What is it and what does it consist of
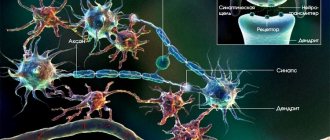
White matter of the brain is a collective concept that refers to a complex of nerve structures through which electrical and chemical impulses are transmitted. The nerve cell can be thought of as a trading post where travelers sell and buy goods, relax and discuss prices. However, for successful commercial activities, traders need roads, thanks to which they make long journeys from one point to another, delivering valuable cargo. It’s the same in the brain: the white substance ensures the delivery of nerve impulses.
The white matter of the nervous system serves as a springboard for the gray matter. The latter, unlike white, acts as a generator and collector of information. The white substance transmits the nerve impulse and is not responsible for its creation. On the other hand, there are opinions of many experts that white matter determines the speed and quality of brain functioning, namely the number of formed nerve pathways. Indeed, the development of the mental component of the mental sphere in children usually means the formation of white matter in the brain.
The white substance is opposed to the gray one. Gray matter is a collection of nerve cell bodies and their appendages (glial tissue, capillaries, partially short processes and early axons). The functions of gray matter include providing programs for higher nervous activity, such as thinking, memory, and perception. The contrast is not only functional, but also anatomical. If the gray matter is the cortex (the final layer of the brain), then the white substance is located between the cortex and the deep structures of the brain.
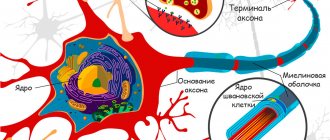
Speaking of structure, the substantia alba differs from the gray matter: the white matter of the brain consists of bundles of long processes - axons, covered with a myelin sheath. This layer, consisting of fat components, provides a person with an electrical impulse transmission speed of up to 100 m/sec on average. An axon that does not have myelinated fibers transmits information up to 10 m/sec. The white color of the substance is provided by myelin, and on a section the subcortical ball of the substance looks whitish-cream.
So, the white matter of the brain is represented by myelinated axons that connect different parts of the brain. Anatomically, the processes are divided into long ones, responsible for communication between distant parts of the brain, and short ones, connecting nearby structures (brain convolutions). They are located as follows:
- Short . They lie directly under the cortex of the brain and are called subcortical.
- Long or intracortical. This part of the white matter is located in the deep parts.
In addition, white matter is conventionally divided into 3 types, depending on anatomical features:
Associative connections . Fibers of this type of white matter provide a general connection between areas of the cortex, but located in the same hemisphere. For example, association fibers connect the area of general sensitivity (parietal cortex) with the frontal cortex.
Commissural fibers . These structures are represented by cerebral adhesions and articulate similar areas, but on different hemispheres. For example, the hearing area on the temporal cortex of one hemisphere with the same area in the other part of the brain. The largest structure here is the corpus callosum. In the physiological aspect, the structure ensures the interconnection of both hemispheres. The corpus callosum has not been fully studied.
Projection fields . This type of white matter connects the cerebral cortex with structures morphologically located below. Functionally divided into two subtypes:
- Efferent fibers. Along these pathways, the nerve impulse is sent from the cortical centers to the underlying structures;
- afferent. These fibers ensure the delivery of electrical signals from underlying structures (internal organs, tissues) to the brain.
There are phenomena where people who do not have this unifying structure (corpus callosum) have phenomenal memory. Experts say that this is due to the corpus callosum, which acts as a kind of barrier that limits the flow of electrical impulses. In the case where it is not present, the areas are connected to each other directly, without any collector system or filters.
The white matter of the medulla oblongata is represented by short and long fibers. The latter include the pyramidal tracts running through the anterior clusters of the spinal cord. The fibers of the medulla oblongata form several tracts:
- Rubrospinal;
- Vestibulospinal;
- Reticulospinal tract.
Through these structures, information flows from the nuclei of the medulla oblongata, reticular and vestibular nuclei to the spinal cord.
The white matter of the midbrain forms a cluster represented by the cerebral body, located deep in the cerebellum. Branching, the fibers of the body pierce all the convolutions of the coordinating center of the brain. The fibers of the white matter of the cerebellum form pathways leading to the cerebral cortex and neighboring brainstem structures.
Functioning of axons
Through neural processes, different parts of the cerebral cortex are connected and the body’s vital functions are coordinated. As a result of the creation of connections between neurons through electrical impulses, leading to the formation of centripetal and centrifugal signals, human activity is manifested in great diversity. The furrows and convolutions form four lobes in each hemisphere:
These lobes of the brain are more developed than others and have greater mass. The work of the white matter of the frontal lobes contributes to the formation of voluntary movements, regulates complex forms of behavior, mechanisms for reproducing speech and writing, and thinking processes. The white matter pathways of the brain contribute to absolutely all motor processes. In modern neuropsychology, the nerve centers in the frontal lobes are a software unit that controls and regulates complex forms of life activity.
The following centers are located here: 1) understanding of oral speech, 2) perception of sound signals, 3) vestibular analyzer, 4) center of vision, 5) center of smell and taste, 6) center of music. The functioning of the temporal lobes is asymmetrical. If a person is left-handed, then the right hemisphere will have greater functionality; if you are right-handed, then the left hemisphere will be more active (dominant). The functioning of the white matter of this hemisphere makes it possible to understand speech and learn based on the information heard. By combining olfactory, auditory and visual information, draw conclusions, creating images of a harmonious emotional background and long-term memory. The functions of the non-dominant hemisphere include: recognition of music and rhythm, voice intonations, recognition of faces and their expressions, learning using visual images.
The centers located here give a person general sensitivity: pain, tactile and temperature. There are also centers that carry out complex coordinated movements, brought to the point of automatism, and actions of a purposeful nature, acquired through training and continuous practice throughout life. These are eating, walking, dressing, writing habits, certain work activities and other actions that are unique to humans. The left dominant side provides the ability to write and read; is responsible for actions leading to the desired result; is responsible for feeling the position of your body as a whole and its individual parts; for determining the right and left sides. In the right non-dominant lobe, the process of transforming all information coming from the occipital lobes takes place, a three-dimensional picture of the surrounding world is created, orientation in space is ensured, and distances between landmarks are determined.
White matter functions
Primarily, the white matter of the brain is responsible for coordinating information in the central nervous system. Thanks to the white substance, the brain is capable of “communication” between its own areas. In addition to the brain, the substantia alba is also located in the spinal cord, but its set of functions in the periphery is different. The white matter of the spinal column is responsible for the sensory and motor components of nervous activity. White matter acts as a conductor. The white substance also provides:
- Connection of similar structures of the hemispheres;
- connection of various parts of the cerebral cortex with other parts of the nervous system, in particular with the spinal cord.
Prevention of operational disruptions
Physical activity, even in older people, affects the structure of white matter.
Ordinary morning exercises, or even better, sports exercises, intense walking - all this improves the blood supply to myelin fibers.
In addition, the load leads to densification of the white matter, which has a positive effect on increasing the speed of signal transmission.
A healthy lifestyle leads to improved brain function, which significantly improves the condition of the whole body. Intellectual activities along with physical activity, games in the fresh air, a variety of active recreation - all this will certainly help maintain memory and clarity of mind at any age.
Difference from gray matter
Gray matter differs from white matter not only functionally, but also anatomically. Location: gray matter is located on the surface of the cerebral hemispheres and is its upper layer. The white matter is located between the gray and deep structures of the brain.
Structure
gray matter consists of soma neurocytes and its appendages
white matter consists of myelinated fibers
Function
gray nuclei are responsible for specific specific functions of the nervous system
White matter is a conductor of nerve impulses
To further understand the differential differences, you can go to the article difference between white matter and gray matter.
Preventative measures for brain health
The speed of nerve impulses directly depends on the integrity of the white matter. Its healthy state determines its normal functioning. It has been scientifically proven that with increasing age, the quality of white matter and its functionality decline. Therefore, you need to comply with some simple conditions:
- Exercise regularly at any age - from simple morning exercises to serious sports.
- Monitor your health and consult a doctor on time.
- If diseases that can cause brain damage occur, treat under the supervision of a doctor.
- Remove bad habits from your life that can worsen your health.
- Increase immunity using hardening procedures.
- Keep your emotional state under control.
- Give food for brain activity: read, write, solve crosswords and other puzzles.
- During pregnancy, be under constant supervision of a specialist.
An active physical life and intellectual pursuits in both work and leisure will prolong normal performance and clarity of mind, and maintain strong memory. Teach children to take their health seriously as early as possible. Play sports and games that develop intelligence. It’s good to work together, proving its usefulness by example.
Only humans have higher nervous activity, and this is their direct difference from other species of mammals. The conditioned reflex actions that he masters in the process of life put him at the highest level of development.