Hemorrhagic stroke is a serious disease that requires immediate medical attention. One of the tasks of the “Special Medical Assistance” advisory service in Moscow is to provide all stages of treatment for hemorrhagic stroke, including surgical treatment.
A hemorrhagic stroke is a bleeding in the brain, most often caused by high blood pressure. Unfortunately, about half of all cases of this disease in the acute period end in death, and more than 2/3 of survivors become disabled. The outcome depends primarily on the timeliness of medical care.
Modern surgical treatment for hemorrhagic stroke
Only in specialized centers is it possible to conduct a thorough diagnosis and adequate surgical or therapeutic treatment of hemorrhagic acute stroke. However, most often a free ambulance will take the victim to the nearest city hospital, where first aid will be provided, limited by the capabilities of the institution. And surgical treatment of stroke, unfortunately, can not be performed in all hospitals.
Therefore, relatives of patients are increasingly turning to specialized advisory services that can provide:
- safe transportation;
- rapid hospitalization;
- expert monitoring of victims in intensive care units and departments of medical institutions.
Only in highly qualified centers will they conduct the necessary research, assess all the risks, and then choose the necessary treatment tactics.
Another important point that affects the patient’s further capacity is rehabilitation and care after surgical treatment of hemorrhagic stroke. The success of postoperative therapy largely depends on the experience of specialists and the availability of modern equipment.
Expert: It’s never too late to operate on a patient with ischemic stroke
“But the affected area of the brain cannot be returned.”
— In the place where the embolus has blocked the vessel and there is no blood flow at all, an area of absolute ischemia is formed, next to it is relative ischemia, next to this is an area with already more active blood flow, and then with normal one. The small area where the disaster occurred has already died, it is useless to fight for it. The neighboring one, where there is not enough blood flow, increases gradually, its expansion stops in the place where the blood supply is sufficient for life. The essence of our work is to fight for the area of relative ischemia, and this must be done as quickly as possible, because the death of this area occurs from several hours to days and even weeks. The prognosis of the disease—the degree of disability—depends on how quickly we take the necessary actions in each specific situation. The fact is that in the acute period, at the site of the lesion, protein-fatty tissue is formed, similar to a thick jelly, which over time turns into a cyst - healthy tissue is protected and demarcates healthy tissue from unhealthy tissue in the form of a capsule. But the body is so perfect that it immediately, due to the enormous number of small vessels, begins to compensate on all sides for the segment where there is little blood flow.
— Is that why it is necessary to start thrombolytic therapy (thrombolysis) while still in the ambulance?
- Under no circumstances should the ambulance team use thrombolysis for cerebral problems. The main thing is diagnosis, working with symptoms (low blood pressure, for example) and quick delivery to the hospital. Thrombolysis is used only after the patient has undergone a computed tomography (CT) scan in the hospital and it has been proven that ischemic brain damage occurs. If the vessel is blocked by a thrombus, then it is needed. And if the plaque ruptures and detritus enters the lumen of the vessel, thrombolysis is ineffective. The main thing required from an ambulance is speed of delivery. The doctor makes a diagnosis, contacts the dispatcher, the dispatcher contacts the nearest hospital where there is a vascular center; he reports there that they are transporting a patient with a stroke. They are preparing for emergency diagnostics.
In the vascular center, within an hour, maximum two hours, diagnosticians are required to provide the doctor with data on the patient’s condition, the type of developing brain damage, data from laboratory and instrumental studies, in short, provide the doctor with all the information so that he can make a decision on what needs to be done to influence the lesion so as to stop its growth.
At the same time, a multidisciplinary team begins to work, which determines what to do with the patient, and does it very quickly. We have the first 3-4 hours to dissolve the embolus: perform thrombolysis.
- What if more time has passed?
- Then emergency removal of the blood clot is necessary - thromboextraction. This is a very effective technique if performed when no more than 6-8 hours have passed since the moment of the vascular accident. Such operations are performed by highly qualified x-ray surgeons using special equipment.
— Now the city has created second-level neurology departments - for those who had a stroke, but they turned to the doctor late and the so-called “therapeutic window” was already closed for them - they are treated conservatively. Therefore, ambulances do not take such patients to the vascular center.
- It is not right. The brain dies within 150-170 hours. But the biggest death comes in the first hours, and we must essentially fight for every cell. Therefore, the sooner treatment begins, the more cells will be preserved, which means the more capable the person will be. It is important that the patient is taken to the vascular center in any situation, even if the stroke occurred three days ago. There he must be fully examined and a decision made appropriate to this period of development of the disease.
“But in many of them, after eight hours from the moment of the disaster, rescue efforts stop.
“To prevent this from happening, since the opening of the center we have supplemented it with a very important specialized service - vascular neurosurgery. From the very first hours, we evaluate the already examined patient and immediately, if it is impossible to perform thrombolysis and thromboextraction, we think about how to restore blood supply surgically - remove the atherosclerotic plaque using open vascular revascularization. It allows you to prevent repeated episodes of embolus release. This operation is required not only for those who sought help late, but also for those whom the ambulance delivered during the so-called “golden hour”: many patients have giant atherosclerotic plaques that cannot be dissolved (thrombolysis) or removed using thromboextraction. They cannot be removed except through open surgery.
Open vascular revascularization is performed within a period of one day from the moment of the vascular accident and up to two weeks (even up to a month). This period is explained by the fact that many patients have serious concomitant diseases (severe hypertension, myocardial ischemia, urinary tract pathologies...), and they can also cause death. For successful surgical treatment, we must prepare the patient for surgery. Therefore, in parallel with the treatment of concomitant pathology, conservative therapy for vascular lesions is carried out, which slows down the increase in the ischemic focus. That is, we cannot influence those cells that have died, but we use drugs to preserve nerve cells located near the lesion - in the risk zone. After the operation, treatment continues against the background of restored blood supply: with full blood flow, it proceeds faster and more fully. Patients' organ functions are restored to the point where they can return to work with a fully restored neurological status. These types of surgical interventions are also very complex - they are performed by highly qualified vascular surgeons using microsurgical techniques.
— Which vascular centers in St. Petersburg perform revascularization?
- In our hospital, Research Institute of Emergency Medicine named after. Dzhanelidze, there is experience in performing these operations in city hospital No. 3, Aleksandrovskaya hospital. In St. Petersburg there are opportunities for the successful use of such operations due to the fact that, unlike other regions of Russia, we have introduced vascular departments into the regional vascular centers. And our vascular surgeons do not wait for the patient to be discharged from the neurological department of the center and hospitalized in the vascular surgery department - the effectiveness of planned operations is many times lower than urgent ones. Vascular surgeons at the center work as part of a multidisciplinary team and perform them as quickly as possible.
— Is it true that stroke is more severe in women and their loss of function is more permanent?
“This may be true, but we must remember that this is a serious and dangerous disease for everyone, regardless of gender. The fact that in women more tissue dies during ischemia and a longer recovery process may be explained by the fact that in men the brain is more adapted to ischemia. Because most often atherosclerotic plaques form in men. In addition, women are more often affected by stroke, which occurs for a rare reason - congenital vascular dysplasia (tortuosity, angulation, elongation and other forms of deformation of the vessel supplying the brain). Blood clots can form in the corners and folds of such deformed vessels, which can also cause a stroke. Most often, such pathological deformations are observed in women, because their blood vessels are especially susceptible to changes, especially during the period of fertility. If there is a tendency to hypertension, then these deformities develop more often.
In general, stroke is different from stroke, because its causes can be different, and this is important for choosing treatment tactics. For example, in contrast to the most common angioembologenic stroke, in which emboli form in the vessels, cardioembologenic strokes occur - in patients who have had a heart attack, blood clots can form on the inner surface of the left ventricle in the area of the infarction and break off. This happens especially often when there are also cardiac arrhythmias. This is also an ischemic stroke, but its cause is heart problems.
In young people, strokes are most often caused by taking hormonal drugs, dietary supplements for muscle building, or excessive physical exertion. Cyclists, skiers, snowboarders, boxers, and wrestlers more often suffer from stress; for example, with a sudden movement or throwing back the head, an excessive load occurs on the carotid artery and intimal dissection occurs - spontaneous micro-tears of the intact inner lining of the vessel. A blood clot forms on them, which subsequently causes stroke in young people. The complexity and severity of the situation is that their brain is not at all adapted to ischemia.
— How to prevent stroke?
— On average, in St. Petersburg there are from 20 to 25 thousand strokes a year - ischemic and hemorrhagic. With ischemic stroke, we mainly come to patients over the age of 55-60 years with large disintegrating plaques that stenoses the vessels. And these people have never in their lives performed diagnostics that would allow them to identify stenosis in advance. Ideally, every person over 50 years old should contact an ultrasound specialist at least once every two years and examine the vessels that supply the brain. And if an atherosclerotic plaque is detected with a tendency to increase at a rate of about 2 mm, or even more, per year, you should consult either a vascular surgeon or a neurologist. If the degree of stenosis of the carotid artery (reduction in its internal diameter) is more than 50%, observation with the participation of a doctor is necessary. Hemorrhagic stroke can also be prevented by constant monitoring and adequate treatment of high blood pressure; this prevents ruptures of intracerebral vessels, although not 100 percent.
© DoctorPeter
Etiology and pathogenesis
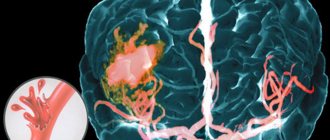
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs in a person due to a number of disorders (this can also include the consequence of a traumatic blow). One of the reasons why cerebral circulation may be impaired is pathological diseases: vasculitis, arterial hypertension, vascular abnormalities that were detected from birth, hypertension. Also, bleeding in the brain occurs due to poor blood clotting. The cause of violations may be the use of amphetamine and cocaine.
During a hemorrhagic stroke, a person feels unwell. Symptoms appear in various forms:
- balance problems;
- severe headache;
- nausea;
- perception is disrupted;
- Pain in the eyes;
- cardiopalmus;
- noise in ears;
- paralysis of the muscles of the face, arms, legs.
The consequence of all alarming symptoms is the rupture of intracerebral vessels under the influence of high blood pressure.
Causes
Hemorrhagic stroke is poorly diagnosed, although the causes and mechanism of its development are well studied. Various factors can provoke the development of hemorrhoidal stroke:
- Hypertension, arterial hypertension.
- Vascular aneurysm.
- Long-term use of anticoagulants.
- Diseases of the brain, spinal cord, cardiovascular system, diabetes.
- Congenital vascular defects.
- Blood diseases.
- Systemic diseases.
- Kidney and liver diseases.
- Alcoholism, drug addiction, tobacco addiction.
- Obesity.
- Stress.
- Hard physical labor.
- Hereditary predisposition.
A persistent increase in blood pressure leads to the formation of fibrinoid-hyaline necrosis of the walls of arterial vessels and can cause rupture of the walls of the aneurysm and the development of bleeding. The hematoma compresses the surrounding brain tissue, causing brain swelling. Blood from ruptured vessels can permeate the nerve tissue of the brain or, under pressure, break into the ventricles of the brain, the subarachnoid space.
Treatment approaches
The patient requires urgent hospitalization and medical care. After normalization of health, it is necessary to undergo in-depth diagnostics (computed tomography and MRI, cerebrospinal fluid sampling). After consultation with a neurosurgeon, treatment is prescribed.
There are two treatment options for the disease:
- Conservative. The neurologist prescribes treatment, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body and the diagnostic results. Conservative treatment consists of taking medications. The patient is prescribed drugs to regulate intracranial pressure and cerebral edema, antispasmodics, antihypertensive drugs, calcium antagonists. Intensive use of medications is necessary in the acute stage of hemorrhagic stroke. The patient also needs to be observed by a doctor to diagnose a decrease in cerebral edema.
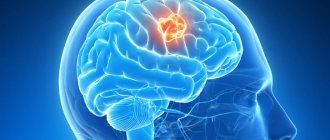
- Surgical treatment of hemorrhagic stroke. Before performing an operation, doctors must exclude contraindications, stabilize the patient’s condition, and study the results of neuroimaging in detail. Surgical treatment of stroke cannot be avoided if a hemorrhage of medium or large volume occurs. Specialists choose the type of intervention.
Diagnosis of strokes
First of all, it is necessary to conduct a detailed neurological examination. Instrumental diagnostic studies and laboratory tests are also prescribed. In case of a stroke, in the first hours, an MRI or CT scan of the brain is performed, if necessary, CT or MR angiography, color Doppler mapping of blood flow, ECG or Holter monitoring, echocardiography as indicated, monitoring of blood pressure, saturation, assessment of the risk of developing bedsores, assessment of swallowing function [ 1, 3, 6].
Tests for stroke
- Complete clinical blood test, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
- Biochemical blood test with determination of C-reactive protein and homocysteine, glucose level, platelet count, activated partial thromboplastin time, INR.
- Interleukin 10.
- Extended coagulogram.
- Determination of acid-base status.
- General urine analysis.
To prepare for neurosurgical intervention, a blood test is additionally performed for hepatitis, syphilis, HIV, blood group and Rh factor determination.
Indications and contraindications for surgical treatment of stroke
Not all cases of the disease require aggressive tactics and surgical intervention. Examination by specialists and data from instrumental diagnostic methods allow an adequate assessment of the patient’s general condition.
Contraindications to surgical treatment of stroke are:
- severe concomitant diseases;
- old age over 65-70 years;
- large volume of hematoma;
- depressed consciousness - coma.
Depending on the indications, our consultants will be able to select the best specialized hospital for the victim.
Consequences of a stroke
There are transient ischemic attack (less than a day), minor stroke (from 1 day to 3 weeks) and stroke with persistent residual effects. The consequences of a stroke are expressed mainly in motor and sensory disorders, the formation of muscle contractures (pronounced constant restriction of movements in the joints), speech and swallowing disorders. General symptoms may also remain, including confusion, disturbances in thinking, will, and emotional regulation. Complications can develop: from epilepsy to bedsores, encephalopathy and anxiety-depressive syndrome [1, 3].
Types of surgery
Neurosurgeons distinguish several methods by which a hematoma can be removed:
- Direct surgery. The hematoma is removed by encephalotomy, then careful hemostasis is performed. When suturing, microsurgical techniques are usually used.
- Puncture-aspiration method. Fibrinolytics are administered. This method is effective if the hemorrhage is of medium size and the patient is in a stable condition.
- Endoscopic method. Modern method of surgical treatment. During surgery, endoscopic technology is always used. Using an endoscope, they penetrate into the hematoma cavity, after which a set of specific manipulations is carried out. Surgical treatment of hemorrhagic stroke is excluded in case of unstable hemodynamics.
After surgery, the patient should remain under observation. The rehabilitation period is long and difficult, can last up to two months. Special conditions are required for the patient’s recovery (a set of procedures in a rehabilitation center).
Rehabilitation treatment after stroke at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences
After a stroke, life goes on, and what it will be like depends largely on the quality of treatment and rehabilitation in the first 2–3 months after the illness. In the rehabilitation department of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences, individual programs are drawn up for patients aimed at restoring motor functions, correcting attention, speech and memory disorders, and other neurological disorders.
Doctors of various specialties participate in rehabilitation: physiotherapists, speech therapists, psychologists and neuropsychologists, nutritionists, occupational therapists and other specialists. The joint work of professionals, as well as the use of innovative equipment, reduces the risk of complications and speeds up the recovery process.
To schedule a consultation and clarify the cost of services, you can call or use a special form on the website.