Description of the disease
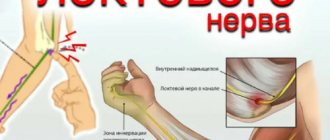
Vessels, nerves, synovial membranes, and tendons pass through the carpal (carpal) canal. The median nerve is also located here - the main nerve of the arm, running from the brachial plexus to the fingertips. Responsible for coordination of movement, fine motor skills of the hands, contraction and expansion of blood vessels from the action of external stimuli, regulates the functioning of the sweat glands. The width of the canal is limited on three sides by bones and the transverse ligament.
The carpal tunnel itself is quite narrow, which contributes to the formation of various pathologies. Any additional narrowing entails compression of the processes of nerve fibers and blood vessels, and blood supply is disrupted. Pathological processes proceed slowly, begin with a loss of physiological sensitivity, and lead to motor and trophic disorders. The picture of the disease has clear symptoms with a characteristic clinical picture, which makes it easy to make a diagnosis even at the initial stage.
Symptoms of the disease
- 1. Reduced sensitivity of the hand.
First, patients begin to notice numbness in their fingers immediately after waking up. Over time, the periods of paresthesia increase, and feelings of burning, pain, cold or heat are added. Carpal tunnel syndrome is characterized by a simultaneous, radically opposite change in sensitivity. In one area it increases, but the other part of the palm does not feel anything.
- 2. Burning pain in the palms with shooting in the fingers.
Initially, the pain is felt in the area where the nerve is pinched, then it gradually begins to affect the entire arm: from the shoulder to the fingertips. This is accompanied by swelling of the wrist. As a rule, the dominant hand hurts: the right hand in a right-handed person, the left in a left-handed person, but bilateral symptoms also occur.
- 3. Muscle weakness and impaired motor activity.
As a result of prolonged pinching and inflammation of the nerve fibers, the hand loses muscle strength, and movement restrictions appear. It becomes difficult to operate small objects, such as buttoning buttons. The function of grasping and then holding objects weakens. Gradually, a decrease in the performance of the hand leads to muscle atrophy and deformation of the hand.
- 4. Lesions of the autonomic nervous system.
This is expressed in a pale and sometimes bluish color of the hand, dry skin, brittle nails, and cold hands.
Naturally, carpal tunnel syndrome affects the general physical and mental condition of the patient. He loses his ability to work, his quality of life decreases. Regular pain and a constant feeling of discomfort intensify at night, which interferes with normal sleep and causes insomnia.
A characteristic feature of this disease is that the patient can relieve discomfort on his own, without resorting to medications. To do this, just lower your hands down, move your fingers, shake your hands, stretch them, do massage, gymnastics. These manipulations help restore blood supply, but, unfortunately, not for long, since they do not get rid of the causes.
Symptoms.
- Painful numbness in the hand. The pain can be transmitted down the arm, sometimes to the shoulder. Numbness is localized on the palmar surface of the I, II, III fingers and the radial side of the palm.
- Paresis of fingers I, II, III, especially when clenched into a fist. There may be thenar atrophy.
- Clumsiness of the hand and difficulty with precise movements.
- Increased sensitivity in fingers I, II, III, more pronounced in the tips.
- Phalen test: clenching your hand into a fist for 30-60 seconds results in pain or tingling.
- Tinel's sign: Tapping over the carpal tunnel of the hand causes pain and tingling in the area of the median nerve in the hand.
Innervation zone.
Diagnostics
It is easy to make a diagnosis of this disease; it is enough to interview the patient and conduct several tests, since carpal tunnel syndrome has clear distinctive features. Among them are the symptoms described above and preservation of the functions of the little finger, which is not affected when the nerve and vessels in the carpal tunnel are pinched.
The doctor also performs palpation and the following tests:
- Hoffman-Tinel test: tapping the area of the median nerve. With carpal tunnel pathology, the patient feels numbness, tingling, and burning in the palm of his hand.
- Phalen test: bending the hand at the wrist joint as much as possible, the patient feels pain and numbness in the palm.
- It is difficult to hold your arms raised above your head for more than 1 minute; pain and numbness of the limbs begin.
- It is impossible to connect (touch) the thumb with the little finger.
- To confirm the correctness of the diagnosis, determine the extent of the lesion and associated complications, additional examinations are prescribed:
- Electroneuromyography to evaluate the conduction of nerve impulses is the gold standard for diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Ultrasonography helps detect damage and inflammation.
A neurologist, physiotherapist and hand surgeon can make a diagnosis and carry out treatment.
Carpal tunnel syndrome - Causes and treatment
Posted at 01:13h in Services by doctor
Tunnel syndrome belongs to the group of compression-ischemic neuropathies - diseases of the peripheral nerves not associated with infectious and vertebrogenic factors. A pinched median nerve in the carpal tunnel is caused by thickening of the nerve fibers or hardening of the surrounding tendons. The causes of the pathology can be mechanical injuries, inflammation of the joints, tumors, and endocrinopathies. When nerve tissue is compressed, the blood supply to the nerve is disrupted. Similar changes are observed when the same wrist muscles are regularly overstrained.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is an occupational disease of individuals who perform similar movements with the hand during work. This pathology affects grocery store cashiers, computer users, artists, hairdressers, violinists, miners, wrappers, and guitarists. In women, the disease is much more common than in men, which is due to the relatively small volume of the carpal tunnel. The first clinical signs of the disease appear at 30-45 years of age, and its peak occurs at 50-60 years of age. Carpal tunnel syndrome is a chronic disease with frequent exacerbations and remissions, manifested by pain, paresthesia, and motor dysfunction. These clinical signs have varying degrees of severity.
The same group of neuropathies includes cubital tunnel syndrome. Injuries to the elbow joint lead to inflammation and damage to the tendon arch. It thickens, the channels narrow. Individuals who experience constant compression of the ulnar nerve are most susceptible to developing ulnar nerve tunnel syndrome.
Next, we will take a closer look at carpal tunnel syndrome, which makes up the vast majority of cases of the disease.
There are two types of compression-ischemic neuropathy of the hand:
- Primary is an independent pathology that does not depend on other processes occurring in the body. Primary neuropathy is usually caused by overuse of the wrist muscles, as well as prolonged and excessive stress on the joint.
- Secondary – a symptom or complication of any disease in the body. Systemic connective tissue diseases, arthrosis, arthritis are manifested by tunnel syndrome.
Carpal tunnel syndrome was discovered by English surgeon Paget in 1854. He was the first to describe the clinical signs of the disease and the mechanism of its development. Currently, the pathology is diagnosed extremely rarely. Its pathogenesis and etiology have been little studied, so tunnel syndrome is poorly recognized and detected. If this problem is left unattended, negative consequences may develop.
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
All measures taken are aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease - complete or partial elimination of compression of the median nerve. The treatment method depends on the severity of the syndrome. Choose between conservative and surgical treatment. It is also the doctor’s job to identify the cause of the disease in order to limit movements that worsen the symptoms.
Conservative treatment
Patients are prescribed to wear an orthosis, which holds the wrist joint in a position that is safe for blood vessels and nerves. It is recommended to wear it constantly, during the day and at night. According to statistical data, orthotics are effective in the early and middle stages of the disease. It is recommended to switch to a salt-free diet and limit fluid intake to reduce swelling.
Medicines are also prescribed:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids orally or by injection to relieve pain and restore joint mobility.
- Vascular drugs to improve blood supply to tissues.
- Diuretics to relieve swelling.
- Vitamin B6 to relieve symptoms and increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Physiotherapy helps to speed up the therapy process and achieve a positive result faster: electrophoresis, UHF, magnetic therapy and other methods. A course of physical therapy and massage are often prescribed. The complex combination of these methods of therapy and the use of medications leads to remission in 59% of patients. The rest are forced, on average, after 1-2 years to turn to a hand surgeon for surgery.
Surgery
If conservative treatment is ineffective and the disease is advanced, surgery is prescribed. They are dealt with only by hand surgeons - highly specialized specialists who perform surgical procedures on the hand. The purpose of the operation is to release the median nerve and reduce pressure. There are two ways to open the carpal tunnel:
- An open surgical procedure in which an incision of about 3 cm is made on the wrist. Having gained access, the surgeon cuts the ligament, increasing the volume of the carpal tunnel.
- Endoscopy has a shorter incision length, which is up to 1.5 cm, but is performed in two places. They are necessary to insert a microchamber, which can be used to dissect the ligament.
Both types of surgery are performed under local anesthesia. Sometimes excision of tissue around the nerve and tendons with scarring, ovaries and cords is required. On average, the procedure is carried out within 20 minutes.
At first, the patient may feel pain in the scar area and physical weakness of the wrist. It will take several months until complete recovery; the period is individual in each specific case. Rehabilitation consists of gymnastics, massage, and physiotherapy. During the recovery period, many have to give up their type of activity if it affects recovery.
According to statistics, up to 90% of patients who undergo surgical treatment completely restore the physical activity of their hands and get rid of the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. Relapses occur in 8 - 12% of cases.
Alternative treatments.
You can relieve the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome without medication or surgery. To do this you need:
- Reduce the load on your hands and wrists, and eliminate activities that worsen the condition.
- Secure the arm with a splint, orthosis or elastic bandage to limit mobility.
- Relieve swelling with ice, limit fluid and salt intake.
- Perform hand exercises aimed at stretching the joints. We recommend exercising under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
If there is no improvement, then you should not delay consulting a doctor.
Treatment
Physical therapy
Since carpal tunnel syndrome has been shown to be associated with obesity and low mobility, correcting these factors will help improve the condition. An exercise bike, a bicycle and other exercises requiring prolonged grip are not indicated for this disease.
The use of physiotherapy devices may provide temporary relief. For example, short-wave diathermy provides significant temporary improvements compared with placebo, including reduction in symptoms and pain, and improvement in hand function.
Ergonomics and hand therapy
Wrist braces, which keep the hands in the correct position, have been shown to be effective as an at-home treatment when used at night for a minimum of 3 to 4 weeks.
They are inexpensive and safe, so in the initial diagnosis of the disease, a neutral night splint should be considered first.
Specific muscle strengthening programs and gliding exercises have not been shown to be effective. Massage and manual techniques that improve nerve glide have no proven therapeutic effect. Changes in the ergonomics of the workplace (table, chair, body position settings), changing equipment or tools are not effective in cases where the syndrome has already been confirmed.
Making a custom tire
Most people with early stage hand tunnel syndrome respond well to conservative therapy, which primarily consists of using a night brace for three weeks. Ready-made splints from orthopedic stores can provide improvement, but individual ones are more convenient and more effective, and therefore are preferable. It can be said that a special plastic splint molded to the patient's hand (orthosis) is the best choice for the initial treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Drug therapy
Steroid injections into the carpal tunnel have been shown to be effective over the long term when other treatments have failed. Blockades can be indispensable in case of contraindications to surgical treatment, for example, during pregnancy. Ultrasound measurements of the median nerve of the arm predict the effectiveness of steroid blocks. Ultrasound navigation when performing a blockade does not lead to a reduction in complications or an increase in the effect of the blockade.
Anticonvulsants such as gabapentin or pregabalin, which are prescribed for various neuropathic pain, may also be used for carpal tunnel syndrome.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and/or diuretics sometimes have some effectiveness in patients with special conditions (fluid retention or flexor tendon tenosynovitis)
However, in general, for all patients with carpal tunnel syndrome, the effectiveness of gabapentin, diuretics, or NSAIDs is controversial. According to the American Orthopedic Association guidelines, systemic medications (pills, intramuscular injections, IVs) are no more effective than placebo for treating carpal tunnel syndrome. In addition, it is worth noting that supplements with B vitamins (B-6 and B-12) also do not provide proven benefits.
What happens if you don't get treatment?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is not life-threatening and is a slowly occurring pathological process. The disease has a favorable prognosis for recovery, but due to neglect of their health, some people are in no hurry to visit a doctor. Over time, this leads to a decrease in motor activity, muscle strength, and impaired fine motor skills. If left untreated, irreversible processes will begin and the median nerve will atrophy. This will lead to the loss of functionality of the brush, which will no longer be possible to return.
Reasons for the development of the syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome disease develops under the influence of several factors. A decrease in the diameter of the carpal tunnel may occur due to compression of the nerve. Swelling of surrounding tissues and for both reasons simultaneously. The root cause is trauma, both one-time and microtrauma inflicted regularly due to lifestyle or work activity.
1. “Dangerous” professions.
Among the professions at risk:
- drummers;
- programmers;
- gamers;
- artists;
- pianists;
- secretaries;
- sign language interpreters;
- seamstresses;
- engineers;
- assembly line workers and others.
Most often, the syndrome is diagnosed in women over 40 years of age, mainly due to their professional choice and hormonal changes in the body. However, the disease can occur at any age.
2. Accompanying illnesses.
- A number of medical conditions increase the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome, including:
- Injuries, dislocations, fractures, causing hematomas and swelling.
- Neoplasms, tumors of ligaments and tendons.
- Frequent intratunnel pressure and swelling of the limbs.
- Chronic heart failure and other diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
- Diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases and other endocrine pathologies.
- Obesity, regardless of the causes of its occurrence.
- Chronic arthritis, sclerosis, collagenosis and vasculitis.
- Tuberculosis and non-tuberculous bacterial infections.
- Kidney failure.
- Alcoholism, smoking, drug use.
3. External factors.
- Work in low temperature conditions. For example, fishermen, butchers, public utility workers.
- Working with heavy tools and vibrating devices. For example, builders, repairmen, industrial workers.
Any of the listed effects or a number of factors together causes a narrowing of the carpal tunnel and pathology develops. Most often, the disease develops according to the following scheme: trauma - aseptic (non-infectious) inflammation, spreading to the carpal tunnel - swelling of the subcutaneous fat layer. Then everything goes around in a new circle:
increasing pressure on nerves and blood vessels leads to even greater trauma and inflammation, causing progression of the disease and transition to the chronic stage.
Causes
It is worth mentioning from the outset that carpal tunnel syndrome can be associated with various factors. On the one hand, it can be noted that the symptoms are more pronounced after or during the load on the hand, on the other hand, it cannot be said that the load on the hand is the cause or causes the disease. Associated does not mean is the cause.
Demography:
- Elderly age
- Female
- Increased body mass index, especially after rapid weight gain
- “Square” wrist shape
- Brachymorphic type of body structure (short arms, short legs)
- Dominant hand
- White Caucasian
Many factors are inherited (“square” wrist, thick palmar ligament, body type). Also, conditions associated with carpal tunnel syndrome have a hereditary predisposition (diabetes, thyroid disease, nephropathy, neuropathy).
Diseases/medical problems:
- Fractures of the distal radius
- Acute wrist injury (sharp flexion/extension)
- Neoplasms, injuries occupying a place in the carpal tunnel (tenosynovitis of the flexors, hygromas, hematomas, aneurysms, abnormal muscles, various tumors, edema)
- Diabetes
- Thyroid disorders (usually myxedema)
- Rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases of the wrist joint
- Recent menopause
- Hemodialysis
- Acromegaly
- Amyloidosis
Carpal tunnel syndrome due to specific stress on the hand:
- Long power grip
- Prolonged stay in an extremely uncomfortable position
- Repeating the same movements multiple times
- When using the mouse and keyboard for a long time
- Prolonged exposure to vibration/cold
Other development factors:
- Lack of aerobic exercise
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Using crutches/walkers/canes