Repeated ischemic stroke occupies one of the first places among diseases leading to disability and death. If life expectancy after the first stroke averages eight to nine years, then a second acute cerebrovascular accident can reduce it to two to three years. Therefore, in modern neurology clinics, one of which is the Yusupov Hospital, a large role is given to secondary stroke prevention.
It is proper prevention and treatment that can prevent the recurrence of a vascular accident, because, according to statistics, the probability of a second stroke within a year after the first is about 15%, and after a few years - up to 30-40%.
Who's at risk
After a primary stroke, the body retains mechanisms that provoke the following development of events: intravascular thrombus formation, vascular atherosclerosis. The patient, as a rule, also has a number of concomitant diseases, often in advanced forms: hypertension, diabetes mellitus, arrhythmia, heart failure and others. Preventing recurrent ischemic stroke in such cases is a rather difficult task, but thanks to the efforts of qualified specialists at the Yusupov Hospital, it is feasible.
Repeated ischemic stroke sometimes threatens even patients who are unaware that they have already suffered a vascular accident: patients with short-term disturbances of cardiac or cerebral circulation, the so-called transient ischemic attacks, manifested by the sudden onset of headache, dizziness, numbness of the arm or leg - symptoms which are often ignored, despite the fact that they are the first alarm bells preceding a stroke. The threat of vascular attack increases even more with transient loss of vision, speech, weakness in the upper or lower limb, sudden amnesia and other symptoms.
In this case, the patient should not hesitate; it is recommended to seek medical help as soon as possible at the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital to obtain a doctor’s consultation. You will undergo the necessary examinations: ultrasound examination of large vessels (first of all, it is necessary to examine the carotid arteries), an electrocardiogram, ECHO-CG, detailed blood tests for the lipid profile and the tendency to form blood clots, the level of homocysteine - an amino acid that causes early atherosclerosis and thrombus formation, as well as several times increasing the risk of stroke and heart attack.
A similar examination is also recommended for patients who have suffered a hypertensive crisis, attacks of angina pectoris (pain in the heart area), or arrhythmia. These conditions often precede a stroke and are manifestations of transient ischemic attacks.
Make an appointment
Why does a stroke occur?
WHO experts believe that in the 21st century, stroke will become the most common disease. An increase in the pace and intensity of life, water and air pollution, exposure to occupational factors, alcohol consumption and smoking, excess caloric content and insufficient quality nutrition, a sedentary lifestyle, poor heredity - this is quite enough, but there are other reasons, the main one of which is population aging. An increase in stroke cases in the population of older age groups could explain everything, but...
- Over the past 5 years, a third of the total number of patients with cerebrovascular accidents were people under the age of 50;
- Arterial hypertension in adolescents is detected 3 times more often;
- From 1990 to 2000 in Russia, the absolute number of people dying annually from diseases of the circulatory system increased by 307,000
All these data indicate that stroke is getting younger.
Causes
There are several reasons for the development of a recurrent stroke, including factors beyond a person’s control that provoke the development of a recurrent stroke:
- Patient's age
- Hypertonic disease,
- Alcohol, drug addiction, smoking,
- Poor nutrition
- Failure to follow doctor's recommendations
- Stress,
- Obesity,
- Sedentary lifestyle,
- High cholesterol levels
- Increased irritability
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system,
- Improper work and rest schedule, night shifts, disturbed sleep,
- Diabetes.
The most common type of vascular disorder is ischemic stroke, which accounts for up to 85% of cases. This type of stroke is caused by blockage of blood vessels supplying the brain or their critical narrowing.
The development of ischemic stroke is caused, first of all, by a person’s destructive lifestyle, which means: alcohol abuse, heavy smoking, poor diet, physical inactivity (lack of physical activity). Such habits lead to a deficiency of oxygen in the brain, associated with inadequate heart function, the loss of the vessels’ elasticity and ability to expand, due to which the blood flow increases, which is necessary for the normal functioning of the central nervous system.
Repeated ischemic stroke occurs due to a number of main reasons:
- psychological and emotional stress;
- excessive stress, heavy physical labor (most often, relapses occur during the summer season, if the patient spends a long time in an uncomfortable position, upside down, and also under the scorching sun, as a result of which dehydration occurs, increasing the risk of vascular accident);
- deterioration in quality of life;
- deterioration of the environmental situation;
- indifferent attitude towards one’s own health (neglect of prevention, poor lifestyle).
There is an exit
In 2002, for the first time in Russia, a specialized interdisciplinary service “STOP-Stroke” was created in the multidisciplinary clinic CELT for the effective prevention of vascular accidents. Over three years, more than 2,000 people took part in the stroke prevention program. The creation of a preventive angioneurology service became possible due to the fact that CELT has created all the necessary conditions for timely diagnosis of changes in the heart, blood or cerebral vessels that can lead to acute cerebrovascular accident. A modern laboratory quickly determines cholesterol levels, blood viscosity and blood clotting. Safe and informative ultrasound diagnostic methods provide insight into the condition of the brain vessels and allow timely detection of dangerous atherosclerotic plaques and critical narrowing of the arteries. Echocardiography and daily monitoring of ECG and blood pressure provide a complete picture of the work of the heart. When necessary, computed tomography and angiography supplement doctors’ opinions on the condition of the blood vessels and brain. All this data is needed in order to identify possible preconditions for a stroke. After all, not only high blood pressure can lead to a brain catastrophe. Often the danger lies in the properties of the blood - the tendency to form blood clots or, for example, in an increase in the level of homocysteine - an amino acid that “damages” the vascular wall and contributes to the development of atherosclerosis.
Symptoms and consequences
The symptoms of a second stroke are not always the same as those of the first stroke, and they are sometimes quite difficult to determine. Therefore, at the first manifestations of discomfort, it is advisable to turn to professionals - to the neurology center of the Yusupov Hospital, where the patient will quickly undergo a comprehensive examination and be prescribed immediate treatment, thereby minimizing the risk of developing severe complications. Our specialists will organize transportation of the patient to the hospital.
The main symptoms that should cause alarm in a patient who has previously suffered a first stroke:
- the muscles of the face, body or limbs become paralyzed or numb;
- vision deteriorates sharply, vision decreases, blindness occurs;
- speech abilities are impaired;
- consciousness is disturbed: slight drowsiness is felt, fainting occurs, coordination of movements is impaired;
- Nausea and vomiting occur.
The severity of the attack depends on the volume of the affected part of the brain and the location of the affected area. Among the likely consequences of repeated ischemic stroke in the absence of adequate medical care are the following:
- loss of control over the senses;
- loss of ability to think;
- impairment or loss of motor function;
- death (in patients who have suffered a recurrent ischemic stroke, survival is significantly reduced).
Patients suffer a repeated ischemic stroke much more severely than the first, and it is sometimes impossible to predict what consequences it will accompany. In some cases, the nature of the resulting pathologies becomes irreversible. Therefore, the main role belongs primarily to stroke prevention.
How to avoid another stroke
The relevance of ischemic stroke is beyond doubt, especially in Siberia. Novosibirsk has earned dubious fame by entering the Guinness Book of Records for the number of cardiovascular diseases. According to the Novosibirsk Stroke Registry, up to 35% of men and 25% of women in active working age die from the disease. The situation is aggravated by various disabling consequences of stroke, which significantly worsen the quality of life of patients and their family members. However, few people know that ischemic brain lesions can now be successfully treated using modern technologies of vascular microneurosurgery.
A stroke, or cerebral infarction, is an acute disturbance of the blood circulation in the brain, which results in the death of nerve cells from oxygen starvation. The most common (up to 88%) is ischemic stroke, when compression or blockage of blood vessels occurs as a result of thrombosis, embolism or other diseases of the blood vessels, heart or blood.
Stroke is the most dangerous cerebrovascular disease that affects people of working age, leading to prolonged hospitalization, high disability and a deterioration in the quality of life of their families as a whole.
For approximately one year after a stroke, hemodynamic changes in the blood supply to the affected area of the brain occur, the severity of which depends on the location and diameter of the blocked vessel. Neurological disorders typical of a stroke include partial or complete paralysis, speech impairment, as well as disorders of memory, hearing, vision, sensitivity, and coordination of movements.
In addition, patients who have suffered an ischemic attack remain at a very high risk of developing a recurrent stroke. During the first year, the risk can be as high as 30%, which is 15 times higher than in people who have not had a stroke.
In this regard, it is extremely important for such patients to find out from their doctor how high the risk of stroke recurrence is and to take protective measures to prevent it.
Penumbra Zone - Rescue Zone
Numerous studies have shown that ischemic brain damage can be partially reversible. The degree of restoration of brain function depends on the level of decrease in cerebral blood flow in the ischemic area, which is heterogeneous.
Thus, in the peripheral parts of the stroke zone, cerebral blood flow is higher than in the center. The degree of reduction in blood flow there remains sufficient for minimal life support for neurons, and brain cells there seem to freeze, so irreversible changes in them may not develop for some time. This borderline, poorly vascularized, but nevertheless living area of the brain is usually called the ischemic penumbra zone, or penumbra.
It is important that the cells of the penumbra zone can be saved in the next six months after a stroke and significantly improve the neurological condition and quality of life of the patient.
The essence of cerebral revascularization
Revascularization, or extra-intracranial microanastomosis (EICMA), is a neurosurgical intervention aimed at restoring cerebral vessels and adequate blood flow in it.
The blood supply to the brain is carried out by four arteries: two carotid and two vertebral. In addition to the internal carotid artery, which supplies the brain, there is an external carotid artery, which is responsible for blood circulation in the face and other areas, but does not enter the skull. The superficial temporal artery (everyone can feel it at the level of the zygomatic arch) comes out of the external carotid artery and can actually become a universal donor for supplying the damaged area of the brain.
The essence of the operation is to isolate the superficial temporal artery, immerse it in the skull and connect it to the cortical artery of the brain.
At the same time, all relationships between the vessels are preserved and a durable bypass anastomosis (connection of two vessels) is created between the system of the external and internal carotid arteries.
As a result of the operation, blood begins to flow freely into the brain along the path newly created by the neurosurgeon, bypassing the blocked vessel.
Due to the restoration of blood flow, the cells of the penumbra zone, which were in a state of suspended animation, “come to life.”
Effect of revascularization
Revascularization allows you to avoid the consequences that develop in the post-stroke period, prevent disability, and also quickly and effectively restore functions lost as a result of a stroke.
It should be noted that no drug treatment gives a similar effect. In addition, the operation helps prevent the development of recurrent strokes, the consequences of which can be disastrous for the patient.
It is also important that during revascularization the brain itself is not affected, so the operation is relatively safe - it is well tolerated even by somatically burdened patients after a stroke. Extra-intracranial microanastomosis is performed using high-precision magnifying optical equipment using ultra-thin atraumatic suture material, also used in eye microsurgery.
The group of neurosurgeons at CNMT has many years of successful experience in performing operations similar to cerebral revascularization (about 170 operations).
Who is indicated for revascularization?
First of all, for patients who have suffered a stroke, as well as a transient ischemic attack, or the so-called “mini-stroke”, which is a harbinger of a stroke. Symptoms of a mini-stroke include sudden, short-term (usually within 1 hour) numbness in an arm or leg, and disturbances in vision or speech.
Patients with occlusive cerebrovascular diseases (high stenosis, thrombosis of the internal carotid artery) against the background of a decrease in their own reserves of collateral circulation of the brain.
After a stroke, the neurological condition and quality of life of the patient can be saved and significantly improved. To identify indications for revascularization, the patient must undergo an MRI of the brain to determine the area of the stroke, ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck to assess the state of cerebral blood flow, and make an appointment with a neurosurgeon.
First aid
When the first symptoms of a stroke appear:
- Place the patient on the bed.
- Call an ambulance.
- Place the patient on his back or side if vomiting begins or he loses consciousness.
- Unfasten clothes and belt.
- Open the window to allow fresh air into the room.
- Place a cold wet towel or ice in a bag wrapped in cotton cloth on your head.
- Measure the patient’s blood pressure, pulse, and monitor blood pressure and breathing until the doctors arrive.
- If necessary, give medications that were previously prescribed by the attending physician.
- Constantly talk to the patient, try to get answers to questions from him, and do not lose contact.
Forecast
As is already known, the five-year survival prognosis is disappointing. Loss of intellectual and motor abilities after a second stroke can be lifelong. Most patients after a relapse suffer from irreversible changes and pathologies in the cerebral cortex.
After lesions, patients usually experience disability. In more than half of patients, after suffering a recurrent stroke, a coma occurs, which does not allow the doctor to give a positive prognosis about recovery from it.
Rehabilitation of patients after repeated ischemic stroke in the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital is based on traditional, latest and original methods for the recovery of patients who have suffered a stroke.
Thanks to the extensive practice and rich knowledge of the clinic’s specialists in the field of rehabilitation medicine, comprehensive rehabilitation of patients is carried out at the highest level, meeting international standards.
For optimal rehabilitation, patients are provided with comfortable conditions of stay: cozy rooms, good nutrition and attentive attitude of the staff.
Call by phone and the coordinating doctor will answer all your questions.
Make an appointment
Factors influencing recovery time after stroke
Stroke is one of the main causes of disability in old age, most often occurring as a result of untimely medical care or lack of competent rehabilitation. In 80% of cases, the success of recovery after a stroke is determined by the prompt action of medical staff. It is especially important to provide assistance in the first 3-4 hours after the onset of an attack. Rehabilitation must begin as early as possible, because the quality and duration of a person’s future life depend on it.
Other factors also influence the timing of rehabilitation after a stroke:
- The mechanism of stroke. There are 2 main types of strokes – ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic occurs in 80% of cases and is caused by a lack of blood supply to any part of the brain. With this type of stroke, if treatment is prescribed correctly and on time, the body has a good chance of recovery. Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by bleeding into the deep parts of the brain. The life prognosis is unfavorable, the probability of death reaches 50-70%.
- The degree of damage to brain tissue. The most serious violations of the basic functions of the body are observed with an extensive stroke affecting large areas of the cerebral cortex. In this case, if the person managed to survive, rehabilitation may take several years, and full recovery may never occur.
- Age and presence of concomitant diseases. The older a person is, the more difficult it is for him to cope with a blow, and in the presence of chronic diseases, especially the cardiovascular system, this often becomes impossible.
- What a seizure. Repeated strokes always increase the risk of death. While it takes an average of 8 months for an elderly person to recover from the first blow, it can take a year or more to recover from the second.
- Psycho-emotional state of the patient. In order to cope with such a serious illness, enormous willpower and desire to live are required, which not every patient has.
Life after ischemic stroke
If the patient experiences an acute period of stroke, then residual disorders are possible in the form of:
- complete immobilization;
- paralysis on one side of the body;
- partial paralysis of a limb;
- paresthesia (numbness with loss of skin sensitivity);
- speech and swallowing disorders;
- vestibular disorders;
- hearing loss;
- pelvic paralysis with inability to control bowel and bladder movements;
- decreased intelligence;
- changes in psyche and character;
- impossibility of self-service.
Recovery of various impaired functions in patients with ischemic stroke occurs at different rates. Thanks to the use of innovative techniques in the rehabilitation clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, movement disorders go away faster, and it may take longer to restore speech. After discharge from the hospital, patients need support from loved ones and continued rehabilitation under the supervision of specialists from the Yusupov Hospital.
Prognosis in older people
In patients with ischemic stroke, age is one of the most important factors that influence the prognosis and quality of life after the acute period of the disease. In older people, ischemic stroke is much more severe than in younger patients. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital take an individual approach to the treatment of elderly patients; when prescribing medications, they use doses recommended for a certain age. When using innovative methods of kinesitherapy, the age characteristics of the body are taken into account.
The prognosis after an ischemic stroke suffered by an elderly person is influenced by the following factors:
- localization of the ischemic focus;
- prevalence of cerebral infarction zone;
- a disease that caused a stroke;
- severity of neurological symptoms.
Coma caused by cerebral edema is the most severe neurological manifestation of a stroke, sharply worsening the prognosis.
Factors that positively influence the results of rehabilitation of elderly patients and improve the prognosis are:
- a small lesion confirmed by computed tomography;
- maintaining the patient's full consciousness;
- minimal number of neurological damages;
- absence of pronounced atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels according to the results of Dopplerography of the arteries of the head and neck;
- the patient's profession requiring constant mental stress;
- normal blood pressure;
- absence of arrhythmias and other heart diseases.
Signs of a stroke
Even if these symptoms appear and disappear, you need to seek medical help as soon as possible:/p>
- unsynchronized smile, distortion of half the face;
- an unsuccessful attempt to stick out the tongue - the organ has an uneven shape and “sinks”;
- unclear, confused speech, inability to pronounce simple phrases;
- “heavy” head, dizziness;
- sudden weakness of one half of the body;
- paralysis of limbs, face;
- progressive “stiffness” of the muscles (especially in the neck);
- lack of coordination, unsteady gait;
sudden numbness, tingling in the face, arms, legs;
- blurred vision, difficulty focusing;
- inability to look at a bright light source;
- convulsions;
- vomiting, nausea;
- difficulty swallowing;
- shortness of breath;
- loss of memory, consciousness.
With an aneurysm, the first symptom is a severe headache, as well as vomiting, spasms of the neck muscles, and confusion.
Risk factors
- high pressure;
- overweight;
- atrial fibrillation - irregular heartbeats provoke the formation of blood clots, which can then migrate to the brain, which increases the risk of stroke by 5 times;
- diabetes – the disease weakens blood vessels, causing the formation of emboli;
- physical inactivity;
- smoking – thickens the blood, which leads to blood clots;
- high cholesterol – provokes the formation of atherosclerotic plaques;
- gender – stroke is diagnosed more often in men, but mortality is higher in women;
- sleep disorders - due to apnea, insomnia, the brain does not have the opportunity to recover;
- vitamin D deficiency;
- increased blood clotting;
- genetic predisposition to heart disease, hypertension, diabetes;
- Fabry disease;
- blood vessel abnormalities;
- Alcohol abuse – liver dysfunction increases the risk of stroke;
- excessive consumption of artificial sweeteners (including diet soft drinks);
- taking drugs (cocaine, heroin, amphetamines).
Stroke treatment
Tomography (computer and magnetic resonance imaging) can help diagnose a stroke. If an embolism is suspected, a lumbar puncture is performed. If CT or MRI cannot be performed for some reason, echoencephalography is performed.
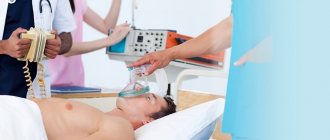
It is necessary to act quickly - the sooner therapy begins, the higher the chances of saving life and restoring functionality. Ideally, you need to get to a medical facility within the first hour after a stroke. Prompt restoration of blood supply and oxygen supply to the brain gives a chance for full recovery. Before the ambulance arrives, you should not take food or water, so as not to provoke suffocation in case of paralysis of the swallowing organs and the risk of food getting into the respiratory tract. For the same purpose, when vomiting, the patient's head should be turned to the side. The head and shoulders should be on the same line, you can put a pillow (the angle should not exceed 30°). Avoid sudden, intense movements and remove tight clothing. In case of loss of consciousness or lack of rhythmic breathing, cardiopulmonary resuscitation is necessary, including the use of a defibrillator.
In a medical institution, therapy is carried out according to appropriate protocols. For ischemic stroke, drugs are used that destroy blood clots and improve blood flow. In some cases, emboli must be removed surgically (usually with a catheter inserted into an artery in the groin area).
For hemorrhagic stroke, medications are given to prevent clots from forming. Surgery may also be required. During the period of bed rest, it is important to monitor the condition of the respiratory system, preventing the development of pneumonia, and also to avoid the appearance of bedsores by promptly changing underwear, doing massage, and often turning the patient over.
Treatment
A patient with a recurrent stroke most often ends up in the intensive care unit. At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors begin treatment and early rehabilitation immediately after diagnosis. The prognosis is most favorable when patients are admitted to the neurology clinic within the first 4 hours from the appearance of the first signs of acute cerebral circulation. Doctors at the neurology clinic prescribe adequate treatment, thanks to which the nerve cells around the ischemic site completely restore functional activity.
The use of thrombolysis therapy by neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital for elderly patients significantly improves the prognosis. As a thromolytic agent, doctors at the neurology clinic use the most effective drug - tissue plasminogen activator. After the clot dissolves, blood flow through the affected vessels is restored, the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the ischemic area and the area around the cerebral infarction improves. The outcome of ischemic stroke is improved by the use of ancrod (an enzyme from snake venom) in the first 3 hours after the development of acute cerebrovascular accident and for five subsequent days.
To prevent further formation of blood clots and re-embolism, elderly people are given:
- direct anticoagulants (sodium heparin or low molecular weight heparin);
- antiplatelet agents;
- drug from the thienopyridine group Ticlopidine.
If there are contraindications or a high risk of complications from taking these drugs, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe Clopidogrel to patients. Drugs with neuroprotective and neurometabolic effects improve the plasticity of nerve cells. The tone of cerebral arteries in elderly people increases under the influence of vasoactive drugs.
In elderly people, ischemic stroke often occurs against the background of severe arterial hypertension. During the 7-10 days of the acute period of stroke, cardiologists at the Yusupov Hospital when the patient’s systolic blood pressure is less than 200 mm. rt. Art. do not carry out antihypertensive therapy, since hypotension worsens the oxygen saturation of brain areas susceptible to ischemia. In patients with systolic blood pressure above 200 mm. rt. Art. it is reduced very slowly to numbers of 10 mm. rt. Art. exceeding the pressure to which the patient is adapted. After the acute period, cardiologists select individual antihypertensive therapy.
Numbers, numbers, numbers...
“I was paralyzed,” “suffered a stroke,” cerebral hemorrhage, softening of the brain, apoplexy—all this is a stroke
.
half a million
die from acute cerebrovascular accident .
Every fifth person
who has had a stroke develops a second acute cerebrovascular accident within a year, in which the likelihood of death increases.
According to statistics, in the structure of general mortality of the population, stroke as a cause of death ranks third
after coronary heart disease and malignant neoplasms.
Stroke is a disease that can make a person disabled. After it, approximately 60 percent
of patients become disabled.
Many of them find themselves confined to a bed for life, unable to move independently and even provide minimal care for themselves. In the minds of the average person, stroke is a disease of older people. Perhaps this was the case twenty
ago.
Nowadays, strokes are getting younger every year. Cases of stroke in 30-40 year old people are not uncommon. One third
of all patients are people of working age.
At the same time, it must be emphasized that the older a person is, the higher the risk of developing a stroke. Every ten
years, the risk of developing acute cerebrovascular accident approximately
doubles
.
Russia ranks 2nd
in the world in terms of the number of strokes.
Bulgaria is in first place, China is in third. In Russia in recent years, the increase in the incidence of stroke is 5 times higher than, for example, in the USA. In Moscow alone, 80-120 people have a stroke every day. In our country there are 1.5 million people who have had a stroke. The diagram shows the dynamics of stroke incidence per 1000 population over the past decades.
Rehabilitation
Early rehabilitation significantly improves the prognosis after a stroke. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital begin to carry out rehabilitation measures from the first day the patient is admitted to the neurology clinic. The intensity of the rehabilitation program depends on the patient’s condition and the degree of his disability. At the Yusupov Hospital, the department for seriously ill patients is equipped with special multifunctional beds. Using the devices of a multifunctional bed, medical personnel can periodically change the patient’s position, carry out hygiene procedures, and care for the patient. Changing your posture helps avoid the formation of bedsores and congestion. To reduce the risk of developing contractures, joint pain, pneumonia, and deep vein thrombosis at the Yusupov Hospital, specialists carry out passive rehabilitation from the first days of treatment.
To improve the prognosis of older people, rehabilitation specialists at the Yusupov Hospital after a stroke use the following innovative methods for restoring impaired functions:
- PNF;
- Voita therapy;
- minor manual therapy;
- Castillo-Morales method;
- kinesio taping;
- Mulligan concept;
- Bobath therapy.
Recommendations after a recurrent stroke
All patients who have suffered a stroke are at risk of relapse of the disease. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital give recommendations to patients on nutrition and prevention of recurrent stroke:
- Dieting. Refusal of spicy, smoked, fatty and sweet foods, alcohol, caviar, eggs, liver. The menu includes more vegetables, fruits, and grains.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Refusal of heavy physical labor, night shifts, and work with high psycho-emotional stress.
- Sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- During the rehabilitation period, measure blood pressure every day, after completion of rehabilitation at least 3 times a week.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor in a timely manner and strictly on time.
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations.
- Do the recommended therapeutic exercises daily.