Glioblastoma of the brain is a type of malignant neoplasm characterized by a high degree of aggressiveness. A tumor in the brain is characterized by rapid and aggressive growth. Early signs are usually absent, but as carcinogenesis progresses, a corresponding clinical picture appears. The main type of treatment is surgical removal of the pathological focus, supported by radio and chemotherapy. Glioblastoma is prone to frequent recurrence, so the prognosis is negative.
What is glioblastoma of the brain
Glioblastoma can develop from cells in the brain or spinal cord. The tumor begins with neuroglial cells that perform auxiliary functions. They support the vital activity and functioning of neurons. The neoplasm belongs to the highest (fourth) degree of malignancy; it can often form from gliomas (astrocytomas) of the third degree of malignancy. In any case, the tumor behaves extremely aggressively, grows quickly, invades neighboring tissues, has no clearly defined boundaries, and recurs quickly and often, which will significantly complicate the treatment of glioblastoma. The metastatic process is poorly developed.
Note. This type of brain cancer most often occurs in men between 40 and 65 years of age. It has not yet been possible to understand why this happens.
Glioblastomas account for approximately 20% of the total number of all primary intracerebral tumors, but despite this, the disease is diagnosed quite rarely: up to 3 cases per hundred thousand people. Without adequate treatment, death occurs within a few months because the pathological tissue grows rapidly and attacks healthy structures. Most often, glioblastomas form in the temporal or frontal zone of the brain. The general name refers to the following forms of the disease:
- giant cell glioblastoma;
- glioblastoma multiforme;
- gliosarcoma.
The most common form is glioblastoma multiforme. This species is extremely aggressive, because many vessels are formed in the neoplasm, and they early undergo necrosis.
Glioblastomas are the most aggressive tumors of the glioma group. Below is a generally accepted classification according to the degree of malignancy:
- First degree of malignancy, for example, astrocytoma. These are benign tumors, have no signs of cancer, do not metastasize, are characterized by slow growth and almost never degenerate into cancer.
- Second degree of malignancy, for example, diffuse astrocytoma. In this case, gliomas are classified as low-grade, i.e., benign formations. Atypia is observed in the cells - one of the signs of malignancy. These formations can become malignant and progress to the following stages.
- The third degree of malignancy (anaplastic astrocytoma) has all the signs of cancer, except for necrosis; the tumor is poorly differentiated, grows and invades other tissues. Easily progresses to an aggressive type of cancer of the 4th degree.
- The fourth degree of malignancy (glioblastoma) is the most aggressive type of cancer. There are all the signs of malignancy, treatment is difficult, the patient’s life is at risk.
What's happened
Glioblastoma is a malignant tumor that develops in the brain and has an aggressive spread. This is a serious illness. The lifespan from the moment the first symptoms appear will be three months if a person does not treat this disease in any way.
If, nevertheless, the patient receives treatment in the form of radiation therapy, chemotherapy, surgery (preferably as a complex), then the life expectancy will increase to two years.
There is an assumption that this pathology occurs due to the fact that brain cells begin to function incorrectly.
The occurrence of this particular disease among cancer patients is one case in a thousand.
If glioblastoma appears in a child under two years of age, then the chances of recovery are very high. The prognosis during pregnancy will be unfavorable due to the fact that in this condition many treatment methods will be contraindicated for a woman.
Causes
As is the case with other types of cancer, it has not yet been possible to understand the exact reasons for the formation of malignant tumors that form in the head. Formations can be primary (from dividing, growing or degenerating neuroglial cells) or secondary. In the latter case, carcinogenesis in the brain tissue begins with metastatic cells. Provoking factors are:
- lower grade brain tumors, such as astrocytomas;
- poor environment, employment in hazardous enterprises, compounds containing lead are especially harmful;
- exposure to ionizing sources;
- genetic factors;
- head and upper spine injuries;
- as consequences of alcohol abuse (the role of smoking in this case has not been established);
- malaria (possibly malaria mosquitoes carry a virus that causes cancer);
- neurofibromatosis;
- defeat by oncogenic viruses.
Note. In the presence of astrocytomas in the brain, in approximately every tenth patient they are modified into glioblastomas.
What does the diagnosis of glioblastoma of the brain mean?
The disease is a malignant tumor that develops in the skull. The cancer is formed from glial stellate cells (astrocytes), which are able to multiply - unlike neurons. In the brain of a sick person, uncontrolled division of astrocytes occurs with concomitant active tissue growth. Brain tumors most commonly affect children and young adults.
The maximum number of cases of brain gioblastoma occurs among the male population in the age group of 40-60 years. This diagnosis accounts for 20% of all recorded intercerebral tumors. Neoplasms can affect the frontal lobe, cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and brainstem. Glioblastomas differ in their degree of malignancy, which is determined by biopsy (an examination of tumor cells in a laboratory setting).
Classification of tumors
There are 4 degrees of malignancy of brain tumors. At the initial stage, glioblastoma is a cross between a benign and malignant formation. As a rule, at the first stage there are no signs of a pathological process. During the second stage, cell atypicality develops, while tumors grow slowly. At the third stage, there are no necrotic processes yet, but glioblastoma begins to grow faster and becomes malignant. The final stage is the fourth. It is characterized by tissue necrosis and progresses rapidly. Types of disease:
- Brain stem tumor. This glioblastoma cannot be removed through surgery, since the brain stem contains sections responsible for the vital functions of the body. The trunk connects the brain to the spinal cord and includes the nuclei of the cranial nerves, vasomotor and respiratory centers. This explains why typical symptoms occur in oncology: respiratory dysfunction, arrhythmia, and others. The prognosis for such glioblastoma is poor, and survival rate is extremely low.
- Glioblastoma multiforme. This species is distinguished by the presence of a huge number of different tissues and cells, the formation of new structures. The diagnosis accounts for about a third of all cases of neoplasms inside the cranium. The source of the development of glioblastoma multiforme are glial cells, which, under the influence of certain factors, turn into atypical ones. As a rule, the tumor occurs in the cerebral hemispheres, less often it develops in the trunk or parts of the spinal cord.
- Glioblastoma of polymorphic cell type. This is a common form of cancer. It is diagnosed using cytological research techniques. The cytoplasm of tumor cells occupies a small area compared to other structures and is weakly stained during diagnosis. Cancerous tumors are distinguished by nuclei of different structures: cells can be round, oval, bean-shaped, or with uneven outlines.
- Isomorphic cell tumor. Glioblastoma of this type is extremely rare. Cancer cells look uniform, but there may be slight differences in size or shape. As a rule, they have a round or oval appearance. Glioblastoma, in addition to cells, consists of cytoplasm and small cellular processes with unclear contours.
Symptoms
Clinical signs at an early stage are usually latent. As the disease progresses, characteristic symptoms appear. The initial signs are weak, but they intensify with the growth of pathological tissue. Negative manifestations can be general (wide-brain - provoked by increased intracranial pressure and intoxication of the body) and local, which depend on the location of cancer formation in the brain.
General signs of glioblastoma:
- headache, dizziness, often the pain intensifies while lying down and is not relieved by simple analgesics;
- nausea and vomiting, which do not depend on food intake; the patient does not feel better after vomiting;
- loss of appetite, decrease in body weight;
- weakness, decreased performance;
- decreased brain activity: memory and attention suffer, difficulty concentrating;
- the psycho-emotional state changes: the person becomes nervous, aggressive, depression and apathy are possible.
Local (focal) neurotic signs can manifest themselves in disruption of the visual, speech and auditory analyzers, impaired sense of smell, coordination, balance, convulsions, paresis, paralysis of limbs or body parts, and epileptic seizures are possible.
Symptoms of the disease
Detecting cancer is difficult. Pathology is not diagnosed without tests and studies. And the initial course of the disease is usually asymptomatic.
Unfortunately, it is possible to detect a blastoma either by chance during an adjacent examination, or at a late stage. As the tumor develops, filling the space of the skull with new tissue, it gives a number of symptoms that patients treat. Symptoms of the disease include:
- Loss of appetite.
- Headache. Feelings of fullness from inside the skull (cerebral edema).
- Nausea, vomiting, general weakness and malaise.
- Violation of the vestibular apparatus - dizziness, changes in gait.
- Problems with the heart and lungs.
- From the side of the central nervous system - memory, sleep, and speech deteriorate.
- Vision deteriorates, intraocular pressure appears.
- Changes in the sensitivity of the limbs.
- Coma.
Diagnostics
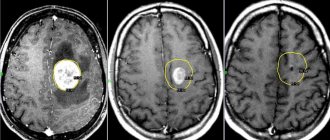
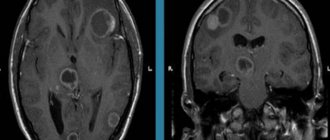
The success and consequences of treatment for brain cancer largely depend on at what stage of carcinogenesis the tumor is detected. The earlier glioblastoma is detected, the better the treatment. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance (MRI) imaging using contrast remains the gold standard in head examination. Recently, PET – positron emission tomography – has been widely used. The most accurate diagnosis and all its features can be determined by cytohistological analysis of the selected material (biopsy). These are the main diagnostic measures; in addition to them, the following can be carried out:
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- angiography of head vessels;
- molecular tests;
- immunohistochemical tests;
- histological typing;
- genetic analysis of genes.
Diagnosis of glioblastoma in Israel
An examination by a specialist allows you to guess which part of the brain is damaged and determine the necessary list of laboratory and instrumental studies.
- MRI is a very relevant modern diagnostic method that is not accompanied by irradiation of the patient’s body. As a result, doctors receive a layer-by-layer image of the patient’s body, which can be viewed in different projections using a special program. Tomographs in Israeli clinics are the latest generation devices and have the highest resolution, as a result of which doctors can detect even the smallest tumor.
- If the tumor is not located deep in the brain tissue, then doctors can remove a small fragment of the tumor for histological examination. This is the only way to reliably determine the histological type of tumor. A biopsy of a tumor located inside the cranial cavity is always a very serious intervention, since it requires penetration. This is always associated with a certain risk of complications. A tumor located deep in the brain tissue is rarely biopsied due to the difficulty of performing this procedure.
- Stereotactic technologies are currently being actively developed and allow doctors, before intervention, to enter patient data into a program that will subsequently monitor the accuracy of all manipulations. This significantly reduces the likelihood of complications, both during tumor biopsy and during surgery.
- Positron emission tomography is a diagnostic method that allows you to detect even the smallest tumor foci measuring a few millimeters in size.
- CT scans also give doctors an image of a patient's brain that can be viewed layer by layer. In general, the technique is very similar to MRI, but has a number of features.
Stages
There are several stages of cancer development:
- Stage I. Pathological cells are located at the site of formation, do not grow into neighboring tissues, and growth is still relatively slow. The clinic is absent or weakly expressed.
- Stage II. The tissue grows, which leads to an increase in its size, and growth into neighboring tissues is observed. General cerebral signs appear, there may be convulsions and mild seizures of the epileptic type.
- Stage III. The tumor is actively growing, spreading into neighboring tissues, and the first regional metastases begin to form. Clinical signs are quite pronounced. The quality of life is deteriorating.
- Stage IV. The cancer grows and spreads quickly, and the clinical manifestations are very strong. The metastatic process intensifies. Palliative treatment is indicated. Removal of glioblastoma of the brain is not performed at this stage; the life prognosis is extremely negative.
How long do people live with stage 4 glyblastoma?
The average survival rate of patients after a diagnosis of stage 4 organic brain damage is about 2 months. This figure is arbitrary, since each patient’s tumor growth differs in intensity, the degree of damage to brain structures, as well as the resistance and reserve forces of the body. Medicine has known cases where patients with stage 4 cancer, undergoing regular courses of treatment, successfully lived for several more years. Such cases constitute a small percentage, since by the time the final stage occurs, the disease has already managed to metastasize throughout the body, affecting important brain structures.
Treatment of glioblastoma of the brain
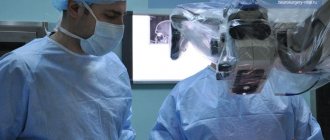
Treatment of glioblastoma is selected individually, depending on the stage of carcinogenesis and the general condition of the patient. How long they live after removal of glioblastoma will directly depend on how far into the disease the surgery to remove the tumor was performed. In the initial stages, when the tumor is still small, it is possible to remove glioblastoma using new methods. These endoscopic techniques are minimally invasive and allow excision of the affected tissue without craniotomy. Microsurgery is performed using intraoperative fluorescent navigation. Before surgery, the patient is injected with a solution that stains the neoplasia tissue, which allows better visualization of the tumor. In this case, the removal of glioblastoma of the brain takes place with minimal trauma, the consequences of the surgical intervention quickly heal, which reduces the rehabilitation time.
Craniotomy (open brain surgery by opening the skull) is often performed because, as a rule, the tumor reaches a large size by the time of diagnosis, so it can only be removed by trephination or resection of the skull.
Due to the spread of the tumor, the unclearness of its boundaries and proximity to vital areas, it is not always possible to completely remove the tumor. In this case, surgery to remove glioblastoma will be considered palliative treatment. This will reduce intracranial pressure, significantly reduce negative manifestations and increase life expectancy. The consequences of surgery to remove glioblastoma will depend on how much pathological tissue is removed. The best result is when the tumor is completely removed.
Important. For this type of brain cancer, surgical treatment can reduce negative symptoms and increase life expectancy by a year or more.
Treatment of glioblastoma of the brain in Russia is characterized by high standards that are not inferior to similar therapy in Western clinics. The advantage of domestic cancer centers is the lower cost of treatment and the availability of insurance programs. Treatment of glioblastoma is always complex. The operation is supplemented with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Before surgery, these methods help stabilize tumor growth and reduce its size, and after surgery, kill or significantly weaken the remaining cancer cells.
It is important to note that in advanced stages of glioblastoma, surgery is often not possible. In this case, treatment of inoperable glioblastoma is carried out using radiotherapy (which becomes the main method of treatment) supported by the administration of cytostatic drugs. However, as practice has shown, glioblastoma cells exhibit high resistance to ionizing radiation.
To eliminate unfavorable symptoms, symptomatic treatment is prescribed:
- analgesics;
- anti-inflammatory;
- narcotic painkillers;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- sedatives;
- antinausea, antiemetic drugs and others.
Symptoms of glioblastoma
Intracranial hypertension. It manifests itself primarily as a headache of a bursting nature, intensifying in the morning, which does not go away after taking conventional analgesics, and is often associated with nausea. Vomiting and visual disturbances due to swelling of the optic nerve are often observed. Convulsive attacks. They can be generalized, with loss of consciousness, or local (limited muscle twitching in one area). Cognitive decline
Thinking slows down, logical connections are lost, memory and attention deteriorate. Neurological deficit syndrome. Manifested by the loss of certain functions regulated by the part of the brain on which the tumor presses
Focal damage to the central nervous system can manifest itself:
-paralysis or paresis of the limbs;
-loss of sensitivity;
- distortion of perception of surrounding objects and people (agnosia);
-visual impairment;
-aphasia (speech disorder);
-impaired coordination and balance.
Psychiatric symptoms. Localized in the frontal lobes, the tumor causes personality disorders: the appearance of foolishness, deviant behavior or, conversely, apathy and adynamia is possible.
Consequences of the operation
The rehabilitation period after minimally invasive techniques is relatively easy. After craniotomy or resection, recovery is difficult. The patient is subject to careful postoperative diagnosis (in order to understand the success of treatment) and constant monitoring, since glioblastomas belong to the group of tumors that are characterized by relapses. Often patients need to learn again to adapt, talk, walk, etc., so rehabilitation specialists, psychologists, speech therapists, physiotherapists and other specialized specialists are involved in postoperative therapy. Physical overload is contraindicated. The patient must unquestioningly comply with all the doctors’ requirements.
Important. Glioblastomas are prone to relapses after surgical treatment. Their cells are low-sensitive to radiotherapy and often do not respond well to chemotherapy.
Consequences and prognosis
Those who become ill are given a life span of no more than 5 years, and sometimes less. It is necessary to detect cancer as early as possible - at a stage when it is still curable.
Even with a successful operation, the probability of getting sick again is about 75%. Cancer comes back again and again. Given the delicacy of the tumor location, the likelihood that living tissue will not be affected is very small.
The functioning of various systems may be disrupted during the removal operation, in particular the central nervous system and the musculoskeletal system. Not to mention brain activity in general.
As malignant tissues develop and grow, they have a compressive effect on vital neural networks in the cerebral cortex. As a result, malfunctions appear in the body.
Certain diets aimed at a healthy balanced diet for glioblastoma, acceptable physical activity, psychological health - all these factors affect life expectancy, but to a lesser extent.
Depends largely on:
- type of glioblastoma;
- stage of cancer;
- tumor size;
- localization (frontal, parietal, right and left temporal lobes, etc.);
- genetic inheritance;
- health of the body as a whole;
- age (older people suffer the disease the worst) and gender;
- lifestyle, bad habits;
- environment.
There is no cure for stage 4 glioblastoma. Photos of patients in the last stage of cancer are presented below. We are talking about recovery only when the disease is detected at stages 1-2, and then in rare cases.
The main problem is the lack of a clear tumor boundary. Therefore, even when removed, part of it remains, and cell division continues. As a result, after 2-3 months the tumor grows again, so it cannot be cured, nor can one live with it for a long time. There are chances at stage 2 - 60% of patients continue to live. Cases of cure occur at the 1st stage, less often at the 2nd stage.
Life prognosis for glioblastoma
How long a person will live with this type of cancer is an individual question. Much depends on the type of glioblastoma, duration of the disease, quality of surgical treatment, age and general condition of the patient. Without treatment (after diagnosis), only 10% of patients will live more than 3 months. With proper therapy and successful surgery, it is possible to extend life by one and a half or two years; in 5% of cases, patients can live about five years or even longer. The most critical prognosis when diagnosing glioblastoma multiforme of the brain. In this case, even with successful surgery and adequate anticancer therapy, life expectancy rarely exceeds more than a year.
Classification
Depending on the type of cells, there are 3 types of tumors:
- giant cell glioblastoma, when the neoplasm includes large cells containing two or more nuclei;
- glioblastoma multiforme, the tissue of which includes overgrown blood vessels, foci of necrosis, etc.;
- gliosarcoma, consisting of glia (auxiliary cells of nervous tissue) and connective tissue cells.
The difference in the location of the tumor allows us to distinguish the following types:
- cerebral (the tumor is located in the temporal, frontal or other areas of the brain);
- stem, when the tumor is located in the brain stem (the tumor is inoperable, since surgical intervention leads to disruption of the musculoskeletal system).
According to histological classification, there are 3 types of glioblastoma:
- isomorphic cellular, when the tumor consists of cells of the same type;
- multiform, in which the neoplasm consists of cells of different types;
- polymorphocellular (glioblastoma cells of different sizes and shapes).
Another basis for classification is the number of malignant cells of the neoplasm. In accordance with this, there are 4 stages of glioblastoma.
- The first stage is transitional. Diagnosis is impossible due to the complete absence of manifestations. Only a portion of benign cells develop into cancerous ones.
- The second stage is slow cell growth.
- The third stage is the development of a malignant tumor. Rapid growth of atypical cells occurs.
- The fourth stage is the manifestation of a vivid clinical picture. Stage 4 glioblastoma is most often diagnosed. The patient's life expectancy after diagnosis is several months.
Types of glioblastoma
There are 4 main types of glioblastoma depending on the cells predominant in the tumor tissue. Each type has a specific pathology and degree of malignancy.
Multiform pathology
This type of glioblastoma is distinguished by the species diversity of cancer cells. The basis for the development of neoplasms is glia, which is the connective tissue of a network of neurons. The trigger for degeneration is the impact of unfavorable factors.
Active growth of atypical cells contributes to the spread of cancer to other parts of the nervous system (for example, with the subsequent development of glioblastoma of the spinal cord). Treatment of multiform pathology has certain difficulties. They are due to the fact that each type of cancer cell is susceptible to different methods of therapy and has different rates of growth and development. Multifocal glioblastoma is considered the most dangerous.
Giant cell form
During the study of the material, large pathological cells are revealed. They include multiple cores. The disease is considered less dangerous.
Gliosarcoma
The neoplasm is characterized by bidermality. The tumor is a mixture of glial cells and connective tissue cells. Gliosarcoma is difficult to treat.
Polymorphic cell form
Atypical cells are large and vary in shape. The examination reveals a small amount of cytoplasm. The kernels have different structures and sizes. Polymorphic cell glioblastoma is more common than other types.
Forecast
With standard treatment for the disease, the average survival rate for adults with glioblastoma is about two years. For patients with more aggressive disease treated with teramolamide and radiation therapy, the average survival is about 14-15 months, and the two-year survival rate does not exceed 30%. However, studies from 2009 reported that nearly 10% of patients with glioblastoma could survive five years or more.
Children with tumors (stages 3 and 4) have a higher chance of survival than adults; The five-year survival rate for children is about 25%.
Additionally, glioblastoma patients in whom the MGMT gene has been disabled by a process called methylation also have long survival rates. The MGMT gene is considered an important predictor of response.
However, not all glioblastomas have the same biological abnormalities. This may be the reason why different patients respond differently to the same treatment and why different patients with the same tumor have different results.
Researchers continue to study the common features of brain tumor patients who have had high survival rates; and how personalized and targeted treatments can be optimally used to treat brain tumors.
Many cases of complete recovery of people who have suffered this terrible disease have been documented around the world, so life expectancy with glioblastoma can be the same as that of healthy people. Statistics should not deprive people of hope for recovery.
Clinical picture
Glioblastoma, especially the multiforme type, may be accompanied by specific signs already in the first stages that allow one to suspect the presence of brain damage.
Specific signs
The cause of the clinical picture is the spread of the pathological process to important parts of the organ responsible for motor and speech functions.
In the early stages, headache occurs. At first it is temporary and appears after physical activity.
Over time, when the tumor increases in size and begins to put pressure on neighboring structures, the painful sensations become constant and severe. They cannot be relieved with painkillers.
Prognosis for glioblastoma
Glioblastoma of the brain is a neoplasm that belongs to the 4th degree of malignancy.
With glioblastoma, the patient sleeps all the time and becomes lethargic. Nausea also occurs in the morning.
Over time, the neoplasm also affects the visual apparatus, which manifests itself in the form of deterioration in the quality of vision and double vision. In later stages, complete loss of vision is possible.
Patients experience memory problems and decreased intelligence, which is due to the effect of cancer cells on the meninges. The sense of smell is impaired, as a result of which a person ceases to perceive odors and their perception changes. Often this sign becomes a reason to contact a specialist.
When conducting a neurological examination, a violation of movement coordination is established. This symptom indicates damage to the vestibular apparatus.
As the disease progresses, paralysis, decreased sensitivity of the limbs, and numbness of the skin are noted.
There is also a disturbance in speech, breathing, and the appearance of hallucinations. In some cases, death may occur during sleep as a result of asphyxia.
General signs
In addition to the occurrence of specific symptoms, in the presence of a malignant tumor, general symptoms also appear. First of all, weakness, nausea, apathy, and irritability are observed. Patients experience loss of appetite, resulting in weight loss.
If hemorrhages occur, laboratory testing confirms anemia. This condition is accompanied by weakness, headaches and dizziness.
Symptoms
Glioblastoma or grade 4 brain cancer according to the international classification of diseases ICD 10 is coded C71. Next, depending on the location of the neoplasm, a numerical value follows:
- 0 – final section;
- 1 – frontal lobe;
- 2 – temporal;
- 3 – parietal;
- 4 – occipital;
- 5 – ventricles, except 4;
- 6 – cerebellum;
- 7 – trunk and 4th ventricle;
- 8 – glioblastoma extending beyond one specified location.
Encryption C71.9 is also sometimes used - unspecified tumor location. When writing an accurate diagnosis, the cytological nature of the neoplasm (glioblastoma) and its clinical manifestation are further indicated: hypertensive-hydrocephalic or vestibular syndrome.
Hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome is primarily characterized by excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles and subarachnoid space of the brain. In this regard, the following signs of the disease are observed: attacks of severe headaches, systematic nausea and vomiting, blurred vision, drowsiness, loss of appetite, convulsions and loss of consciousness in severe cases.
Vestibular syndrome manifests itself in a disorder of the motor function of the body. This is expressed in dizziness, confusion and instability of body position (a feeling of movement, rotation of the body, although the person is in a standing or lying position). Like the previous manifestation of cancer, the syndrome may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anxiety, changes in blood pressure and heart rate, since in this case the tumor affects the functioning of the nerve centers of the reticular formation.
As the size of the neoplasm increases, the severity of brain disorders will increase, while at the initial stage there are disturbances in the perception of information by the organs of touch, taste, hearing, and vision; there is a disorder of cognitive functions of the brain. This is expressed in deterioration of memory, perception, difficulty in performing intellectual tasks, mental disorders, even personality degradation.
Against the background of increased intracranial pressure, the patient may experience a hemorrhagic stroke followed by cerebral bleeding, which leads to a sharp deterioration of the condition. In this case, in the absence of medical care, the death of the patient may occur.
At the last stage of development, glioblastoma is manifested by impaired sensitivity, the appearance of convulsions and numbness of the extremities. Paralysis and epilepsy may also develop. This manifestation of the disease is extremely dangerous for the patient’s life, so he simply needs qualified medical care in a hospital setting.
Due to the fact that glioblastoma is an aggressive type of brain tumor and rapidly increases in size, its manifestations are certainly noticed by patients, but due to the extensive symptoms, the disease may be incorrectly identified. In this case, it often happens that the necessary medical care is provided too late and the patient dies.
Thus, it turns out that depending on the location of the glioblastoma of the brain, certain symptoms of destruction of the brain matter will appear, and depending on its size, the strength of neurological disorders will appear.
Glioblastoma: where does the tumor come from? Why young and successful?
The human brain is the most poorly understood part of the body. Scientists have been studying the structure and functions of the hemispheres for many years, studying the features of regeneration and growth of nerve cells, their renewal. An even more difficult area to study is brain oncology, the study of various types of brain cancer, treatment methods - both surgical and medicinal, and the use of radiation therapy. It's not just scientists who are concerned about issues related to brain cancer. Not long ago, Zhanna Friske, Anastasia Khabenskaya, Dmitry Hvorostovsky and Mikhail Zadornov passed away. And the headlines of all publications are full of the fact that Anastasia Zavorotnyuk is also struggling with a similar disease. What kind of scourge is this, and why does it affect the rich and famous? What can cause brain cancer and is it possible to cure it?
Diagnosis: glioblastoma
Oncological diseases have long ceased to be rare and unique diseases. However, if we talk about brain lesions, this is a rather rare diagnosis. On average, brain cancer accounts for up to 1-2% of all patients with cancer. But at the same time, of all brain tumors, approximately ¾ are malignant and rapidly growing pathologies, from which our celebrities have died. Glioblastoma is a type of astrocytoma, a cancer that originates from individual brain cells (astrocytes).
They are grade IV malignant tumors, where most of the tumor cells multiply and constantly divide. They receive blood and nutrition from the vessels of the brain, additionally “eating” healthy brain cells. The tumor consists primarily of abnormal astrocytic cells, but also contains a mixture of different cell types (including blood vessels) and areas of dead cells (necrosis). Glioblastomas quickly spread to nearby areas of the brain. They can also spread to the opposite hemisphere of the brain through connective fibers (corpus callosum). Glioblastomas extremely rarely spread beyond the brain - they metastasize, they kill their host due to the rapid destruction of the brain.
How does a tumor occur?
Glioblastomas can occur spontaneously if just one brain cell mutates. They begin immediately as an aggressive stage IV tumor, without any previous, for example, benign formations. These tumors are the most common form of glioblastoma and tend to be more aggressive. Secondary glioblastomas, which form from astrocytic tumors of a lower grade (II or III), occur less frequently; they grow more slowly and have a chance of cure.
Is there hope?
Unfortunately, today the prognosis for glioblastoma is disappointing. Patients live on average from 2-3 months to a year. Considering the fact that the tumor is detected quite late, there is very little time left. Only 2% of patients live with this diagnosis for up to 5 years. Oncologists say that today they cannot cure this type of brain cancer, although there are prospects for developing new drugs, but this will take many more years. Another unpleasant thing about ganglioblastoma is that it can relapse at any time. This usually happens after 5-10 years of life, but recurrent cancer is usually more aggressive than the first episode.
Usually people come to the doctor when the condition is no longer unbearable and the symptoms cannot be ignored. But at this time the tumor has already grown to a large size and affects a large area of the brain. In the early stage there are no special and pronounced manifestations. There may be slight malaise, fatigue, and sleep problems. But our celebrities usually associate this with a tough touring schedule, flights, and workload. And an ordinary person is unlikely to suspect such a diagnosis.
Later, glioblastoma develops nausea with vomiting and convulsions, a painful headache due to increased pressure inside the cranial cavity. When certain areas of the brain are affected, visual or hearing impairment, memory loss, loss of consciousness, mental and speech disorders appear.
Men or women: who gets sick more often?
Scientists believe that this cancer most often affects men. Average age is from 40 to 60 years. But in recent years, women have also become more likely to suffer from astrocytomas, which is associated with a number of external influences and changes in health.
In men, glioblastoma can be provoked by head injuries, constant contact with occupational hazards at work, high concentrations of heavy metal salts, bad habits, busy work schedules and stress. There is evidence that radiation invisible to the eye (including from the abundance of technology around us), some viruses that penetrate the body, and genetic anomalies inherited from parents can have a negative impact.
In women, in addition to these factors, provocateurs can be serious hormonal imbalances or various attempts to deceive nature and rejuvenate the body using various newfangled techniques that appear every year.
In the prime of life!
First to the wife of Konstantin Khabensky - Anastasia, then to Zhanna Friske, and now Anastasia Zavorotnyuk. They learned about their diagnosis after giving birth, such a joyful event in life. Immediately there was a discussion and version that the cause of cancer was pregnancy and childbirth, or the procedures that preceded them. Yes, scientists put forward one version of the influence of assisted reproductive technologies and hormonal shifts as one of the factors. But it is important to emphasize that all this is rather a catalyst, and not the true cause of tumor growth. It is possible that previously dormant genes in one of the brain cells, inherited and encoding tumor growth, awakened as a result of stress from a hormonal surge and started the growth of glioblastoma. Therefore, it is impossible to blame IVF or pregnancy at any age of a woman.
Is cancer a disease of the rich and famous?
No, it’s wrong to say that; people suffer from brain tumors, regardless of their social status and fame. But famous people are always well-known, so their problems are more actively discussed in the media. And there may be an opinion that only they can have such problems. But glioblastoma is diagnosed in hundreds of ordinary people every year, and simply no one knows about them.
Plus, wealthy and famous people more often pay attention to their health, undergo examinations, monitor their nutrition and condition in order to actively tour and withstand the frantic pace of life. Therefore, I determine diagnoses from them, which, due to late treatment or ignorance of the disease, in ordinary people can be recognized after death. But brain cancer is an extremely difficult diagnosis, and it is very difficult to recognize it early.
Can rejuvenation techniques provoke cancer?
The issue is now being actively discussed that many women who are faced with glioblastoma could have provoked it with anti-aging procedures. In particular, we are talking about the use of stem cells. These are a kind of “universal soldiers” of the body, capable of transformation into any tissue of the body and actively reproducing. Can they potentiate cancer? Perhaps, but there is no scientific evidence of this, but there is also no confirmation of their perfect safety during rejuvenating procedures or when administered inside the body. Knowing the characteristics of cell division and biochemical processes in the body, it is impossible to talk only about the effect of stem cells on cancer. Rather, many factors can play a role at once - stress, illness, injury, hormonal changes and heredity. There is still much we do not know about the origin of brain cancer (and many other sites).
Why does brain cancer kill with this level of medicine?
All this is due to a number of reasons. Firstly, the brain is very complex; it contains many different types of cells that perform different and very important functions. To date, neuro-oncologists (brain tumor specialists) have identified about 120 different types of cancer lesions. They vary depending on the location of the tumor focus, the cells that are affected by cancer, age and existing manifestations.
Symptoms similar to cancer can also occur in non-cancerous diseases, which is why diagnosis is difficult. People get to neurologists late, and to oncologists even later, and then it’s too late to do anything. But even if a tumor is detected at an early stage by undergoing an MRI or CT scan of the brain, it is important to distinguish whether it is malignant or benign. Everything is complicated in the brain; even a non-cancerous, benign tumor can kill if it compresses vital centers. The skull is a closed and relatively small cavity, where even 1-2 cm of tumor is a significant irritant. A biopsy can determine an accurate diagnosis; for this, neurosurgeons need to literally climb into the patient’s head and remove a piece of the tumor. It’s good if it lies on the surface, but if it is located deep, the biopsy itself can kill the patient. Not all people are ready to take risks, leaving themselves to live at least for some time. And even if a biopsy is performed, the type of tumor is determined, not all of them are operable - that is, it is not always possible to completely remove them without killing the patient and leaving cancer cells to grow again.
Does anyone take more risks than others?
Are there certain risk groups - professions, age or type of activity - that may increase risks? It’s difficult to say - our celebrities who died from brain cancer were relatively young, took care of their health and nutrition, and led a healthy lifestyle. Yes, they had stress, flights, concerts, workloads - but others are also exposed to them! Therefore, “stardom” and “celebrity” are not a risk factor, just as a healthy lifestyle is not a guarantee that there will be no cancer.
According to oncologists, who have been studying the problem of tumor development for many years, cancer arises as a defect, a critical breakdown in genes that does not lead to cell death. Although this occurs randomly, some external influences can also contribute to the provocation of cancer. There is a proven connection with smoking, drinking alcohol, and exposure to carcinogens. Although the risk increases, it is not 100%.
But today the connection between brain cancer and stress has not been proven, although it is impossible to deny the fact that constant stress and overwork weakens the immune system, which monitors the destruction of cancer cells. But if cancer has already developed, stress can make its progression more active.
There is no connection between cancer and frequent air travel and radiation from space, which is much higher during flight. However, disruptions in biorhythms due to long-distance and long flights can make a certain contribution to metabolic disturbances.
There is also no connection with the influence of mobile phones or other electronics or household appliances. Perhaps we simply have not yet studied the subtle mechanisms, but to date there has been no connection between brain cancer and frequent cell phone use.
What are the treatment options for glioblastoma?
Glioblastoma is difficult to treat because some cells may respond well to certain treatments while others may not be affected at all. Because of this, the treatment plan for glioblastoma may combine several approaches. The first step in treating glioblastoma is a surgical procedure (biopsy) to make a diagnosis, relieve pressure on the brain, and safely remove as much of the tumor as possible. Glioblastomas are diffuse and have finger-like tentacles that extend into the brain, making them very difficult to remove. This is especially dangerous when tumors grow near important areas of the brain that control functions such as language and movement/coordination.
Radiation and chemotherapy are used to slow the growth of residual tumor after surgery and for tumors that cannot be removed by surgery. With standard treatment, the average survival rate for adults with glioblastoma is approximately 11-15 months. There are factors that can help improve the prognosis, for example, a younger age at diagnosis (less than 50 years), almost complete removal of the tumor. But in general, these terms are up to a maximum of two years.
Diagnostic methods
In order to determine the location of brain glioblastoma and its course characteristics, it is important to conduct a comprehensive study.
MRI or CT
The procedure is carried out using a contrast agent, which allows the tumor to be visualized in the images, its size, location and borders to be determined.
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are highly informative methods of instrumental diagnostics, as they allow layer-by-layer scanning of tissues and analysis of the structure of the tumor.
Biopsy
In order to establish an accurate diagnosis, patients are prescribed a biopsy, which is carried out by sampling a section of tumor tissue. The resulting samples are sent for laboratory testing.
Analysis of the biopath allows you to confirm the presence of cancer cells in the tumor and make an accurate diagnosis. The procedure in this case is complex and is carried out only by a highly qualified doctor.
PAT
Chitron emission tomography is used to detect the re-development of pathology if the patient has a history of treatment for such a formation.
PET is also used to determine the presence of a primary tumor.
Radiography
X-ray examination is prescribed to identify metastatic lesions. But with glioblastoma, metastases do not always occur in distant organs. Most often, the disease spreads only to brain tissue.
But x-rays also make it possible to determine the extent of the spread of the pathological process and determine the presence of necrosis.
The patient will also have to undergo a blood test. Laboratory testing is prescribed to determine tumor markers, the inflammatory process, and various changes in composition.
What is glioblastoma?
A large number of scientists are working on the question of what glioblastoma of the brain is and how to fight this disease, because according to statistics, even with properly selected therapy, the patient’s life span is quite short - about 5 years after the diagnosis of the tumor.
Previously, it was believed that such a neoplasm develops from healthy auxiliary stellate cells of the nervous tissue of the brain - astrocytes. However, recent developments in this area indicate that the cause of the disease is the presence of “windows of malignant vulnerability,” that is, the pathology is formed not from mature, but from slowly growing glia in which neoplastic transformation occurs. In this case, the impetus for the development of pathology is genetic deviations and mutations.
According to the WHO classification, glioblastoma multiforme of the brain belongs to the 4th class of malignancy, since it has 3 or all 4 morphological signs of pathology: nuclear atypia, mitotic figures, microproliferation of the endothelium and zones of necrosis, while the 4th component must be present.
Physiologically, glioblastoma is considered the most aggressive and dangerous type of cancer of the central nervous system, since due to its atypical cellular structure it grows rapidly.
Typically, glioblastoma begins to form on its own from the white matter of the brain, and only in 15% of clinical cases, such a neoplasm begins as a metastasis of another cancerous tumor in the body. As medical practice shows, secondary glioblastomas are diagnosed in middle-aged people.
Glioblastoma can be located in any part of the brain, but its “favorite” location is the frontal and temporal zone of the cerebral hemispheres. Depending on how strongly it affects the nerve centers, corresponding neurological abnormalities will appear.
Glioblastoma of the brain develops rapidly and exhibits a diffuse pattern of spread in the medulla, but in most cases this cancer proceeds without the formation of metastases to other parts of the body. The consistency of the neoplasm can be soft or hard, and in size: ranging from a few millimeters in diameter to the size of the hemisphere itself, while around the tumor there is always an infiltration zone in which healthy nervous tissue undergoes necrosis.
The growth of glioblastoma multiforme is always accompanied by hypertension, since, reaching large sizes, it compresses and displaces other brain structures. For the same reason, hydrocephalus is a frequent accompaniment of the disease.
Prevention measures
Since experts have not established the exact reasons for the development of the tumor, no special preventive measures have been developed. In order to reduce the risk of developing the disease, it is recommended to follow general rules, including:
- Timely treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases when the pathological process affects the head area.
- Elimination of exposure to radiation, ionizing radiation, chemicals and toxic substances.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Patients are advised to stop smoking and drinking alcohol, as they have a negative effect on the entire body.
- Avoiding hypothermia and overheating. In the cold season, you need to wear a warm hat, and in the summer, wear a Panama hat, scarf or cap.
It is also important to undergo regular preventive examinations. This will help to promptly identify the disease and carry out treatment. If unpleasant symptoms occur, there is no need to postpone visiting a specialist. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Glioblastoma of the brain is a malignant lesion. In the initial stages, it develops slowly, which allows treatment and full recovery.
But already at stage 3 the prognosis is unfavorable. That is why, when identifying a pathology, it is important to follow all the doctor’s clinical recommendations and undergo treatment. After surgery, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations to exclude relapse.