Stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation, leading to severe consequences including death and disability. The disease is widespread; more than 400,000 new cases of pathology are registered annually in Russia alone and about 6,000,000 worldwide. At the same time, the age of patients is rapidly “getting younger” and today there is a risk of stroke in people under 40 years of age.
Prognosis of life and its duration for people after a stroke depend on many factors, in particular on the quality and speed of emergency care, the usefulness of rehabilitation measures, as well as the desire of the patient for a speedy recovery. You can achieve a positive result, reduce the degree of disturbances caused, prevent serious consequences and restore lost functions with the help of the well-coordinated work of a team of professionals at the Yusupov Hospital and the support of family and friends.
Statistics
The first month is the most dangerous, since during this period there is a high probability of death of the patient (read about periods of stroke here). You can recover from an ischemic stroke much faster than from a hemorrhagic stroke. Positive dynamics are possible only if you follow the doctor’s recommendations.
After a hemorrhagic stroke, one third of patients die within a year.
Important! According to statistics, the average life expectancy after a stroke is from five to ten years, depending on complications.
Lifespan
It is impossible to say exactly how long a person will live after a stroke.
However, when the disease recurs, rehabilitation is more difficult (read about how many strokes a person can suffer in this material). According to statistics, life expectancy reaches more than ten years. The percentage of pathology and mortality is quite high. In the first month, 30 percent of patients die, and within a year, about half die. A new attack occurs in 10 percent of patients. In case of relapse, death occurs within six months in 70 percent.
Expert opinion
Zemlyanukhina Tatyana Vyacheslavovna
Ambulance and emergency paramedic at the Clinical Emergency Hospital #7 in Volgograd.
Ask an expert
Any condition, even such a critical one, is not a reason to say goodbye to a person or count down the days until his death. Science knows many examples of people returning to their normal lives despite having suffered a stroke. Life expectancy for each person will be individual and it does not even depend on gender, age or other indicators. The sooner you begin to take measures to rehabilitate and eliminate the consequences, the higher the likelihood of partial recovery.
For illness on the left side
There is no exact answer to how long you can live, but survival will depend on:
- Pathologists.
- Localizations.
- Patient's age.
Up to 80% of patients survive a year after a stroke.
Right side
After a stroke on the right side, 70-80 percent of patients survive. A second stroke is statistically often the cause of death. About 50% of people can live 5-7 years.
Causes of recurrent stroke
Experts note that in approximately half of the cases, a recurrent stroke occurs due to the fact that a person ceases to consider himself sick, as a result of which he ceases to follow the recommendations of doctors. The patient, gradually returning to his normal life, stops following:
- your blood pressure;
- the condition of blood vessels;
- the condition of the heart muscle;
This is why doctors say the main reason for a recurrent stroke is neglect of one’s health.
Why is it so important to monitor all of the above indicators?
- Pressure. If for the first stroke only a sharp jump in pressure will be dangerous, then for a second stroke even a slight increase in pressure will be enough.
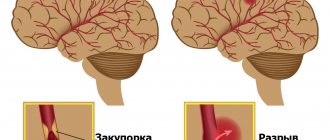
- Vessels. Here it is very important to carefully examine all the vessels of the brain and check for the presence of aneurysms that can “rupture”, which will lead to hemorrhage in the brain. If aneurysms are found, they must be removed immediately. No less dangerous to the health of a patient who has suffered a stroke are atherosclerotic plaques, which significantly impede the blood supply to the brain.
- Heart. It is important for the patient to undergo an ECG and exclude the possibility of blood clots. For prevention, doctors may advise the patient to take courses of blood thinning medications.
People who have suffered a stroke need to constantly monitor their blood pressure, blood cholesterol levels, and also follow the principles of a healthy diet.
Dependence on complications and consequences
The ability to regain skills depends on brain damage. The forecast will depend on:
- Severity of damage.
- Volume of damage.
- Social factors.
- The patient's motivation to work on himself.
After a stroke, about 8 percent return to work. Half of the patients have limited ability to work and require constant assistance and care.
Attention! With extensive hemorrhage and cerebral edema, the prognosis will be disappointing. In most cases, everything ends in death.
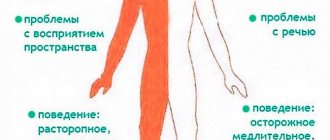
If the body is paralyzed
In case of acute disturbance of left-sided cerebral circulation, speech suffers. More attention is paid to this problem than with other manifestations of the disease.
Patients with disorders of the left side often end up in the hospital and live no more than five to seven years. The right side is responsible for movement, so there is paralysis of the left limbs. The death of neurons leads to the fact that the patient does not remember past information and is lost in time and space. In this case, life expectancy depends on care.
For dementia
In severe strokes, consciousness may be absent. The disturbances will progress, and cerebral edema is fixed.
Most often, recovery in this case is almost impossible. Life expectancy depends on care, but on average it ranges from one to three years.
In a coma
If the patient is in a coma, the likelihood of further recovery is very low and he is unlikely to survive. Typically, such patients survive two weeks after the attack.
Find out more about the consequences of a stroke in this material.
Stroke raises global blood pressure
7K 3 4 min.
Scientists have presented for the first time a systematic analysis of the situation with strokes in the world. They found that over almost 30 years, their number increased by 70%, and the number of deaths doubled. Experts call Russians a population at “ultra-high” risk of stroke, emphasizing that men do not primarily take care of their health. In addition, the situation is complicated by the coronavirus pandemic: the number of strokes may increase not only due to the risk of thrombosis in patients with COVID-19, but also due to overcrowding in hospitals and a general negative psycho-emotional background.
Photo: Oleg Kharseev, Kommersant / buy photo
Photo: Oleg Kharseev, Kommersant / buy photo
A team of scientists working on the Global Burden of Disease Study conducted a systematic analysis of the incidence, prevalence and mortality of stroke from 1990 to 2021. They assessed statistics on patients of different sexes and ages, with different income levels, in 204 countries and territories, including Russia. The authors note that such a large-scale study is being conducted for the first time. Its results were published in The Lancet Neurology (the leading journal in the field of clinical neurology); in Russia, Medvestnik was the first to draw attention to it.
According to scientists, from 1990 to 2021 there were 101 million cases of stroke - this figure is called the "prevalence" of the disease in the study. Moreover, in 2021 alone, 12.2 million cases of the disease were registered, and 6.55 million people died. Another important indicator is the patient's disability-adjusted life years (DAY), equivalent to the years of “healthy” life lost due to ill health, disability, or death. It turned out that between 1990 and 2019, humanity lost a total of 143 million years of “healthy” life. However, low-, middle- and upper-middle-income countries accounted for 86% of all stroke-related deaths and 89% of GIBIs.
The report's authors estimate that over 29 years, the number of strokes in the world has increased by 70%, their prevalence by 85%, stroke mortality by 43%, and GIBI by 32%.
Among people under 70 years of age, prevalence rates (the actual number of such patients) increased by 22%, and incidence rates (indicating how quickly a disease is spreading) increased by 15%.
Cardiologist of the medical network, associate professor of the department of physical education at the Pirogov Russian National Research Medical University Irina Kondratova calls “alarming” the trend that stroke has become “much younger” in recent decades. According to her, this problem is “extremely important”, since in addition to the high mortality rate, the percentage of disability is also high: only 15–20% of people return to work after a stroke.
Researchers associate the increase in alarming indicators with exposure to risk factors associated primarily with excess body weight. In addition, environmental risks (pollution, rising and falling air temperatures), dietary risks (for example, a diet high in red meat, a diet low in vegetables, alcohol consumption), insufficient physical activity, high blood sugar play an important role , increased systolic (upper) blood pressure, smoking, including passive smoking.
Globally, stroke was the second leading cause of death (11.6% of total) after coronary heart disease (16.2%) and the third leading cause of death and disability combined (5.7%) in 2021, according to the study. after hereditary disorders (7.3%) and coronary heart disease (7.2%).
In Russia, according to the study, in 2021 there were 445,959 cases of stroke and 327,885 deaths from it; The prevalence of stroke since 1990 was 3,020,719.
Among the risk factors for disability, high systolic blood pressure ranks first in the country, followed by increased body mass index and high blood glucose levels.
Cardiologist, advisor to the general director of the International Medical Cluster Foundation (Skolkovo) Yaroslav Ashikhmin confirms that the number of strokes in the world is constantly increasing. The situation, he said, is complicated by the fact that risk factors accumulate over the course of life. Among them, Dr. Ashikhmin highlights air pollution (microparticles, penetrating through the lungs, harm not only them, but also blood vessels), increased body weight, high cholesterol and smoking. In addition, the doctor urges you to especially monitor your blood pressure: an increase of 5 mmHg increases the risk of stroke by 20%. According to Dr. Ashikhmin, Russians are a population at “ultra-high” risk for stroke. “People don’t value their lives, they smoke, they don’t play sports, they eat what they want, they drink alcohol,” the doctor regrets. “In addition, there’s stress. If stress levels are high, then even though a person maintains healthy habits, blood pressure will increase, which means the risk of stroke will increase.”
Elina Aranovich, head of the department of therapy and oncology at the Yusupov Hospital, adds that blood pressure is not primarily monitored by young patients. Lack of adherence to treatment and reluctance to consider oneself sick are more common in men. And it is this category, according to Ms. Aranovich, that more often dies or is disabled as a result of strokes.
The study is limited to 2021, but another significant disease has emerged in 2021 that may negatively impact the statistics.
“Coronavirus, like any viral disease, occurs with vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels) and increases factors affecting thrombus formation. This is an additional risk for the development of strokes,” says SM-Clinic cardiologist Elena Yevtushenko.
She adds that the study of the consequences of COVID-19 continues, but there are no reasoned statistics yet. Elina Aranovich notes that a decrease in the volume of care for patients with vascular problems due to overcrowding in hospitals, an unfavorable psycho-emotional background, and physical inactivity due to the lockdown also affected the incidence of strokes. In turn, Irina Kondratova draws attention to the fact that the structure of strokes has changed - the proportion of hemorrhagic stroke, that is, bleeding in the brain, has increased. “Although there are no reliable statistics yet, an increase in the number of strokes has indeed been recorded. We will see detailed data only at the beginning of next year,” she concluded.
Natalia Kostarnova
Statistics for seniors over 80
The prognosis for the older generation is disappointing. High risk of death. But still, how long do they live after a recurrence of the attack? The answer is below. If a recurrent stroke occurs, the average life expectancy is no more than seven days. The older the person, the less chance of recovery.
The chances of surviving a stroke in older people over 80 are minimal.
It all depends on the overall picture of the disease. Some survive only six months after their first stroke.
Stroke and patient age
The high prevalence of the disease leads to many questions, in particular, many are interested in how long they live after a stroke. This largely depends on the age of the stroke patients. Previously, it was believed that the risk of cerebrovascular accidents was high only among people of mature age (approximately 50 years or more). But nowadays, stroke is registered in people of an earlier period. Of course, the speed of metabolic processes and recovery is higher at a younger age, but diagnosing the disease during this period is difficult, which affects the speed of care and further prognosis.
According to statistics, at the age of 25-45 years, in most cases, a hemorrhagic stroke develops, which develops as a result of a rupture of a cerebral vessel. In patients over 45 years of age, the most often diagnosed ischemic stroke, which occurs due to blockage or compression of blood vessels in the brain. This is largely due to the presence of concomitant pathology.
The risk of developing circulatory disorders increases significantly after 55 years of age, doubling every 10 years, so in 75% of cases, stroke develops in people over 65 years of age. It is worth noting that at this age there is also a high risk of relapse of the disease, which worsens prognosis and quality of life.
In older people, the pathology occurs in a severe form, causing many different complications, this may be due to:
- age-related changes in brain tissue;
- decrease in the speed of metabolic processes;
- the predominance of aging over reparative processes;
- persistent hypertension, difficult to treat;
- the presence of cardiovascular diseases;
- increased levels of cholesterol and other harmful substances, as well as other somatic pathologies.
Even an ischemic stroke, which does not develop as rapidly as a hemorrhagic one, occurs in an aggressive form in elderly people, which negatively affects the recovery process and increases the degree of disability.
How can you increase your chances?
Each person is individual and their body copes with illness differently. Some stop walking and working, while others simply become less active. Anyone can recover, the main thing is to follow the doctor’s recommendations and listen to your body.
The sooner you start rehabilitation, the faster your brain will recover. In the beginning, gymnastics and massage will help. The rehabilitation program includes exercise therapy and classes on robotic simulators.
Important! Stroke also affects the psyche. Often, the help of a psychiatrist is required.
What does the deadline depend on?
- Patient's age. A young body is more resilient and the younger the age, the faster the recovery process (read about why stroke affects children and people under 30 years of age in this material).
- Consequences of a stroke. Keeping a sick person in a supine position provokes bedsores, and an acute respiratory infection can turn into pneumonia.
- Proper organization of life. It is necessary to create a safe environment for the patient and prevent falls and injuries. Older people's bones do not heal well and take longer to heal.
- Healthy lifestyle. The patient should give up alcohol and fatty foods in order to speed up recovery (read about whether you can drink alcohol after an attack and whether a stroke occurs due to alcohol consumption). You need to eat more vegetables and fruits.
Our experts have prepared articles about the types of stroke, signs and treatment of this disease, as well as prevention and risk factors.