The brain is one of the most complex structures studied in physiology. It consists of several parts, each of which is unique and no less difficult for science. The brainstem, which is a part of the brain, seems to be its most interesting component, because responsible for the functioning of many systems. In recent years, scientists have been able to study it in detail and give precise characteristics. Knowledge of the structure and functions of the brain stem will allow you not only to increase your erudition, but also to avoid some diseases associated with the head.
What is the brain?
The human brain is an organ that is the center of the entire nervous system. In total, it contains more than 20 billion neurons that transmit information to the necessary centers of the human body. Signal transmission is carried out by an electrical impulse. All parts of the brain are responsible for their specific capabilities and functions. There are 5 departments in total:
- oblong;
- finite;
- intermediate;
- rear;
- average.
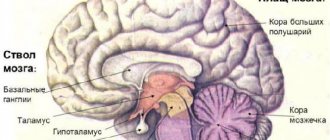
The brain also includes: the thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pons, cerebellar cortex and vermis with nuclei, cerebral cortex, basal ganglia.
The brain has a naturally formed defense. The brain's protection consists of three membranes: soft, hard and arachnoid. But the main element that is responsible for the safety of the organ is the skull.
The medulla oblongata is a continuation of the spinal cord. It contains two substances: white and gray. White is the information transmission channels, gray is the nerve nuclei.
The oblong part passes into the Valoriev Bridge. It includes nerve fibers and gray matter. The blood artery supplying the brain passes through this part. The pons continues into the cerebellum, another important section.
The cerebellum is the central link in the brain system. It consists of two small hemispheres covered with white and gray matter. The most multifunctional part of the brain.
The midbrain is connected to the cerebellum by two legs. The structure of the trunk is directly related to the location and access to other departments. The middle section has 4 tubercles (2 visual and 2 auditory). The brain communicates with the spinal cord through nerve fibers that arise from the tubercles.
The two large hemispheres are completely covered with cortex. It is in this cortex that all processes associated with thinking occur. Between the hemispheres is the corpus callosum, which connects them. Each hemisphere is divided into lobes of the forehead, temples, crown and occiput.
The brain stem is responsible for reticular information. It is the connecting link between the brain and spinal cord. The department is quite interesting, which has motivated multiple studies.
What are reflexes? How is breathing regulated when a person sleeps? Why does the pupil move? How does a person feel and distinguish tastes? These and many other questions forced a thorough study of such a part of the brain as the brainstem.
to contents ^
Stem section
The first living beings to appear on Earth had only a medulla oblongata. It was he who provided them with all the necessary instincts that helped them survive. But this is not enough, because... they needed to constantly develop their reflexes and thinking. After some time, new organisms began to be born with larger brains. Such changes occurred shortly before the appearance of man, with whom the formation of the cerebellum occurred. The remaining parts of the brain began to form only hundreds of years later.
The brain stem, which appeared during evolution, was responsible for ensuring respiratory function and blood supply to all necessary parts of the body. As it developed, it began to consist of a huge number of different centers, which began to form a very complex system. Now this section is a necessary part of the brain, without which life is impossible.
It is located between the large opening of the head in the occipital region and the slope of the inner part of the skull. The trunk extends the spinal cord, connecting it with the main one located inside the head. Its length is about 7 cm, and it includes several separate parts that are very important for the body.
How and why was the brain stem formed?
All the functions of the stem department have long been defined. His research is carried out by neurophysiologists, anatomists and other doctors. The basis for the emergence of a full-fledged trunk was the medulla oblongata. The brain stem is a very complex system in which many processes occur simultaneously.
The first creatures that came onto land had only a medulla oblongata, which allowed them to be guided by primitive instincts. During evolution, it was necessary to improve reflexes, reactions and thinking. The big brain appeared much later, when animals already had thinking. After the appearance of erect man, the cerebellum formed in the cranium. And with subsequent generations, the brain acquired more and more convolutions, cortex, nerve nuclei and other elements that are characteristic of modern man.
Useful to know: Convolutions and grooves located in the brain: structure, functions and description
Now the main tasks of the trunk are to ensure breathing and blood circulation, and their regulation. The structure fully supports human life, so pathologies are extremely dangerous. Cerebral edema is quite dangerous. In this case, the barrel moves lower, where it is clamped in the occipital foramen. Then full functioning is impossible, which causes a lot of consequences.
to contents ^
Structure
The structure of the brain stem consists of 3 main elements. The midbrain is formed by the peduncles and quadrigeminal. Gives off 3rd and 4th pairs of nerves.
The Varoliev bridge is more compacted. Located in the middle part. Formed by the base, quadrigeminal, tegmentum and various elements of the cranial ventricle system. Gives off from 5th to 8th pairs of nerves.
The largest part is the medulla oblongata. A special groove will separate the oblong part from the bridge. Gives off the 9th to 12th pairs of nerves and one nucleus of the 7th pair.
The brainstem also includes nerve cells with nuclei, which are called the reticular formation of the brainstem. Such formations have two types of neutrons in their structure: dendrites and axons. The first ones do not have many branches. Axons have T-shaped branching. Together they create a network called the reticulum. This is where the term reticular formation came from. They are directly connected to the central nervous system, directing and transmitting information to other processing centers. Information may have an afferent type of conduction, or efferent. The afferent type directs signals to the formation, the efferent type – from it.
The functions performed directly depend on the structure of the department.
to contents ^
Device
The author faces a difficult task. Usually, even in reference manuals written concisely, the chapter on the structure, functions of the brain stem and its disorders takes up a hundred or two pages of small text. But brevity is the sister of talent. With this in mind, let us begin our review of this most important section of the central nervous system, the truncus encephali, or trunk, into which the structures of the spinal cord directly pass. We will look at its parts and structures, analyze the external and internal structure and functions of the sections that form the truncus encephali.
There is no need to be afraid that the designations are in Latin. Even in the era of witch burnings and obscurantism, every more or less literate person in Europe knew Latin. And it will be useful for us, educated people, space explorers, to remember the noble language that gave rise to modern civilization.
general information
This most ancient part of the brain is located in the caudal (tail) part of the brain, closest to the spinal cord, into which it directly passes. The brain stem (truncus encephali) is divided into three sections:
- medulla oblongata, or medulla oblongata;
- bridge, pons;
- midbrain, mesencephalon.
Below the medulla oblongata, its continuation down to the 2nd lumbar vertebra is the spinal cord. Above the midbrain is the diencephalon, and they are separated by a bridge.
In addition, it is from the trunk that 10 pairs of cranial nerves exit (and enter, respectively) on each side. In total, a person has 12 pairs of these nerves, but the first two pairs - the olfactory and optic nerves - are direct outgrowths of the brain. The remaining cranial nerves (cranial nerves) belong to the nerves of the caudal group, and phylogenetically developed from the branchial arches. Therefore, an important function of the brain stem is the coordination and control of these diverse nerves, which are discussed below.
A myriad of conducting paths are “pressed” and concentrated in a small volume of the trunk . Everything that connects the head with the body passes through the structures of the trunk along the sensory, motor and vegetative bundles. Some of these paths on their way form a transition to the opposite side of the trunk, some switch to other neurons.
It is in the brain stem that many nuclei of these ten pairs of cranial nerves lie, the main function of which is to control these nerves. The structure of these nuclei is complex: there are sensitive, there are motor (motor), and there are secretory nuclei (vegetative).
In addition to the nuclei, the trunk contains red nuclei and substantia nigra, which belong to the structures of the extrapyramidal system, which controls muscle tone and unconscious movements. In the trunk there are pontine nuclei and olivary nuclei of the medulla oblongata.
The trunk includes such a curious formation as the plate of the roof of the quadrigeminal. It is responsible for transmitting visual and auditory impulses that occur unconsciously. It is there that it is possible to switch parts of the visual analyzer to the auditory ones in humans.
You ask: “what does it matter”? Here's what it is. If there is a sudden loud bang or a shot near you, you will blink involuntarily. This will happen completely unconsciously. Reflex protection of the organs of vision in the event of a danger signal received through the organs of hearing is one of the many functions of the upper sections of the trunk. There is no need to connect the cerebral cortex and the parts responsible for consciousness here. No time to think! It is enough to “switch the wires” from the sensitive part of the reflex arc directly to the motor ones, which is what nature did.
The entire brain stem, including the pons, is immersed in a branched network of neurons that forms the reticular formation. Its anatomy is very complex. This formation is very important for “plant life”; it is responsible for coordinating breathing and blood circulation in humans.
In addition, a significant part of the reticular formation has an activating effect on overlying structures, including the cortex. It is she who is responsible for the presence of consciousness and wakefulness during the day.
A little about trunk damage
Since this article does not involve a detailed presentation of neurological syndromes and symptoms, we will briefly describe how lesions of the medulla oblongata manifest themselves.
In a very small space of the trunk there is an abundance of pathways and nerve nuclei. Anatomically, this part of the central nervous system is considered to be the most complex in the human body. Therefore, even a very small, millimeter-sized lesion poses a big health problem. Most often, the main symptoms of trunk damage include symptoms such as :
- dysfunction of the cranial nerve on the side of the lesion;
- paralysis of the limbs of the same name on the other hand, since the motor bundles in the pons form a decussation.
In the domestic literature, such diseases are called alternating syndromes. There are about a dozen of them. They are called by the names of the researchers who discovered them (Fauville, Dejerine, Millard - Gübler, Wallenberg - Zakharchenko, Weber, Avellis, Benedict, etc.). Their reason may be different. Sometimes the lesion is formed by a tumor, sometimes by an ischemic stroke.
We took a very brief look at the general structure of the brain stem. Now let's talk in a little more detail about the structures that make up the human brain stem.
Cranial nerves
But first, we will briefly describe the function of the ten pairs of cranial nerves, since without this it is impossible to assess the structure of the human brain stem. In order not to turn the article into a textbook, we will not give data on the localization and symptoms of lesions of these nerves, but will give a general, overview picture.
There are 10 pairs of nerves in the brain stem, and they have many types of different fibers:
- sensitive somatic – carry information from the skin, tendons, transmit pain, sensitivity, temperature sense, touch, etc.;
- sensitive vegetative – transmit pain from internal organs. It is known that the 10th pair - the vagus nerve - descends into the abdominal and thoracic cavity, innervating the heart, intestines, etc.;
- special sensory (vision, hearing, taste, smell);
- general motor (to skeletal muscles that are subject to our will - blinking, chewing);
- autonomic motor (which work without our desire - innervation of the salivary glands, smooth muscles of the bronchi, myocardium);
What nerves emerge from the trunk? Let us briefly summarize their functions and names, as well as the number of cores, in a makeshift table. Each core has a pair on the other side. If you want to rack your brains more thoroughly, you can take any serious textbook on anatomy and neurology.
The illustration shows some projections of the nuclei of the cranial nerves in a “profile”.
- 3rd pair, or oculomotor nerve. Provides movement of the eyeball, dilation and contraction of the pupil, provides muscle sensation (that is, with our eyes closed we understand which direction our eyeballs are looking). Has 2 cores;
- 4th pair, trochlear nerve. Innervates one muscle of the eye, has one nucleus;
- 5th pair, trigeminal nerve. Consists of sensory and motor, vegetative fibers. Provides sensitivity to the skin of the face, oral mucosa, conjunctiva. Attacks of neuralgia and toothache are “his doing.” Also innervates the muscles of mastication. Has 2 cores;
- 6 pair, or abducens nerve. Innervates one lateral muscle of the eye, has one motor nucleus. The simplest nerve. When affected, one eyeball turns toward the nose, as the healthy antagonist muscle continues to pull the eyeball toward itself. You have seen such people many times. Manifested by convergent strabismus;
- 7th pair, facialis, facial nerve. Innervates all facial muscles, nasal and lacrimal glands, is responsible for salivation and taste in the anterior 2/3 of the tongue, and also provides sensitivity to the skin of the ear, membrane and ear canal. It has 2 nuclei in the stem part and 2 in the ganglia on the periphery;
- 8th pair, vestibulocochlear nerve. Carries special impulses: balance and hearing. It has 2 ganglia (nodes) on the periphery; there are no nuclei in the brainstem;
- 9th pair, glossopharyngeal nerve. It has two complex nuclei in the brain and 3 nuclei on each side in the ganglia. Responsible for taste, salivation, sensitivity on the back of the tongue, pharynx, pharyngeal reflexes and sensitivity of the middle ear;
- 10th pair – vagus. The longest nerve, after the sciatic. It has two nuclei in the rhomboid fossa and 2 in the ganglia. Innervates the muscles of the pharynx, carries parasympathetic innervation to the lungs and heart. Slows down the heart rate, reduces blood pressure. Bilateral transection of the vagus, or bilateral damage to the autonomic nuclei leads to death;
- 11th pair – accessory nerve. It has one core, “dealing with” the muscles of the larynx and pharynx;
- 12th pair – hypoglossal nerve. It has one motor nucleus and makes the tongue move.
All pathways of these nerves enter and exit the brainstem. Isn't it true that the anatomy of the trunk has become a little more complicated? And this is without the fact that almost every nerve is divided into several independent branches. But that is not all. Let's begin with a review of the structure of the parts of the human brainstem.
Functions
The brain stem can implement vital functions thanks to the following cranial nerve nuclei:
- motor. Directs the functionality of the muscles of the eyelids and eyes. Also controls reflexes of the eyelids and eyeball. Directs the work of the chewing muscles;
- sensitive. They participate in the work of all reflexes associated with digestion - from swallowing to the gag reflex. Taste buds work thanks to the sensory nuclei. Also responsible for sneezing;
- parasympathetic. The movement and size of the pupil depends on the command from a given core. Also monitors the ciliary muscle. Another name is the trochlear nerve nucleus;
- upper salivary. Controls the functioning of the salivary glands. Responsible for the timely and sufficient release of oral fluid and saliva;
- vestibular. They control and direct the work of the vestibular apparatus, which is responsible for the balance of the body;
- double. One nucleus that completely controls the swallowing reflex. Sensory nuclei also help with function;
- cochlear. Two nuclei that are responsible for hearing receptors. They transmit signals to the center related to the cerebellum.
That is, the brain stem helps a person move, think, hear, see, touch and other capabilities necessary for full life. In addition to such capabilities, it controls all head reflexes. The trunk processes the impulses it receives from the central nervous system and gives commands to the organs through the spinal cord.
Useful to know: What is the right hemisphere of the brain responsible for?
to contents ^
Cranial nerve nuclei
One of the most important components of the brain stem is the cranial nerve nuclei, which extend from its base. They are located between the rear and oblong parts, with a small number of them located on the bridge. The nuclei consist of nerve endings that have a direct effect on the trunk. They are presented in the form of branches that penetrate through its most important parts.
Each core has its own purpose. The following nerves emerge from this zone:
- Olfactory;
- Visual;
- Oculomotor;
- Facial;
- vestibulocochlear;
- Block;
- Discharge;
- Trigeminal;
- Glossopharyngeal;
- Sublingual;
- Additional;
- Wandering.
Their full functioning is very important for the human body. Dysfunction of any nerve can have serious consequences that impair quality of life and even lead to death.
Chain reflexes
Chain reflexes also occur in the brainstem. This happens if several pairs of cores are activated simultaneously.
Oculomotor reflexes coordinate gaze. The impulse is transmitted through the cochlear and ternary nerves to the nuclei. The direction of gaze involves the oculomotor, lateral and abducens nerves. The process is monitored by the reticular formations, the cerebellum and the cerebral cortex.
The act of chewing occurs due to contractions of the extensor muscles of the lower jaw. The impulse is transmitted along the ternary nerve. In the medulla oblongata near the pons there is a center that is responsible for the entire chewing process. Afferent signals excite the motor neurons of the masticatory muscles, which raise and lower the movable jaw.
The act of swallowing moves food that has entered the oral cavity into the digestive tract. First, the receptors of the tongue root are excited, then the palate. When food is already in the throat, receptors in the pharynx are activated, which help direct food into the esophagus. This act is ensured by the swallowing center, which is connected to the respiratory center.
Cough is a protective reaction of the human body to irritation in the trachea, larynx or bronchi. The vagus nerve carries an impulse to the cough center. The nucleus is located in the medulla oblongata and is directly connected to the respiratory center. First, take a deep breath. The glottis is closed and the expiratory muscles contract to exhale. This creates high pressure, followed by a sharp exhalation when the glottis opens. The air flow passes exclusively through the mouth.
The sneeze reflex is also protective. In the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity, irritation of the ternary nerve occurs. The sneezing center is located near the cough. The whole process happens the same way, only the air flow comes out not through the mouth, but through the nose.
to contents ^
Tumors of the trunk. Types and treatment
There are 10 types of brain stem tumors:
- Primary. Occur when tissue is damaged;
- Secondary. May occur after tuberculosis, severe flu or other dangerous diseases;
- Parastem. They grow closely with the trunk and gradually deform it;
- Cerebellar. The cerebellar peduncles are affected first. Then it gradually spreads to the stem part;
- Exophytic. They also arise in the cerebellum, after which they spread to the trunk. May form in the membrane of the cranial ventricle;
- Diamond-shaped. They arise in the occipital part where the depression of the same name is located;
- Deforming. They form directly on the trunk or on other parts. They change the shape of the stem part, which greatly affects the performance of the department;
- Diffuse. Unfortunately, they are almost impossible to treat. It is extremely difficult to determine the boundaries of the tumor. It fuses too much with the brain matter.
to contents ^
conclusions
The brainstem is the most important part of the brain, as well as the entire body. The general condition of a person depends on his health. The slightest damage can cause serious consequences: loss of hearing or vision, inability to taste food, or maintain balance. The most dangerous is damage to the respiratory center, which leads to respiratory arrest. Prevention of brain stem diseases consists of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding head injuries and timely elimination of factors that can trigger the pathological process.
Diagnosis of tumors
It can be almost impossible to suspect the formation of tumors. Some immediately show clear signs of presence, others can develop over a long period of time without causing any inconvenience.
The first step is anamnesis analysis. After examining the results, the doctor may order the next test. In a healthy brain, functions should be performed without errors. Therefore, studies are being carried out on the functionality of the nerves of the head.
Useful to know: Forebrain: functions and structural features
You can also perform instrumental diagnostics. The formation can be confirmed by electroencephalography, rheoncephalography or puncture. Research confirms the diagnosis 100%. Instrumental diagnostics allows you to obtain data on the activity of different parts of the trunk.
Modern methods are magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT). Studies visualize formations, which makes it possible to determine the exact size. Studies can also suggest the histological features of the tumor.
to contents ^
Treatment of tumors
The prognosis for the outcome of treatment depends primarily on the type of tumor. Its location and size also play a big role. The most difficult tumors to treat are those that have formed inside the trunk.
Benign formations can be easily removed surgically. There may be exceptions if a surgical knife, entering a foreign body, can damage the brain stem structures. Before and after the operation, the doctor prescribes laser and chemotherapy. They prevent the growth of glioma. They also remove cancer cells that remain after surgical removal and prevent their development.
But patients who develop malignancy account for about 80%. Such tumors cannot be removed by surgery. A popular alternative method is radiation therapy. The tumor is exposed to radioactive radiation. But the method cannot completely kill cancer cells. Therefore, they are used to stop the development of a tumor or avoid relapse.
to contents ^
Modern methods of treatment
If a brainstem pathology is detected, then part of the brain cannot fully decipher the information due to deformation or damage, which can cause atrophy of some organs. Therefore, stereotactic therapy is often used, which can also quickly cope with pathology.
This therapy is a combination of two radiations: “Cyber Knife” and “Gamma Knife”. A computer that is turned on emits radiation, the type and dose of which it determines independently. This method is called “Cyber Knife”. The second method is radiological radiation. Gamma Knife is performed by placing a special helmet on the head that emits waves and particles.
Another treatment option is chemotherapy. Cytostatic drugs stop development, after which the formations are removed. For greater effectiveness, the doctor often prescribes a combination of therapies. Some are larger scale, some are more precise. The brain stem is a hard-to-reach part of the main organ of the central nervous system. Therefore, combining procedures can give excellent results.
to contents ^
Brain stem stroke
Problems of the cardiovascular system always have severe consequences. Blood flow in the area of the stem part, there may be vascular damage due to cerebral infarction. What is an ischemic stroke? This is by far the most dangerous stroke. Brain cells are severely damaged due to poor circulation. Many diseases can lead to the development of such a disease. Hemorrhagic stroke is less dangerous, but destructive to brain tissue.
Strokes are almost untreatable. Therefore, it is extremely important to go to an ambulance as soon as possible. If it was possible to call doctors within an hour, then there is a chance that there will be no death. If you survive a stroke, the patient will have to undergo therapy for a long time. The functions of the brain stem cannot be fully performed. Although such an attack does not affect mental development in any way.
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Diseases
Like any other organ, the brain can fail. The same applies to its trunk. Most problems become the consequences of injuries or other diseases, and sometimes simply manifestations of age. There are several diseases:
- Stroke;
- Tumor;
- Cysts;
- Chordomas;
- Ischemia;
- Malformation;
- Aneurysms;
- Epidermoids;
- Meningiomas.
Most of them appear extremely rarely. The bulk of reported cases of brainstem lesions are stroke and various tumors. They are the most dangerous and require the highest quality and fastest treatment. But why do they arise?
Causes
A particular disease can develop for many reasons. Those most at risk are those who already have serious brain diseases, lead an unhealthy lifestyle, or suffer from regular stress. But even healthy people can get problems with the brain stem. Violations occur for the following reasons:
- Diseases associated with blood vessels, as well as their damage;
- Traumatic brain injuries;
- Poor circulation;
- Nervous breakdowns, severe stressful situations;
- Extreme sports, as well as extreme sports in everyday life;
- Eating junk food or untreated water;
- Alcohol abuse, smoking;
- Congenital diseases associated with the brain stem.
When any diseases appear, they must be treated immediately. Lack of necessary medical intervention can lead to severe irreversible consequences or death.