A rapidly developing acute cerebrovascular accident is called a stroke. There are hemorrhagic and ischemic forms of the disease. The first is a lesion of a part of the brain resulting from a rupture of a vessel. Ischemic stroke is caused by a vascular blockage that interferes with blood flow. It also occurs due to prolonged spasm of the cerebral artery.
A stroke can occur in different hemispheres of the brain. Each of them is responsible for certain functions of the body. Therefore, a stroke of the left hemisphere has its differences from the right one. But in both cases, the patient faces complete or partial paralysis of the body. The disease develops according to the principle of “reverse symmetry”: with a stroke of the left hemisphere, the right side of the body is paralyzed, and with a right-sided lesion, the left side is paralyzed.
Functions of the left hemisphere
The mechanisms of logical thinking are concentrated in the left hemisphere of the brain. This brain side is dominant in some aspects of the body's functioning. She is responsible for:
- Processing of verbal information. It is thanks to the left hemisphere that people can recognize and control words, read and write. It is responsible for speech abilities. Also takes part in memorizing facts, dates and names.
- Analytical functions. The left side recognizes numbers and other mathematical symbols. Responsible for logic and the ability to analyze facts.
- Stage-by-stage processing of information. The left brain hemisphere allows you to analyze data sequentially.
- Mobility of the right side of the body. This area of the brain sends signals to the right limbs of the body.
- Literal understanding. In the left hemisphere, the literal perception of spoken and heard phrases and words occurs.
Expert opinion
Author: Andrey Igorevich Volkov
Neurologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Acute cerebrovascular accident occupies a leading position in the structure of mortality. This is associated with the risk of disease and the development of serious complications. An important role is played by the population’s untimely seeking of medical help. More than 60% of patients become disabled, 10% completely lose the ability to self-care. Left-sided stroke is diagnosed much more often. This is due to the presence of a characteristic clinical picture. Right-sided cerebrovascular accident is accompanied by nonspecific symptoms.
The main task of doctors is to quickly identify the type of disease, the extent of the pathological focus and its location. At the Yusupov Hospital, European CT and MRI units are used for this purpose. Thanks to modern medical equipment, rapid diagnosis is carried out and correct treatment is prescribed. Every minute you have a stroke can have irreversible consequences. Experienced neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital develop an individual treatment and rehabilitation plan. The length of hospital stay is determined by the severity of the condition. The prescribed drugs meet European quality and safety standards.
Consequences of left-sided ischemic stroke
A patient who has suffered a stroke in the right hemisphere has a distorted image of his body, he does not feel motor disturbances and, therefore, does not strive for recovery. Such indifference makes rehabilitation difficult and requires referral to qualified specialists.
At the Yusupov Hospital, highly qualified doctors will select and implement an effective rehabilitation program after left-sided ischemic stroke. The program includes activities aimed at restoring the motor system and psycho-emotional state of the patient. Rehabilitation is based on classical and latest recovery techniques. Patients undergo massage, mechanotherapy, electrical stimulation, kinesthetics, diet and herbal therapy.
The Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital combines the advanced achievements of rehabilitation medicine and a homely atmosphere, thanks to which patients feel the care and attention of medical personnel and receive the necessary assistance from highly qualified specialists.
Which case is more dangerous: right-sided or left-sided?
Left-sided strokes are 57% more common than right-sided strokes. It has more pronounced symptoms, so it is easier to recognize. This allows you to consult a doctor in a timely manner and receive the necessary medical care. It is characterized by impaired speech and adequate thinking. However, unlike a right-sided stroke, a left-hemisphere stroke is more difficult to treat and brings more discomfort to the patient. In any case, rehabilitation after a cerebral hemorrhage requires a significant investment of time.
Causes of left hemisphere stroke
There are many different prerequisites for the development of left-sided stroke. Predisposing factors include:
- endogenous causes;
- exogenous factors.
The second category includes the patient's conditions and lifestyle. Endogenous causes are represented by the immunological characteristics of the body, heredity, age and gender of the person.
The most likely causes of the development of the disease on the left side of the brain are:
- diabetes;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- vein thrombosis;
- disorders of the blood composition and blood diseases that increase its viscosity;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- improper diet;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal, vascular and contraceptive drugs;
- frequent dizziness and migraines;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- obesity;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- sedentary lifestyle, insufficient physical activity
Features and symptoms
Vascular cerebrovascular accident on the left side has both general and specific manifestations. Wernicke's center and Broca's center are located in the left hemisphere cortex, so during a stroke, patients are partially or completely deprived of the ability to speak. They are also temporarily unable to think and reason logically. In addition, inhibited reactions to what is happening around are characteristic. If there is a lesion in the temporal lobe on the left side, the patient’s emotional background is also disturbed. It is possible to develop depression and a depressed state.
Common symptoms of a left hemisphere stroke include:
- severe and sharp headache (often accompanied by sound and photophobia);
- impairment of consciousness and coordination of movements;
- nausea, vomiting;
- blood pressure surges;
- pain in the chest.
The disease develops quite rapidly within a few hours. Poor circulation in the left hemisphere of the brain leads to convulsions, short-term amnesia, and partial or complete paralysis of the right side of the body. Patients also experience a skewed smile, as the right corner of the mouth droops downwards.
Causes of stroke
Circulatory disorders in the left hemisphere of the brain occur due to rupture or blockage of the lumen of the arteries that supply it. This can lead to:
- Atherosclerotic plaques;
- Blood clots;
- Emboli;
- Mechanical compression of the vessel from the outside (in particular, during tumor processes);
- Vasospasm.
The main underlying diseases that provoke the development of stroke are arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis, and diabetes mellitus.
There are two types of stroke: hemorrhagic, due to bleeding in the brain, and ischemic, cerebral infarction caused by stenosis or occlusion of the cerebral arteries.
Blockage or stenosis of a section of an artery leads to oxygen starvation of the dependent tissue section. If blood circulation is not restored within 7 minutes, irreversible changes begin in the tissue and neurons die. The larger the affected artery, the larger the focus of ischemia.
Risk factors:
- Smoking, alcohol addiction;
- Lipid metabolism disorders;
- Migraine with aura;
- Advanced age;
- Cervical osteochondrosis;
- Endocrine diseases, in particular diabetes mellitus;
- Heart defects, arrhythmias, presence of an implanted pacemaker or artificial valves;
- Arterial hypertension, symptomatic or primary;
- Inflammatory heart diseases;
- Deep vein thrombosis;
- Increased blood viscosity;
- Systemic vasculitis;
- Systemic connective tissue diseases;
- Hormonal contraception.
Hemorrhagic stroke is a consequence of the rupture of one or more blood vessels with subsequent hemorrhage. The lesion in such cases is obviously larger, the course of the disease is more severe and the prognosis is worse. Risk factors for developing hemorrhagic stroke are:
- Arterial hypertension;
- Brain aneurysms;
- Vasculitis of various etiologies;
- Reduced blood clotting;
- Overdose of anticoagulant drugs;
- Hypovitaminosis;
- Damages of vascular walls, including atherosclerosis;
- Intoxication.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
In order to reduce the consequences of a stroke on the left side of the brain, it is necessary to immediately provide medical assistance to the victim. Fortunately, the disease can be diagnosed fairly quickly.
Prehospital diagnostics
Any delay in identifying and treating a cerebral hemorrhage can lead to serious damage to its areas and even death of the patient. Manifestations of the disease can be detected before going to the clinic. It has the following early signs:
- semi-fainting state of the patient;
- skewed face to one side;
- unnatural, forced smile;
- loss of balance, poor coordination of movements;
- illogical, difficult speech.
A person experiencing a left-sided stroke experiences a headache and may see double. The presence of even one symptom that does not go away for a long time is a serious reason to call an ambulance.
Instrumental diagnostics
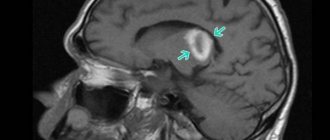
When a patient with a stroke of the left hemisphere is taken to the hospital, the doctor conducts a full examination, which also includes instrumental diagnostics. It allows you to determine the scale of hemorrhage, localize the source of damage and determine the form of stroke. During hardware diagnostics the following is carried out:
- MRI of the brain.
- Computed tomography.
- ECG.
- EchoCG.
In cases where emergency neuroimaging is not possible, a lumbar puncture is performed. This procedure is preceded by an Echo-EG. Performed in order to determine or eliminate displacements of the middle structures. If they are present, lumbar puncture is contraindicated.
The doctor also prescribes a clinical blood test, which is necessary to accurately determine the platelet count. A biochemical analysis is required to determine the level of sugar in the blood.
Differential diagnosis of various types of stroke
One of the diagnostic tasks is to differentiate vascular rupture from other diseases with similar symptoms. Once an accurate diagnosis has been made, the next goal of examining a patient with a left hemisphere stroke is to determine the form of the disease. This is a key point for subsequent therapy.
In the course of differential diagnosis, specialists rely on a combination of various signs characteristic of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
Meningeal symptoms
They appear when there is damage to the meninges, which includes a stroke of the left hemisphere. This group of manifestations includes:
- Brudzinski's sign. There are upper and lower. In the first case, a study of the rigidity of the neck muscles is carried out. The chin approaches the chest, causing the lower limbs and knee joints to involuntarily bend. During a lower examination, pressing on the solar plexus causes the same reaction.
- Kernig's sign. The patient lies on his back, and the doctor bends his leg at the hip joint at an angle of 90 degrees, after which he tries to straighten it at the knee. If this symptom is present, the muscles will involuntarily contract, which will prevent the knee from straightening.
Symptoms of paralysis
After the attack occurs, the patient experiences pronounced symptoms indicating extensive hemorrhage and brain damage. There are 3 types of such manifestations. The victim completely lacks voluntary motor activity. This occurs due to the lack of impulses in the nervous system.
At this stage, it is important to determine what kind of stroke - ischemic or hemorrhagic - the patient suffered. This will determine subsequent treatment tactics and rehabilitation.
The skin loses sensitivity, the person does not feel pain, heat, cold, or touch. Lesions can be both significant, when the deep layers of the skin are affected, and minor, when sensitivity is absent only on the surface of the skin.
Vision problems may occur when the patient loses half of his field of vision, often on both sides. Such disorders do not necessarily lead to blindness; as a rule, a person practically does not notice them. Deformation of the facial muscles is often observed when significant asymmetry of one of the sides occurs.
All of the above manifestations suggest a cerebral stroke. In this case, the patient must be taken to the hospital as soon as possible to undergo examination and prescribe adequate treatment.
Treatment of left hemisphere stroke
Impaired blood circulation in the brain leads to serious consequences. To level them out, treatment of a stroke on the left side must be immediate. Prompt assistance will allow you to correctly diagnose and correctly draw up a step-by-step and comprehensive treatment plan.
First aid to a patient
Before doctors arrive, the patient must be given first aid. This will help improve his condition a little. First aid consists of a number of simple actions that the victim’s relatives can perform:
- The patient should be placed on a surface covered with pillows and his head should be raised.
- The patient may have difficulty breathing, so it is necessary to open the windows.
- It is also necessary to rid the person of tight and constricting clothing: unbutton the shirt collar, remove the belt, take off a jacket with a tight neck.
- If there is vomiting, carefully and carefully turn the patient's head to the side. This position will prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract.
Until the ambulance arrives, you need to stay close to the stroke survivor. He may be in a panic, so you need to try to calm him down.
Drug therapy
In clinical settings, physicians' efforts are aimed at minimizing nerve and muscle damage. The main goal of therapy is to preserve the functionality of the brain and cardiovascular system. The patient is prescribed drugs that restore blood circulation.
Drug treatment is selected according to the form of the disease. Drugs for left hemisphere stroke of ischemic nature include the following groups:
- Thrombolytics. They are used in the first hours after a vascular accident to dissolve blood clots.
- Anticoagulants.
- Medicines that lower blood pressure.
- Neuroprotectors.
- Vasoactive drugs.
In the case of hemorrhagic stroke on the left side, vascular strengthening drugs and drugs that prevent vasospasm are used.
For both types, general medications are also provided, which include diuretics and decongestants, as well as sedatives and hypnotics. During rehabilitation, patients are also prescribed medications to treat bedsores.
Surgery
Surgery is most often necessary for hemorrhagic stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain. Surgical treatment is aimed at removing the intracerebral hematoma. The need for surgery is determined taking into account the following factors:
- general condition of the patient;
- volume of the lesion;
- localization of hemorrhage.
Surgery is indicated only in extremely severe cases when the patient's life is in danger. There are also cases when the hematoma is not removed immediately after a stroke, but during rehabilitation.
As a rule, surgical treatment is used for patients whose hematoma size is more than 50 ml. The operation is also indicated for patients with cerebellar damage.
Consequences
What are the consequences after suffering a stroke on the left side of the body?
The human brain, in particular the cerebellum, is very complex. One of its features is that it is connected to other parts of the body through a special network of neurons. The so-called “nerve threads” that are directed from the right hemisphere can be partially or completely destroyed by hemorrhage, as a result of which the transmission of impulses to the left side of the body worsens or completely stops.
Musculoskeletal disorders
If a stroke develops, in which the left side suffers, one can expect consequences manifested by disturbances in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system:
- Paralysis of the right side - a large proportion of the complex consequences are due to hemorrhagic stroke;
- Hemiparesis, which causes the effect of weakening and drooping of the lateral muscles;
- Dysfunction of various parts of the body, which may persist even after treatment and rehabilitation;
- Articulation impairment;
- Muscular dystrophy is a dangerous consequence of deterioration in controllability of the tongue and, as a result, slurred speech. Many patients begin to communicate only with slurred sounds or small fragments of words.
It should be noted that even if you are completely cured of the disease, after some time a person may complain of numbness of the facial muscles, their convulsive twitching, as well as partial dysfunction.
Behavior and speech disorders
If the stroke affected the left hemisphere of the brain, then in the prognosis doctors often indicate possible problems with logical thinking, as well as oral and written speech:
- Partial or complete loss of language skills;
- Deterioration of speech control;
- Oral and written dyslexia, in which a person begins to confuse not only the words themselves, but also the letters in them;
- Loss of the ability to analyze new information and perceive it correctly;
- While writing or reading, significant difficulties arise. Some people who have had this disease may not even remember how to hold a pen or write letters;
One of the largest and most problematic consequences of pathology can be loss of work due to disability. After all, a patient who could previously quickly and easily perform computational operations and think logically often loses his abilities after an attack. However, even after this you can live quite well: people with disabilities are assigned tasks that they can do.
Emotional disorders
If the left side of the brain was damaged during a stroke, the patient has problems with orientation in space. In addition, he is limited in contact with others due to the manifestation of written and speech dysfunction, and a violation of the analysis of the information received. This condition is somewhat similar to a certain form of autism, as a result of which the person becomes withdrawn.
Experts identify several more characteristic changes in the emotional background:
- The patient loses the ability to correctly correlate the proportions of various objects, as well as the scale of his actions. As a result, people complain about difficulties in doing even simple tasks such as tying their shoes, dialing a phone number, cutting groceries, and more. The reason for this is that it is not possible to correctly assess the shape, parameters and location of an object. In some cases, it is not possible to determine the size of your body;
- A microstroke sometimes leads to the loss of individual body parts, as well as organs;
- Ischemic stroke often causes unconscious performance of various actions, which may result in harm to others;
- Passive behavior;
- A person may not understand why it is necessary to restore the functions of a weakened musculoskeletal system.
If the patient managed to survive the attack, then these are the consequences that become the most terrible. After all, a person does not worry about his own condition, he behaves carefree and, to some extent, complacently. In addition, the clinical picture of the disease (symptoms and defects) is practically unnoticed by them. However, at the same time, he begins to move much more slowly, which is not caused by laziness or a short-term depressive state. In such conditions, the patient needs emergency care.
Rehabilitation after a stroke of the left hemisphere
The process of restoring functions lost after a stroke must be comprehensive and versatile. Brain damage entails a number of physiological and mental disorders. Rehabilitation measures are selected depending on the general condition of the patient. This is a long and difficult journey that the patient’s loved ones go through together. Help and support for a person who has suffered a stroke on the left side of the brain is of great importance. He needs constant care, which also implies strict adherence to all the doctor’s recommendations and instructions.
The following methods have shown good results in recovery after a stroke:
- physiotherapy;
- massage and manual therapy;
- physiotherapy.
Psychologists and speech therapists also work with the patient to help restore lost speech functions and stabilize the patient’s emotional state.
Massage, manual therapy and passive exercises
After the main threats to a person’s life and health after a stroke of the left hemisphere have been eliminated, the doctor prescribes a series of treatment and rehabilitation procedures. Most patients are indicated for massage and manual therapy. Due to the effect on certain receptor zones, the body’s functioning is stimulated. The most commonly used is acupressure. The specialist presses on certain areas on the patient’s body, thereby improving the mobility of the limbs. Also, such manipulations help blood circulation, helping to thin it.
One of the consequences of a severe stroke on the left side is partial or complete paralysis of the right limbs. Due to limited joint mobility, contractures may occur. You can prevent them with the help of massage and passive gymnastics. This is a set of exercises aimed at:
- relieving excessively high muscle tone during paralysis;
- return of precision and clarity to movements;
- increased blood supply to tissues;
- prevention of bedsores.
Keeping the patient moving is very important, since it is long-term immobility that leads to many complications.
Therapeutic exercises
To restore the motor function of the right side of the body after a left-sided stroke, physical therapy is prescribed. The main goal of health-improving gymnastics is to develop movements and improve the sensitivity of the limbs.
These are simple exercises that the patient needs to perform several times a day with a certain number of approaches. They are presented:
- clenching and unclenching your palm into a fist;
- raising your hand up in front of you and slowly lowering it;
- lifting your leg up from a lying position.
More complex gymnastics are performed together with a specialist.
Patients are also prescribed a number of breathing exercises that help get rid of shortness of breath and improve the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
Physiotherapy
This rehabilitation method is used for both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes of the left hemisphere of the brain. The type of procedures, their number, frequency and duration are determined by a specialist. When developing physical therapy tactics, the individual indications of the patient and the degree of acquired disorders are taken into account.
The main rehabilitation measures are:
- magnetic therapy;
- acupuncture;
- vibration therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- laser exposure;
- ultrasound treatment.
The procedures are aimed at:
- reduction of pain syndrome;
- increasing immunity;
- improvement of lymph and blood flow;
- prevention of blood clots;
- decreased blood pressure;
- normalization of vascular tone;
- preventing recurrent stroke;
- relief from hypertonicity and muscle spasticity.
A vascular accident in the brain radically changes a person’s life. Even after undergoing rehabilitation, when lost motor and speech abilities are restored, many patients cannot fully return to their usual rhythm. This is because some brain damage is irreversible, especially in old age. In addition, there is a fairly high probability of another stroke. To prevent this from happening, the patient needs to reconsider his attitude towards life and make fundamental changes in its course. In other words, he should try to improve its quality, first of all by giving up bad habits:
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- uncontrolled use of certain medications.
A sedentary lifestyle often leads to strokes of the left hemisphere of the brain. People with sedentary work and no active recreation are at risk. After the patient has overcome the consequences of a cerebral hemorrhage, he needs to walk more often and more, play sports and properly alternate activity with rest.
A person after a stroke must be protected from stress and unnecessary worries. You also need to relieve him of the stress of work. Relatives and friends will have to take on most of the household responsibilities for the first year after illness. This is especially true for those that require heavy lifting or involve standing on your feet for a long time.
Dangerous consequences
Complications that appear after an ischemic stroke on the left side depend on the location of the lesion on the cerebral hemisphere (hemisphere). Let us consider the consequences characteristic of left-sided ischemic stroke that may persist after treatment and rehabilitation.
Physical activity
If the motor centers are affected, then a person develops:
- sagging of half the face (half-lowered eyelid, swollen cheek, distorted mouth);
- decreased muscle strength (in severe cases, paralysis occurs);
- impaired sensitivity (the skin of the affected limbs reacts poorly to external irritations).
Difficulty in movement and sensory disturbances in left-sided cerebral ischemia occur on the right side of the body.
Internal organs
Ischemic stroke in the left hemisphere is not limited only to disruption of the innervation of muscles and skin; organs located on the right (kidney, lung, and partially the digestive tract) are affected.
The degree of change in the functioning of organs depends on how severe the innervation disorder is:
- Easy. The deviation is minor, the functions are preserved.
- Average. There is a decrease in organ functions. The patient's right side of the chest lags behind when breathing, and there may be problems with digestion and bowel movements.
- Heavy. Paralysis and complete cessation of functions occurs.
Stopping the functioning of the lung, liver or kidney is considered one of the dangerous consequences of an ischemic stroke on the left side. It is noteworthy that the severity of external and internal deviations are not related to each other. People may be paralyzed on the right side of the body, but the functionality of the internal organs is not impaired.
Speech
The centers responsible for speech are on the left. Depending on the area of damage to the hemisphere, the victim will have:
- Difficulty in grammatically constructing sentences. People begin to speak in short, simple phrases reminiscent of telegraph style. Intonation disappears. This occurs when the anterior lobes of the hemisphere are affected.
- Problems with sounds. The patient confuses sounds, placing them incorrectly in words. This is typical for stroke of the posterior lobe.
- Problems with the perception of spoken language. A person hears words addressed to him, but cannot associate them with known concepts. Similar problems arise when trying to read text. Such patients speak mainly in prepositions or conjunctions, with long, but uninformative phrases. The disorder appears with ischemia of the temporal lobe.
- Complete aphasia. Extensive ischemic stroke of the left hemisphere is often accompanied by a complete loss of the ability to speak and perceive speech.
There is also false aphasia, when the impairment of the ability to speak is associated with paralysis of the muscles of the tongue or larynx. Such people understand what is being said to them and can adequately formulate their thoughts, but when they try to speak, the result is slurred, blurred speech or isolated sounds.
Ability to think
The left side of the brain marks the ability for logical thinking. The consequence of a left-sided stroke can be:
- loss of ability to remember numbers (dates, phone numbers);
- inability to perform simple arithmetic operations in the mind (add, multiply);
- difficulty in perceiving abstract concepts;
- difficulty when trying to draw conclusions from the information received;
- difficulty making independent decisions.
Such people do not always understand their condition and often commit stupid or ridiculous actions. They are uncritical of their actions.
- Paralysis of the left side during a stroke - prognosis, treatment and possible consequences
Psycho-emotional sphere
Another consequence of a stroke in the left hemisphere is a change in the psyche. The patient may experience depression associated with limited mobility and dependence on the care of loved ones. The person becomes:
- Maudlin. He often feels sorry for himself and cries, saying that he has become a burden to his relatives.
- Restless. Anxiety and fear appear associated with the fear of being left without outside help.
- Aggressive. The patient finds fault with others, conflicts over trifles. May complain to strangers about poor feeding or care, attracting attention to himself.
- Irritable. Such people are dissatisfied with everything, find fault with little things, and often accuse loved ones of waiting for their death.
Often, those who have suffered a cerebral infarction experience sudden mood swings when, during a calm conversation, a person becomes angry, starting to throw objects or punch the bed.
Prognosis for treatment of left hemisphere stroke
Stroke is a dangerous and complex disease. Unfortunately, no doctor can give an accurate prognosis regarding the patient’s recovery. The success of rehabilitation primarily depends on the timeliness of assistance and initiation of treatment.
Regarding the duration of the recovery period, the following factors must be taken into account:
- size of the lesion;
- presence of emotional disorders;
- the age of the person who experienced a left-sided stroke - the older the patient, the more difficult it is for him to recover;
- deterioration of mental abilities;
- localization of the lesion.
The intensity of stroke development is also of great importance. With a favorable course of the disease, when the patient regains consciousness after a few minutes or hours, the likelihood of complete restoration of lost functions is quite high. The compressed development of the disease is more dangerous, as there is a risk of repeated vascular rupture. However, in this case, most of the functions are restored. A progressively severe variant of the development of the disease is characterized by the fact that a person comes to his senses more than three days after the stroke. In this situation, symptoms rapidly increase and there is a high chance that the patient will receive lifelong disability.
The prognosis for life after treatment for a left hemisphere stroke is individual for each person. However, timely treatment, compliance with doctor’s recommendations, a healthy lifestyle, as well as a reduction in emotional distress help speed up the recovery process.
Rehabilitation for left-sided paralysis
Recovery after a stroke on the left side must begin as early as possible - immediately after the permission of the attending physician. Optimally - during the inpatient stage with continuation after discharge. Areas of rehabilitation for patients with strokes:
- position therapy;
- kinesitherapy;
- drug support.
The effectiveness of rehabilitation measures depends on many factors, including the age of the patient. Over the years, brain cells lose the ability to form new connections; healthy neurons are not capable of functionally replacing dead areas of the central nervous system. Therefore, in old age it is more difficult for a patient to achieve positive dynamics of the condition.
Treatment by position
The therapeutic effect is to reduce the tone of the muscles of the limbs and torso, normalize sensitivity, and prevent the development of complications (contractures, pathological postures and stereotypes).
Basic rules in position treatment:
- The technique is suitable for patients with varying severity of the disease.
- It is important to maintain symmetry in the placement of the limbs. So they will be subject to the same gravitational load.
- The body position should be comfortable, the time spent on the back is limited.
Kinesiotherapy
The technique is aimed at gradually restoring movement in the affected muscles. This process is lengthy and requires effort not only from the patient himself, but also from those caring for him. Recovery stages:
- Simple movements of the shoulder and pelvic girdle.
- Learning to move on the bed and roll over.
- Walking, development of fine motor skills.
Prevention
The basis for preventing left-sided stroke is lifestyle correction. To avoid experiencing the consequences of this serious disease, you need to:
- Watch your weight. Excess weight leads to increased blood pressure and provokes cardiovascular diseases.
- Avoid fatty foods and moderate your intake of foods of animal origin. Add more vegetables and fruits to your diet.
- Quit smoking. Cigarettes have a destructive effect on blood vessels, constricting them and preventing normal blood circulation.
- Exercise regularly and go for walks. Physical activity reduces the risk of developing vascular diseases.
- Drink moderate amounts of alcohol. A complete abstinence from alcoholic beverages is not necessary, although it is best to discuss whether you can drink alcohol with your doctor.
Why can paralysis of the left side occur after an attack?
Any paralysis after a violation of the integrity or blockage of a cerebral vessel occurs because the affected area of the brain ceases to receive nutrients, oxygen and vitamins. On the contrary, toxins accumulate in it, which leads to its damage.
Since each part of the brain is responsible for performing certain actions, the functioning of internal organs and systems, with significant damage these functions cease to be performed.
Paralysis of the left side of the body occurs when damage to the right hemisphere of the brain is extensive and affects a significant area of the organ. In cases where small areas are damaged, only an arm or leg can be paralyzed.
If we talk about the causes of stroke, there are many of them, and each of them can provoke a cerebral hemorrhage:
- If a person has previously suffered from viral infectious diseases that affected or negatively affected the state of the central nervous system.
- If you receive a traumatic brain injury at home, in an accident or during sports.
- Autoimmune diseases leading to various malfunctions of the body.
- An unbalanced diet, an abundance of fatty and unhealthy foods in the diet, which provokes the appearance of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Brain tumors of various origins.
- Poisoning of the body with toxic substances.
- Constant stressful situations, increased nervous excitability.
- Tendency to high blood pressure.
- Having bad habits such as drug addiction, alcoholism and smoking.
- Obesity, tendency to gain excess weight.
- Diabetes mellitus at any stage.
- Patients who have already been found to have elevated cholesterol levels in their blood.
People who have at least one of the listed negative factors are more susceptible to cerebral hemorrhage of any kind.
It is important to remember that paralysis of the left side during a stroke and its prognosis will depend on the quality of medical care, rehabilitation measures, as well as on the desire of the patient to recover.