A rapidly developing acute cerebrovascular accident is called a stroke. There are hemorrhagic and ischemic forms of the disease. The first is a lesion of a part of the brain resulting from a rupture of a vessel. Ischemic stroke is caused by a vascular blockage that interferes with blood flow. It also occurs due to prolonged spasm of the cerebral artery.
A stroke can occur in different hemispheres of the brain. Each of them is responsible for certain functions of the body. Therefore, a stroke of the left hemisphere has its differences from the right one. But in both cases, the patient faces complete or partial paralysis of the body. The disease develops according to the principle of “reverse symmetry”: with a stroke of the left hemisphere, the right side of the body is paralyzed, and with a right-sided lesion, the left side is paralyzed.
Functions of the left hemisphere
The mechanisms of logical thinking are concentrated in the left hemisphere of the brain. This brain side is dominant in some aspects of the body's functioning. She is responsible for:
- Processing of verbal information. It is thanks to the left hemisphere that people can recognize and control words, read and write. It is responsible for speech abilities. Also takes part in memorizing facts, dates and names.
- Analytical functions. The left side recognizes numbers and other mathematical symbols. Responsible for logic and the ability to analyze facts.
- Stage-by-stage processing of information. The left brain hemisphere allows you to analyze data sequentially.
- Mobility of the right side of the body. This area of the brain sends signals to the right limbs of the body.
- Literal understanding. In the left hemisphere, the literal perception of spoken and heard phrases and words occurs.
Expert opinion
Author: Andrey Igorevich Volkov
Neurologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Acute cerebrovascular accident occupies a leading position in the structure of mortality. This is associated with the risk of disease and the development of serious complications. An important role is played by the population’s untimely seeking of medical help. More than 60% of patients become disabled, 10% completely lose the ability to self-care. Left-sided stroke is diagnosed much more often. This is due to the presence of a characteristic clinical picture. Right-sided cerebrovascular accident is accompanied by nonspecific symptoms.
The main task of doctors is to quickly identify the type of disease, the extent of the pathological focus and its location. At the Yusupov Hospital, European CT and MRI units are used for this purpose. Thanks to modern medical equipment, rapid diagnosis is carried out and correct treatment is prescribed. Every minute you have a stroke can have irreversible consequences. Experienced neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital develop an individual treatment and rehabilitation plan. The length of hospital stay is determined by the severity of the condition. The prescribed drugs meet European quality and safety standards.
How to develop the right hemisphere
- Turn on music - don't limit yourself to just children's songs or modern music. A variety of music is needed: let the baby listen to classics, folk melodies, romances.
- Playing a musical instrument and taking singing lessons for children also helps exercise the creative areas of the brain.
- Drawing is one of the best ways to stimulate creative areas. And in modern art schools they teach right-brain drawing, which is aimed specifically at turning off logic and immersing oneself in the creative process.
- Introduce preschoolers and schoolchildren to art. Art history for children is becoming increasingly popular among modern parents.
- Play similes and metaphors. The task is to choose a figurative and vivid comparison for a specific object.
Which case is more dangerous: right-sided or left-sided?
Left-sided strokes are 57% more common than right-sided strokes. It has more pronounced symptoms, so it is easier to recognize. This allows you to consult a doctor in a timely manner and receive the necessary medical care. It is characterized by impaired speech and adequate thinking. However, unlike a right-sided stroke, a left-hemisphere stroke is more difficult to treat and brings more discomfort to the patient. In any case, rehabilitation after a cerebral hemorrhage requires a significant investment of time.
Brain Development
To develop the ability to think logically, learn to concentrate, better understand cause-and-effect relationships and remember well, be sure to develop the left hemisphere with the help of special exercises. Count, solve logical problems and puzzles, solve detective stories and do neuro-gymnastics. All this will improve the functioning of the left hemisphere.
Some of these exercises, as well as many others, are included in the “Memory Development Courses”. Train your brain with us.
Causes of left hemisphere stroke
There are many different prerequisites for the development of left-sided stroke. Predisposing factors include:
- endogenous causes;
- exogenous factors.
The second category includes the patient's conditions and lifestyle. Endogenous causes are represented by the immunological characteristics of the body, heredity, age and gender of the person.
The most likely causes of the development of the disease on the left side of the brain are:
- diabetes;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- vein thrombosis;
- disorders of the blood composition and blood diseases that increase its viscosity;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- improper diet;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal, vascular and contraceptive drugs;
- frequent dizziness and migraines;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- obesity;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- sedentary lifestyle, insufficient physical activity
Features and symptoms
Vascular cerebrovascular accident on the left side has both general and specific manifestations. Wernicke's center and Broca's center are located in the left hemisphere cortex, so during a stroke, patients are partially or completely deprived of the ability to speak. They are also temporarily unable to think and reason logically. In addition, inhibited reactions to what is happening around are characteristic. If there is a lesion in the temporal lobe on the left side, the patient’s emotional background is also disturbed. It is possible to develop depression and a depressed state.
Common symptoms of a left hemisphere stroke include:
- severe and sharp headache (often accompanied by sound and photophobia);
- impairment of consciousness and coordination of movements;
- nausea, vomiting;
- blood pressure surges;
- pain in the chest.
The disease develops quite rapidly within a few hours. Poor circulation in the left hemisphere of the brain leads to convulsions, short-term amnesia, and partial or complete paralysis of the right side of the body. Patients also experience a skewed smile, as the right corner of the mouth droops downwards.
Consequences of right-sided paralysis
In severe cases, right-sided lesions lead to irreversible complications that develop as a result of massive hemorrhage or violation of treatment rules. We list the most common conditions:
- paralysis of both arms and legs;
- lifelong speech dysfunction;
- disturbance of thinking, memorization, social behavior;
- the appearance of bedsores;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases against the background of reduced physical activity;
- enuresis and fecal continence disorders.
The main task of the doctor is to create conditions that ensure full recovery after a stroke on the right side, which will minimize the development of complications.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
In order to reduce the consequences of a stroke on the left side of the brain, it is necessary to immediately provide medical assistance to the victim. Fortunately, the disease can be diagnosed fairly quickly.
Prehospital diagnostics
Any delay in identifying and treating a cerebral hemorrhage can lead to serious damage to its areas and even death of the patient. Manifestations of the disease can be detected before going to the clinic. It has the following early signs:
- semi-fainting state of the patient;
- skewed face to one side;
- unnatural, forced smile;
- loss of balance, poor coordination of movements;
- illogical, difficult speech.
A person experiencing a left-sided stroke experiences a headache and may see double. The presence of even one symptom that does not go away for a long time is a serious reason to call an ambulance.
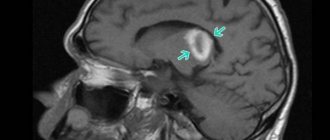
Instrumental diagnostics
When a patient with a stroke of the left hemisphere is taken to the hospital, the doctor conducts a full examination, which also includes instrumental diagnostics. It allows you to determine the scale of hemorrhage, localize the source of damage and determine the form of stroke. During hardware diagnostics the following is carried out:
- MRI of the brain.
- Computed tomography.
- ECG.
- EchoCG.
In cases where emergency neuroimaging is not possible, a lumbar puncture is performed. This procedure is preceded by an Echo-EG. Performed in order to determine or eliminate displacements of the middle structures. If they are present, lumbar puncture is contraindicated.
The doctor also prescribes a clinical blood test, which is necessary to accurately determine the platelet count. A biochemical analysis is required to determine the level of sugar in the blood.
Differential diagnosis of various types of stroke
One of the diagnostic tasks is to differentiate vascular rupture from other diseases with similar symptoms. Once an accurate diagnosis has been made, the next goal of examining a patient with a left hemisphere stroke is to determine the form of the disease. This is a key point for subsequent therapy.
In the course of differential diagnosis, specialists rely on a combination of various signs characteristic of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
Meningeal symptoms
They appear when there is damage to the meninges, which includes a stroke of the left hemisphere. This group of manifestations includes:
- Brudzinski's sign. There are upper and lower. In the first case, a study of the rigidity of the neck muscles is carried out. The chin approaches the chest, causing the lower limbs and knee joints to involuntarily bend. During a lower examination, pressing on the solar plexus causes the same reaction.
- Kernig's sign. The patient lies on his back, and the doctor bends his leg at the hip joint at an angle of 90 degrees, after which he tries to straighten it at the knee. If this symptom is present, the muscles will involuntarily contract, which will prevent the knee from straightening.
Types of paralysis
When a person is admitted to hospital with a stroke, it is important to determine from the outset whether they have paralysis and what its nature is. Paralysis in all parts of the body (left and right sides) is divided into 2 groups.
- Peripheral paralysis. This is a milder form of the disorder, accompanied by selective loss of body function. In this case, motor nerve cells are damaged, numbness occurs, and the person cannot perform complex actions.
- Central paralysis. This condition is associated with the formation of a hematoma in the areas of the brain responsible for movement. This causes complete paralysis of the right leg or arm. Such patients lose the ability to self-care and may remain disabled for life.
Treatment of left hemisphere stroke
Impaired blood circulation in the brain leads to serious consequences. To level them out, treatment of a stroke on the left side must be immediate. Prompt assistance will allow you to correctly diagnose and correctly draw up a step-by-step and comprehensive treatment plan.
First aid to a patient
Before doctors arrive, the patient must be given first aid. This will help improve his condition a little. First aid consists of a number of simple actions that the victim’s relatives can perform:
- The patient should be placed on a surface covered with pillows and his head should be raised.
- The patient may have difficulty breathing, so it is necessary to open the windows.
- It is also necessary to rid the person of tight and constricting clothing: unbutton the shirt collar, remove the belt, take off a jacket with a tight neck.
- If there is vomiting, carefully and carefully turn the patient's head to the side. This position will prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract.
Until the ambulance arrives, you need to stay close to the stroke survivor. He may be in a panic, so you need to try to calm him down.
Drug therapy
In clinical settings, physicians' efforts are aimed at minimizing nerve and muscle damage. The main goal of therapy is to preserve the functionality of the brain and cardiovascular system. The patient is prescribed drugs that restore blood circulation.
Drug treatment is selected according to the form of the disease. Drugs for left hemisphere stroke of ischemic nature include the following groups:
- Thrombolytics. They are used in the first hours after a vascular accident to dissolve blood clots.
- Anticoagulants.
- Medicines that lower blood pressure.
- Neuroprotectors.
- Vasoactive drugs.
In the case of hemorrhagic stroke on the left side, vascular strengthening drugs and drugs that prevent vasospasm are used.
For both types, general medications are also provided, which include diuretics and decongestants, as well as sedatives and hypnotics. During rehabilitation, patients are also prescribed medications to treat bedsores.
Surgery
Surgery is most often necessary for hemorrhagic stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain. Surgical treatment is aimed at removing the intracerebral hematoma. The need for surgery is determined taking into account the following factors:
- general condition of the patient;
- volume of the lesion;
- localization of hemorrhage.
Surgery is indicated only in extremely severe cases when the patient's life is in danger. There are also cases when the hematoma is not removed immediately after a stroke, but during rehabilitation.
As a rule, surgical treatment is used for patients whose hematoma size is more than 50 ml. The operation is also indicated for patients with cerebellar damage.
Etiopathogenesis
If the patient is paralyzed, then a stroke (hemorrhage) has occurred. Violation of the integrity of the arterial wall leads to the formation of a hematoma. As blood accumulates outside the vessel, it begins to put pressure on neighboring brain structures. Under these conditions, nerve cells responsible for key brain functions, such as muscle control, die, causing entire parts of the body to go numb.
A stroke with paralysis of the right side can be caused by the following factors:
- Wrong diet. It is very important to monitor the amount of calcium in the foods you eat, as it is a key element in maintaining the health of arterial walls. A lack of calcium leads to weakening of blood vessels and increases the risk of their damage. In this case, even small blood congestions can provoke hemorrhage.
- High blood pressure. Excessive blood pressure on the walls of the arteries can lead to their damage in the weakest places. As a rule, people at high risk are older people who experience deterioration in the elasticity of the vascular walls due to natural aging and low calcium levels.
- Hereditary predisposition. Recently, it was found that patients with a family history of stroke are likely to have a heart attack or stroke at some point in their lives. These are mainly patients with hypertension. While the specific inherited cause of the disease has not yet been established, it may be weak blood vessels and problems with neurohumoral regulation.
- Excess weight. Fat people tend to have low levels of minerals in the blood and high blood pressure - leading causes of stroke, which can paralyze the body.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system. Impaired blood flow and rupture of a vessel in the brain can provoke pathologies such as heart defects, heart failure, the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots.
- Endocrine diseases. The most common cause of stroke among this group of pathologies is diabetes. People with this condition often suffer from high blood pressure. Also at risk are patients with low levels of thyroid hormones and problems in the adrenal cortex.
- Alcohol and tobacco abuse. Nicotine reduces the strength of arterial walls and increases cholesterol levels in the blood. High-quality alcoholic drinks in small quantities can even be beneficial, but frequent and excessive consumption of alcohol easily provokes hemorrhage with subsequent paralysis.
The causes of paralysis of both the right and left parts of the body are indicated above. Statistics show that bad habits are the most common factor in paralysis, in which it is much more likely to help the patient survive if diagnosed in time.
Rehabilitation after a stroke of the left hemisphere
The process of restoring functions lost after a stroke must be comprehensive and versatile. Brain damage entails a number of physiological and mental disorders. Rehabilitation measures are selected depending on the general condition of the patient. This is a long and difficult journey that the patient’s loved ones go through together. Help and support for a person who has suffered a stroke on the left side of the brain is of great importance. He needs constant care, which also implies strict adherence to all the doctor’s recommendations and instructions.
The following methods have shown good results in recovery after a stroke:
- physiotherapy;
- massage and manual therapy;
- physiotherapy.
Psychologists and speech therapists also work with the patient to help restore lost speech functions and stabilize the patient’s emotional state.
Massage, manual therapy and passive exercises
After the main threats to a person’s life and health after a stroke of the left hemisphere have been eliminated, the doctor prescribes a series of treatment and rehabilitation procedures. Most patients are indicated for massage and manual therapy. Due to the effect on certain receptor zones, the body’s functioning is stimulated. The most commonly used is acupressure. The specialist presses on certain areas on the patient’s body, thereby improving the mobility of the limbs. Also, such manipulations help blood circulation, helping to thin it.
One of the consequences of a severe stroke on the left side is partial or complete paralysis of the right limbs. Due to limited joint mobility, contractures may occur. You can prevent them with the help of massage and passive gymnastics. This is a set of exercises aimed at:
- relieving excessively high muscle tone during paralysis;
- return of precision and clarity to movements;
- increased blood supply to tissues;
- prevention of bedsores.
Keeping the patient moving is very important, since it is long-term immobility that leads to many complications.
Therapeutic exercises
To restore the motor function of the right side of the body after a left-sided stroke, physical therapy is prescribed. The main goal of health-improving gymnastics is to develop movements and improve the sensitivity of the limbs.
These are simple exercises that the patient needs to perform several times a day with a certain number of approaches. They are presented:
- clenching and unclenching your palm into a fist;
- raising your hand up in front of you and slowly lowering it;
- lifting your leg up from a lying position.
More complex gymnastics are performed together with a specialist.
Patients are also prescribed a number of breathing exercises that help get rid of shortness of breath and improve the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
Physiotherapy
This rehabilitation method is used for both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes of the left hemisphere of the brain. The type of procedures, their number, frequency and duration are determined by a specialist. When developing physical therapy tactics, the individual indications of the patient and the degree of acquired disorders are taken into account.
The main rehabilitation measures are:
- magnetic therapy;
- acupuncture;
- vibration therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- laser exposure;
- ultrasound treatment.
The procedures are aimed at:
- reduction of pain syndrome;
- increasing immunity;
- improvement of lymph and blood flow;
- prevention of blood clots;
- decreased blood pressure;
- normalization of vascular tone;
- preventing recurrent stroke;
- relief from hypertonicity and muscle spasticity.
A vascular accident in the brain radically changes a person’s life. Even after undergoing rehabilitation, when lost motor and speech abilities are restored, many patients cannot fully return to their usual rhythm. This is because some brain damage is irreversible, especially in old age. In addition, there is a fairly high probability of another stroke. To prevent this from happening, the patient needs to reconsider his attitude towards life and make fundamental changes in its course. In other words, he should try to improve its quality, first of all by giving up bad habits:
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- uncontrolled use of certain medications.
A sedentary lifestyle often leads to strokes of the left hemisphere of the brain. People with sedentary work and no active recreation are at risk. After the patient has overcome the consequences of a cerebral hemorrhage, he needs to walk more often and more, play sports and properly alternate activity with rest.
A person after a stroke must be protected from stress and unnecessary worries. You also need to relieve him of the stress of work. Relatives and friends will have to take on most of the household responsibilities for the first year after illness. This is especially true for those that require heavy lifting or involve standing on your feet for a long time.
The hemispheres of the brain interact to help us remember events
Do people from left-handed families have better memories? According to a recent study, the answer to this question is yes. The findings also help explain why children do not remember events until approximately 4 years of age, when interhemispheric connections are fully developed.
Stephen D. Christman and Ruth E. Propper, PhDs, of the University of Toledo in Ohio, studied memory as a function of familial left-handedness. Interestingly, people do not necessarily have to be left-handed personally to be the owners of a unique feature: there is evidence that the functions of the two cerebral hemispheres, even in right-handed people with left-handed relatives, are less specialized, interact more and are connected by a more developed corpus callosum (corpus callosum - a bundle of connective fibers) than the hemispheres of people with right-handed relatives. For reasons that are not entirely clear, there is a hereditary predisposition to left-handedness.
Christman and Propper studied two types of memory—episodic (recalling events and recognizing them) and non-episodic (actual memory and implicit memory, the latter of which concerns those things that people “just know”). In one case or another, the strength or weakness of memory may not have much influence in educational tasks, since we can recall things we have learned by 'remembering' them (episodic memory) or 'knowing' them (implicit memory). The main difference is that people who 'remember' can also remember details about the time and place at which they learned a fact.
In the first experiment, which studied 180 right-handed recruits at Lackland Air Force Base in San Antonio, Christman and Propper found that, above chance, for different types of verbal memory tasks, subjects with left-handed relatives had a higher prevalence of episodic memory. and poorer implicit memory performance was observed. From this, researchers suggest that a higher level of interhemispheric interactions enhances episodic memory.
In the second experiment, the researchers examined episodic and semantic (factual) memory in 84 right-handed graduates, examining what happened when they were presented with words and letter strings for one or both hemispheres. When Christman and Propper stimulated one side of the brain, participants remembered facts better. When the researchers stimulated both hemispheres, participants remembered events better—again confirming the role of hemispheric interactions in episodic memory.
Christman and Propper conclude that because the two hemispheres of the brain work together to help us remember events, people whose hemispheres work more closely together (left-handers in left-handed families) remember events better than they remember facts. As a result, the authors say that studies of memory properties should take into account both familial and, perhaps, personal left-handedness of subjects (a weak or strong preference may also be important). Further research may help explain why hemispheric interaction is beneficial for episodic memory, given that factual/implicit memory works better in one side of the brain.
Researchers emphasize that memory performance has nothing to do with so-called “mental superiority.” While the categorization of people as “right-brained” or “left-brained” is common in the popular press, it has not received much support in the scientific literature. Both hemispheres of all people are involved in virtually all tasks.
Finally, the research sheds light on why children do not have any episodic memories until about 4 years of age. The onset of episodic memory roughly coincides with the maturation of the corpus callosum and myelination, the growth of the fatty protective sheath around nerve fibers. In light of these findings, this would imply that the functioning of the corpus callosum is fundamentally important in the formation of memories and may explain why its maturation in early childhood is responsible, at least in part, for the emergence of episodic memory.
R. Kagirov
Prognosis for treatment of left hemisphere stroke
Stroke is a dangerous and complex disease. Unfortunately, no doctor can give an accurate prognosis regarding the patient’s recovery. The success of rehabilitation primarily depends on the timeliness of assistance and initiation of treatment.
Regarding the duration of the recovery period, the following factors must be taken into account:
- size of the lesion;
- presence of emotional disorders;
- the age of the person who experienced a left-sided stroke - the older the patient, the more difficult it is for him to recover;
- deterioration of mental abilities;
- localization of the lesion.
The intensity of stroke development is also of great importance. With a favorable course of the disease, when the patient regains consciousness after a few minutes or hours, the likelihood of complete restoration of lost functions is quite high. The compressed development of the disease is more dangerous, as there is a risk of repeated vascular rupture. However, in this case, most of the functions are restored. A progressively severe variant of the development of the disease is characterized by the fact that a person comes to his senses more than three days after the stroke. In this situation, symptoms rapidly increase and there is a high chance that the patient will receive lifelong disability.
The prognosis for life after treatment for a left hemisphere stroke is individual for each person. However, timely treatment, compliance with doctor’s recommendations, a healthy lifestyle, as well as a reduction in emotional distress help speed up the recovery process.
Signs of right-sided paralysis
If there was a stroke in the left hemisphere, the patient’s right side of the body is affected, the muscles of the limbs are paralyzed and there is no speech. These are the main differences between this condition. Patients also develop the following symptoms:
- Common symptoms are headache, nausea, vomiting and weakness. They appear in the first few days and are considered the body’s response to damage to brain neurons;
- Loss of movement - with central paralysis, the right limbs are flaccid, there is no sensitivity, the patient cannot perform any actions with the right arm and leg. If peripheral neurons are affected, the patient experiences tremor, and some movements are difficult on the same side;
- Reduced memory – there are difficulties in remembering sentences; in severe cases, it is difficult for a person to repeat individual words;
- Paresis of the right facial nerve - this branch innervates all facial muscles on its side. In the absence of control, the muscles relax, the patient’s corner of the mouth and lower eyelid “hang”;
- Spontaneous contractions of some skeletal muscles on the right - usually the arm is bent at the elbow joint, the leg is straightened, and inward rotation of the foot is noted.
The listed symptoms are observed a few minutes after hemorrhage. As health deteriorates, the patient develops stress, accompanied by depression and difficulties in communication.
Prevention
The basis for preventing left-sided stroke is lifestyle correction. To avoid experiencing the consequences of this serious disease, you need to:
- Watch your weight. Excess weight leads to increased blood pressure and provokes cardiovascular diseases.
- Avoid fatty foods and moderate your intake of foods of animal origin. Add more vegetables and fruits to your diet.
- Quit smoking. Cigarettes have a destructive effect on blood vessels, constricting them and preventing normal blood circulation.
- Exercise regularly and go for walks. Physical activity reduces the risk of developing vascular diseases.
- Drink moderate amounts of alcohol. A complete abstinence from alcoholic beverages is not necessary, although it is best to discuss whether you can drink alcohol with your doctor.