done 4-5 times a day with an instructor and independently.
- In the third period, maximum restoration of motor skills and body functions is achieved . These are a variety of activities with equipment and objects, games and dances. In the previous and especially this period, training in the pool (with fences, handrails and crossbars) is useful. For safety, the patient is wearing a cork belt.
To stimulate muscle tone and improve trophism and blood circulation, massage and electric massage of the muscles adjacent to the source of inflammation are useful. A dozen procedures are carried out for a quarter of an hour daily in several courses with three-week breaks.
Treatment at home
It is practiced during the recovery stage of the disease. At the same time, exercise therapy continues, folk remedies are used to relieve pain and minimize the destructive processes of the spinal cord. These are potato and honey cakes for the neck in the form of compresses. Compresses made from equal parts of aloe juice, dry mustard with the addition of vodka and propolis tincture are also useful; they are formed into a mass like plasticine and applied to the neck at night, covered with film.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention against myelitis; vaccination is practiced to prevent the disease. Prevention of infection is facilitated by timely treatment of chronic infections (sinusitis, caries, herpes) and complete cure of acute infectious diseases (influenza, measles).