Synonyms: sciatica, lumbago - for the sciatic nerve, lumbago (colloquial version).
ICD-10 codes:
- unspecified form - M79.2;
- specified ones are assigned to class G, section “Lesions of individual nerves, nerve roots and plexuses (G50-G59)”. Damage to the trigeminal nerve – G50, facial – G51, etc.
Author: Druzhinkina V.Yu., neurologist. June, 2021.
Neuralgia is a lesion of the nerve fiber, accompanied by paroxysmal severe pain along its course. It occurs in acute and chronic forms. Treatment involves relieving pain, prevention involves preventing re-exposure to the factors that led to the development of pathology.
Neuralgia is a term that reflects the involvement of a nerve in a pathological process. It is based on an inflammatory reaction against the background of hypothermia, exposure to microorganisms, compression, and injury.
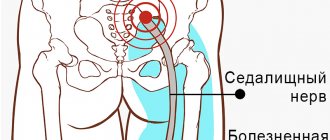
Neuralgia in women and men is not much different. In women, when the intercostal nerves are irritated, pain is more often localized in the heart area, in men - in the hypochondrium.
What is neuritis, nerve neuritis?
Neuritis is a lesion of the spinal or cranial nerves, manifested by syndromes of irritation and (or) loss of their functions in the corresponding area
innervation.
Neuritis occurs during acute and chronic viral and bacterial infections (influenza, pneumonia, dysentery, focal infections). Nerve damage is relatively rarely inflammatory in nature; various degenerative changes are more often found.
Causes
Women aged 35-40 years are more likely to get sick . Inflammation of the nasociliary nerve occurs for various reasons:
- Due to improper treatment of teeth in the upper jaw. Nerve endings connect to the teeth. If a branch is touched or damaged, then inflammation occurs. More often after difficult removal or remnants of roots in the hole.
- Pulpitis, periodontitis, gingivitis, periodontitis. With a long process, the infection penetrates the nerves.
- When installing crowns and dentures, galvanism sometimes occurs. The so-called electric current in the mouth. This occurs from the influence of the material that is used to make prostheses. Or simply poorly installed, putting pressure on the fabric.
- Injuries to the face and head. Accordingly, when the skin and muscles are damaged, the nerve is injured. It becomes inflamed and symptoms appear.
- Consequence of surgery on ENT organs. Through negligence, the doctor damages the nasociliary nerve. Or inflammation progresses against the background of sinusitis and sinusitis.
- Bacteria and viruses. Sometimes the infection can immediately reach the nerve endings. But that rarely happens. More often it occurs as a complication of conjunctivitis, otitis, and sinusitis. If the body is weakened, then there is a greater chance of a bacterial infection.
The intensity of pain depends on the etiology . In addition, patients may have several causes of inflammation.
Neuritis symptoms
The clinic of neuritis is characterized by dysfunction of the innervated structures. Since most nerves are mixed, when they are damaged in the innervation zone, flaccid paresis (paralysis), muscle atrophy, decreased and loss of reflexes, impaired sensitivity and autonomic disorders (swelling, cyanosis, increased sweating, depigmentation, hair loss) occur.
With neuritis of the facial nerve, damage to the root or trunk of the facial nerve occurs at various levels, manifested by homolateral paresis or paralysis of the facial muscles.
Symptoms
Neuralgia develops acutely - the patient immediately develops pain, sensitivity and motor function may be impaired. With a long course of the disease, muscle atrophy is observed in the affected area.
The localization of pain depends on the zone of innervation of the inflamed nerve. All neuralgia are characterized by the appearance of sharp, shooting, burning, unbearable pain. This is due to irritation of sensitive fibers.
When the nerves containing sensory fibers are inflamed, the patient experiences a disturbance in sensitivity.
Options:
- dysesthesia - a change in perception, for example, tickling is felt as pressing or tingling, and hot as cold;
- anesthesia - numbness with loss of pain, tactile, temperature perception;
- hyperesthesia - excessive sensation of even a small impact, as an example - pain with a light touch;
- parasthesia – spontaneously occurring unpleasant sensations in the form of pain, crawling sensations (typical for patients with diabetes).
Characteristic signs of neuralgia are:
- absence of pain during the interictal period;
- increased discomfort when inhaling, coughing (of the intercostal type, inflammation of the solar plexus) or touching the skin where the nerve passes (for other options);
- Any influence can provoke a new attack - a gust of wind, cold air, brushing your teeth, combing your hair, accidentally pressing on the nerve passage points.
Duration of symptoms. The duration of manifestations ranges from a week or two to an indefinite period.
Shortness of breath with neuralgia. The pathology itself does not cause shortness of breath or lack of air, but with inflammation of the intercostal nerves or solar plexus, they are observed at a height of pain, especially in elderly patients. Also, with these types there may be lumbago, burning sensations in the right side.
Heartache. Neuralgia does not cause heart pain, but due to severe discomfort, existing diseases of the cardiovascular system can worsen. This manifests itself in increased blood pressure and an attack of angina.
Irradiation of pain. The pain can radiate to the arm, leg, ear, eye, teeth, chest - those organs and formations that contain the inflamed nerve or its branches. Irradiation to the mammary gland and abdomen is possible. Irritation of the nerves in the face often leads to pain in the teeth.
Numbness . Inflammation in the nerves associated with problems in the cervical spine is often accompanied by numbness in the arm and shoulder; in the lumbar region – legs, perineum; in the chest - chest, back, abdomen.
Temperature with neuralgia. With pathology, an increase in temperature may be observed if the cause is infectious, viral diseases (most often the herpes virus), or disintegrating tumors.
Specific symptoms. Cough with neuralgia is observed with inflammation of the vagus nerve. When the nerves responsible for hearing and salivation are damaged, dry mouth, drooling, and decreased or distorted auditory perception are noted.
What can neuralgia be confused with?
The severity of pain during neuralgia and its rapid increase make the doctor suspect several other, more serious diagnoses. Differential diagnosis is presented in the table:
| Sign of another disease | Sign of neuralgia | |
| Myocardial infarction | The ECG shows characteristic changes, often a serious condition; there may be vomiting, loss of consciousness, and shortness of breath. | There are no changes on the ECG, the pain is not relieved by taking nitroglycerin, there is no shortness of breath, no cold sticky sweat. |
| Angina pectoris | The ECG shows characteristic changes. The pain is relieved by taking nitroglycerin. | There are no changes on the ECG, the pain is not relieved by taking nitroglycerin, it intensifies with movement, there is no shortness of breath. |
| Esophageal hernia | Occurs after eating, especially overeating, drinking carbonated drinks, mushrooms, corn, smoked foods; when moving to a horizontal position after eating. The diagnosis is confirmed by fluoroscopy of the stomach with barium in the Trendelenburg position, and pathology can also be seen with FDGS. | There is no connection with food intake; FGDS and X-ray with barium do not find pathologies. |
| Osteochondrosis | The pain is often aching, constant, and long-lasting. Changes are detected on X-ray, CT or MRI. NSAIDs help well | Sharp, shooting pains; no changes are found during examination. NSAIDs help less. |
| Inflammatory processes in the tooth canal | There are no trigger points, pain when chewing, contact with cold, hot, sour. | There are trigger points. Pressing on the tooth is usually painless. |
| Pancreatitis | Often the pain is of a girdling nature. There are changes on ultrasound - swelling of the gland, uneven structure. Biochemical parameters (amylysis, AST, ALT) are increased. Nausea and vomiting are present. | There are no changes on ultrasound. Biochemical parameters (amylysis, AST, ALT) are normal. No nausea, vomiting. |
| Cholecystitis, liver disease | There are inflammatory changes on ultrasound. Biochemical parameters (bilirubin, AST, ALT) are increased. Nausea, vomiting, yellowing of the skin, discoloration of stools, darkening of urine are present. | There are no changes on ultrasound. |
| Kidney diseases | There are signs of inflammation on ultrasound. In a general urine test, leukocytes, mucus, microorganisms, and blood are detected. An increase in body temperature is often noted. | There are no changes in ultrasound or urine analysis, tapping on the lumbar region is painless. |
| Pneumonia | There is a cough, fever, weakness, shortness of breath. An examination reveals pneumonia. | There are no changes on X-ray or CT. |
Causes of neuralgia
The causes of neuralgia are inflammatory, traumatic, toxic, infectious-allergic, and metabolic effects. Compression of nerves in the bone, musculoskeletal and osteoarticular canals, prolonged microtrauma, especially in combination with hypothermia, and foci of focal infection also play an important role.
In the mechanism of pain syndrome, irritation of peripheral nerve fibers and central changes are important. In various suprasegmental parts of the nociceptive system, a generator of pathologically enhanced excitation may arise, which causes paroxysmal pain of a central nature.
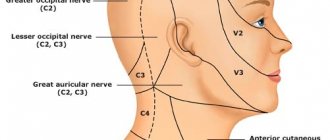
There are neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve, its ganglia and main branches (nasociliary, auriculotemporal nerves, pterygopalatine ganglion), glossopharyngeal nerve, occipital neuralgia, neuralgia of the facial nerve.
Trigeminal neuralgia is clinically manifested by short-term attacks of excruciating pain, most often in the area of the 2nd and 3rd branches of the trigeminal nerve. It is characterized by the presence of trigger zones on the skin and mucous membranes. Touching them provokes attacks of pain. In most cases, an attack of pain is accompanied by severe local and general autonomic disorders: facial hyperemia and swelling on the affected side, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, hypersalivation, possibly increased blood pressure, chill-like tremors, difficulty breathing. Detailed information on trigeminal neuralgia.
There are primary (idiopathic, essential, typical) and secondary (symptomatic) trigeminal neuralgia.
With primary neuralgia (mainly of central origin), attacks occur for no reason or are provoked by any movements of the facial muscles. Secondary neuralgia is usually a complication of the primary disease, has a predominantly peripheral genesis and is often caused by pathological processes in the dentofacial area. The pain is almost constant, periodically intensifying in the form of attacks lasting up to several hours.
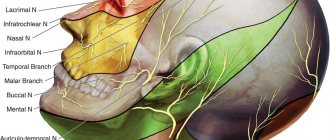
What is nasociliary neuralgia?
Nasociliary neuralgia is an inflammation that affects part of the trigeminal nerve. It manifests itself as sharp pain in the nose and eyes. The disease was discovered by the doctor Charlene in 1931 .
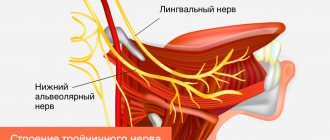
The trigeminal nerve innervates (provides sensitivity) to the muscles, skin of the face, mucous membranes of the nose, mouth, eyes and eardrum. Also goes into the brain.
Divided into three branches:
- Ophthalmic - located in the sinus, orbit and approaches the cerebellum. In the eye area it branches into lacrimal, frontal and nasociliary.
- Maxillary - located in the pterygopalatine fossa of the upper jaw and is divided into the infraorbital and zygomatic nerves.
- Mandibular - goes to the masticatory muscles of the lower jaw.
The nasociliary nerve innervates the anterior part of the nasal cavity, the inner corner of the eye, the root of the nose, the lacrimal sac, and the eyeball.
Neuralgia treatment, how to treat neuralgia, intercostal neuralgia treatment, neuritis treatment
Complex treatment of neuritis and neuralgia (Saratov, Russia) includes a variety of effective techniques. Sarklinik knows how to treat and cure neuralgia neuritis !
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Jabiru | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Phobia, fear, how to get rid of fear, how to overcome, treat and overcome fear, treatment in Saratov
Treatment of irritability and fatigue in Saratov, how to get rid of irritability
Insomnia, treatment of insomnia in Saratov, what to do for insomnia
Nervous exhaustion symptoms signs treatment, exhaustion of the nervous system
Panic, panic attacks: treatment, symptoms, causes, how to fight, get rid of
Comments ()
Main symptoms
The main symptom of neuralgia is pain in the eye and nose area . It can be painful, tolerable, burning and recurrent. Very often nasal discharge and lacrimation are added.
When a person touches the skin, the pain intensifies . The mucous membranes and skin swell and turn red. Plus, conjunctivitis occurs (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye). Pain sometimes occurs when talking, chewing, or inhaling through the nose.
Signs to look out for:
- pain around the eye, worse in the morning;
- involuntary lacrimation;
- increased or absent sensitivity to light;
- the eyelid does not open completely, blinking occurs frequently;
- feeling of dryness in the eyes.
The pain often occurs at night, can last up to several days, or can quickly subside. Localized in the eye area, behind it. A tightening pain may be felt.
With bilateral inflammation, it occurs first on one half of the face, then on the other. Rarely both at the same time.
Possible patient complaints
With Charlin's Syndrome, a person may complain of constant, piercing pain in the nasal cavity . Even strong and painful. When inhaling. The pain is point-like, that is, it is felt on the face in certain places. The patient can point to the points.
It also occurs in the place where the primary disease was: if otitis media, then in the auricle; pulpitis - in the area of the teeth; in the nose - after a herpes rash.
They often complain of pain after treatment has already been carried out . That is, neuralgia takes on a central character. After a long course, the process moves from the branches to the nerve trunk. Therefore, pain is felt even after the cause has been eliminated.
Sometimes it happens that the pain radiates to other places . For example, a patient complains of tooth pain. But there is no pathology in it. This happens because the nasociliary nerve has many branches. These branches innervate the upper jaw, skin, nasal mucosa, eyes, and ears.
What you need to know about trigeminal neuralgia:
- symptoms and diagnosis of the disease;
- treatment methods;
- reasons for the development of inflammation of the ear node and auriculotemporal nerve.
Prevention
It is unlikely that the disease will be prevented 100%, but the risk of its occurrence or exacerbation can be reduced. Preventive actions:
- avoid hypothermia;
- in winter, when there is a cold wind, wear scarves that cover the face;
- do not sleep in an uncomfortable position or tight clothes;
- carefully select crutches;
- do exercises for the spine;
- monitor blood sugar levels;
- do not engage in heavy physical work;
- try to avoid traumatic situations;
- visit an immunologist if the level of immune defense is low (manifested by frequent acute respiratory viral infections, colds, tonsillitis, shingles);
- If a drunk person falls asleep with his arm under him, then there is a high risk of pinching the nerves - the limb must be positioned freely.
Neuralgia is a serious pathology, difficult to tolerate by patients due to the severity and suddenness of attacks of burning pain, sometimes lasting for hours. During treatment, the doctor tries to completely eliminate the disease and prevent it from becoming chronic, so it is important to seek medical help as early as possible.
Treatment
Neuralgia is treated by a neurologist, or in his absence, by a therapist.
Neuralgia can be cured; the prognosis is influenced by timely treatment - the sooner the patient visits a neurologist, the better.
Drugs for the treatment of neuralgia
Basic medications (can be used in the form of injections or tablets, depending on the clinical situation):
- Anticonvulsants are the main active drugs, prescribed to almost all patients to relieve pain. Examples - Finlepsin (INN - carbamazepine), gabapentin.
- Anti-inflammatory – aimed at relieving the inflammatory reaction, swelling, pain. Diclofenac (trade name "Voltaren"), ibuprofen (aka "Nurofen"), meloxicam ("Movalis"), nimesil ("Nise"), ketoprofen ("Ketonal"), ketorolac ("Ketorol") are prescribed. Paracetamol is allowed for pregnant and lactating women.
- Analgesics such as metamizole sodium (aka analgin) are rarely used, mainly in cases of intolerance to anti-inflammatory drugs.
- In cases of severe swelling of the nerve, hormones, such as dexamethasone or prednisolone, may be prescribed in a short course of 3–5 days.
- Muscle relaxants - relax muscles, thereby reducing the load on the inflamed nerve. More often used for neuralgia associated with spinal problems. The drugs are mydocalm and sirdalud. In the absence of these funds, No-spa can be used, but with less effect, since its relaxing effect is aimed not only at the muscles, but also at the blood vessels.
- B vitamins. Play a supporting role, improving the functioning of the nerve fiber. According to separate studies, B2, B6 and B12 reduce neuropathic pain. “Milgamma”, “Kombilipen”, “Neuromultivit” are used.
- For persistent neuralgia, a blockade is prescribed, for example, with novocaine.
To relieve emotional stress, medications based on mint and motherwort are prescribed; in severe cases, antidepressants (amitriptyline has the ability to reduce neuropathic pain) and tranquilizers.
Antibiotics do not treat neuralgia - there is no microbial component.
Physiotherapy
After the acute period has passed (on the 4th day from the onset of the illness and beyond), physiotherapy is prescribed based on well-being and dynamics. In order to relieve inflammation and relieve pain, magnetic therapy is used on the Almag and Almag-2 devices. For intercostal neuralgia, the Kuznetsov applicator is used. An important condition is that the procedures should not cause pain to the patient.
Acupuncture occupies a special place in the recovery process. Properly performed acupuncture activates the nerve and helps prevent complications. Some neurologists are trained in acupuncture and can perform such procedures on patients themselves.
For neuralgia of the facial, ulnar, and radial nerves, special exercises are prescribed. For example, puff out your cheeks, rotate your hand, move your fingers, etc. Their task is to restore the functioning of the nerve fiber and muscles in the innervation zone.
ethnoscience
In folk medicine, there is a recipe for iodine with glycerin, but you should not expect any special effect from it, since there is only a superficial effect on the part of the skin above the nerve, and not on the lesion itself, plus the causes of the pathology are different - if such a recipe may still be appropriate in case of injury , then with an oncological process - no.
In some cases, surgical treatment is used. For example, they separate the nerve and the artery that irritates it, remove bone fragments after injuries, and remove the source of inflammation.
Contraindications for neuralgia
Warming up. Heating the skin and muscles during neuralgia, especially at the beginning of the disease, is not recommended. Heat leads to increased swelling, which compresses the nerve even more. You should not go to the bathhouse for the same reason. Warming ointments can be used on the 3rd–4th day of illness if the cause is hypothermia. It is not forbidden to make compresses with Menovazin on the painful area for distracting purposes - for a short time it can slightly reduce the pain, but in any case this is not a cure.
Massage. It is not prescribed for neuralgia - it will aggravate the situation and cause additional pain. But such rehabilitation measures are indicated if the patient begins to experience muscle atrophy due to long-term pathology. Pepper plaster, mustard plasters - you should not resort to them if you are sick.
Approximate treatment time
- for recovery – 1-3 months;
- rehabilitation – 3-6 months.