Histologically, this tumor is polymorphic and consists of various cells - gemistocytes, primitive neurons, granulocytes, etc. The prognosis for life with glioblastoma is influenced by the degree of malignancy. The tumor belongs to the category of the most aggressive, which is microscopically manifested by nuclear atypia, cellular polymorphism, high mitotic activity, microvascular proliferation and foci of necrosis.
In addition, the prognosis of life with grade 4 glioblastoma is influenced by the aggressiveness of cancer cells and their ability to grow rapidly.
General information
Glioblastoma is the most aggressive and most common malignant brain pathology.
This is a very dangerous disease. From the moment the patient first develops symptoms of the disease, if untreated, the person lives for about three months. By providing complex treatment (surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy ), the life of such a patient can be extended by 1-2 years. Currently, scientists are actively working to more accurately determine brain glioma - what it is, and what are the causes of this terrible disease.
So far, experts believe that the tumor develops due to malfunctions in the functioning of brain cells. This pathology is quite rare. According to statistics, per 100 thousand patients with oncological pathologies, glioblastoma is diagnosed in only one case.
Life expectancy after glioblastoma removal
Glioblastoma can be treated surgically if:
- it is located in an accessible place;
- The operation is not hampered by the patient's condition.
If a tumor grows into several parts of the brain at once, it is not possible to remove it.
To accurately determine how much tissue is to be resected, procedures to visualize brain structures are performed before surgery. This is an MRI scan that uses a contrast agent to reveal abnormal cells.
After surgery, a course of radiation therapy and chemotherapy is prescribed. Irradiation is performed using a cyberknife.
During chemotherapy, the drugs Avastin or Temodal are prescribed. The course of treatment lasts 42 days.
Even if the localization of glioblastoma allows for surgery, only most of the tumor can be excised, but not all. This is due to the fact that the tumor grows inside healthy tissue, and its complete removal will affect other structures of the brain.
Due to the fact that the tumor is only partially eliminated, the risk of relapse after surgery is quite high: the malignant process develops again in 80% of cases. A person diagnosed with glioblastoma can expect to survive 14–26 weeks after surgery. If additional radiation was given after surgery, life expectancy will increase to 40 weeks.
Pathogenesis
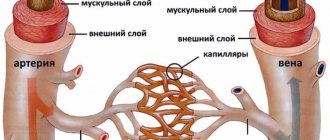
Gliomas are any malignant brain tumors that form glial cells . When malignant transformation occurs, glial cells, namely astrocytes , become less differentiated, losing the characteristics of functional mature cells. In addition, their connection with neighboring cells is lost, and division becomes uncontrolled.
Thus, glioblastoma consists of poorly differentiated astrocytes, it has foci of necrosis and areas of vascular proliferation. A characteristic feature of this formation is a random arrangement of cells, polymorphism of cell nuclei and extensive perifocal edema. The tumor grows rapidly and invades the brain tissue. It is impossible to trace clear boundaries of the affected area. The neoplasm does not metastasize beyond the nervous system.
It is most often found in the frontal and temporal lobes. Very rarely, a tumor forms in the brain stem, spinal cord, or cerebellum.
In some cases, glioblastoma develops from anaplastic and low-grade astrocytomas, but most often this lesion is primary.
The tumor spreads to neuroglial cells, whose functions are related to the nutrition and protection of neurons. These cells do not reproduce in adulthood, but there are precursors of glial cells in the brain. If disturbances occur in their development, glioblastoma may develop.
A characteristic feature of glioblastoma, which determines its aggressive course, is its heterogeneity. The nature of the neoplasm differs in different patients. Moreover, even in one patient, the tumor can contain different cells that are not genetically similar, with different mutations. During the treatment process, cells mutate, actively evolve and develop new methods of survival.
Characteristic signs of glioblastoma
During the research, scientists noted that a significantly lower risk of developing glioma – by 40% – is observed in people suffering from various types of allergies .
Experts explain this by the fact that in such people the immune system is in an activated state and prevents tumor growth.
Definition of pathology
Glioblastoma is a neoplasm in the brain that does not have clear boundaries, which greatly complicates the surgical removal procedure. It is characterized by an aggressive course and quickly proliferates into surrounding tissues. Most often localized in the temporal and frontal lobes. There are 4 degrees of tumor malignancy.
Grade 4 glioblastoma that affects the brain is characterized by the process of metastasis to other organs, which significantly worsens the prognosis after surgery. In carcinogenesis, the process of immortalization (the property of dividing indefinitely) of cancer cells plays a decisive role.
According to the international classification, glioblastoma who grade 4 (grade 4) is characterized by histological criteria - cellular polymorphism (different cells in the composition), nuclear atypia (irregular structure - enlargement of nuclei), vascular thrombosis, mitotic activity (rapid cell division), microvascular proliferation ( penetration into the vascular system), tissue necrosis.
Classification
The following types of tumors are identified:
- Multiform . Glioblastoma multiforme is the most common and most dangerous type of tumor. The lesion is well supplied with blood, and vascular necrosis develops very quickly.
- Giant cell . This variety is different in that the cells have not one nucleus, but several.
- Gliosarcoma . This is a tumor with a sarcomatous component.
It is important to conduct an accurate diagnosis and clearly determine the type of formation. This will make it possible to choose the most optimal treatment.
Primary and secondary types of the disease are also distinguished.
- Primary – develops very quickly, over about three months. This type is more common in older men.
- Secondary - is the result of the degeneration of benign formations. This type of disease most often develops in women after 45 years of age.
There are other, less aggressive types of brain tumors.
Four degrees of the disease are determined:
- The first is that there are no signs of malignancy, but the tumor covers new cells. There is a possibility of recovery.
- Secondly, there are already signs of glioma, the tumor is still growing quite slowly. The chances of recovery are reduced.
- Third, brain tissue is involved in the process, the tumor grows quickly and is malignant. Complete recovery occurs in rare cases.
- Fourth, the tumor grows very quickly, the symptoms are very severe. The tumor is inoperable, the prognosis is unfavorable.
The main stages of manifestation of glioblastoma
Oligodendroglioma is a glial neoplasm of the brain that develops from oligodendrocytes. This tumor grows slowly but can grow to a large size. It forms along the walls of the ventricles, grows into their cavity, as well as into the cortex. The disease lasts a long time, sometimes longer than five years. The tumor is removed surgically.
A variety of such neoplasms are:
- oligodendroglioma (has a second degree of malignancy);
- anaplastic oligodendroglioma (has a third degree of malignancy);
- mixed oligoastrocytoma (has a third degree of malignancy), later degenerates into glioblastoma .
Another type of glial tumor is optic nerve glioma .
This neoplasm develops from the glial elements of the optic nerve. It is treated with radiation or surgery.
Specifics of diagnosis and treatment of glioblastoma at different stages
The cost of cancer treatment abroad is determined by the recommended diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. It is worth considering in more detail what methods are used to make a diagnosis.
When making a diagnosis, several specialists are involved - usually a neurologist, otoneurologist, pathopsychologist and neuro-ophthalmologist). The following examinations are recommended:
- Echoencephalogram;
- Electroencephalogram;
- MRI and MRI;
- Trephine biopsy;
- Biopsy samples;
- Study of cerebrospinal fluid;
- CT with intravenous contrast;
- Scintigraphy;
- Endoscopic examination (ventriculoscopy + surgery);
- Immunohistochemical diagnostics.
What is included in the treatment program:
- Neurosurgical removal
In some cases, glioblastoma is considered inoperable, but if there is even the slightest possibility of eliminating the tumor, then a comprehensive approach is recommended to the patient, including surgery, radiation and chemotherapy sessions. In modern medicine, during removal, a fluorescent identification technique for cancer cells is used, which makes it possible to distinguish pathological tumor tissues from healthy parts of the brain with the highest accuracy.
- Chemotherapy
The necessary drugs are selected individually, taking into account the stage of cancer, the patient’s age and the general condition of the body. Sometimes chemotherapy is combined with radiation.
- Radiation therapy (radiation)
This technique is recommended in the postoperative period. If the tumor is small, radiation is used as an independent treatment. The number of sessions depends on the stage of the disease.
- Radiosurgery
Recommended for use when surgery is not possible or in addition to tumor removal. This modern technology (cyber knife and gamma knife) is the safest. Treatment duration is 1-3 sessions (each 30-90 minutes). During the sessions, anesthesia and internal penetrations into the skull, which are necessary for neurosurgery, are not required. In this case, the effect can be carried out on both one and several tumors simultaneously. The treatment does not require hospitalization, allowing the patient to live in a normal rhythm. Radiosurgery is recommended for all patients who have contraindications to classical radiation.
- An integrated approach to the treatment of glioblastoma abroad
If removal of the tumor is not possible, partial resection with radiation during surgery is performed. For this purpose, local exposure is used with the help of capsules, which allow local influence on the lesion. In combination with systemic chemotherapy, this helps reduce the risk of relapse and metastasis.
- New methods of treating glioblastoma in oncology centers in Israel
An innovative device has been developed with an adjustable electromagnetic field, which makes it possible to selectively destroy abnormal cells without affecting healthy ones.
- Maintenance drug therapy
In the process of complex treatment, modern drugs are actively used, the action of which is aimed at combating tumors. They are prescribed individually for a certain period of treatment. Temodal and Avastin are considered the most effective. In the last stages of the disease, patients are shown regular pain relief and palliative therapy.
Causes
Experts still do not know why glioblastoma develops. The likelihood of developing this disease increases with radiation exposure and congenital mutations. However, scientists have not yet determined a clear dependence on these factors. It is noted that the disease is not inherited, and its development is not associated with smoking, exposure to electromagnetic radiation, or poor nutrition - this has been confirmed in the process of scientific research.
However, risk factors that to varying degrees provoke the development of a tumor are:
- age over 50 years;
- male gender;
- nationality – residents of Asia, Europe, Latin America;
- the presence of genetic pathologies that increase the likelihood of developing gliomas - Turcotte syndrome , tuberous sclerosis , neurofibromatosis , etc.;
- undergoing radiotherapy;
- benign astrocytoma .
There is also an opinion that the development of this disease is increased by certain viruses: human herpes cytomegalovirus , polyomavirus .
Why does glioblastoma appear?
The causes of glioblastoma, like most cancers, are not precisely known. It is believed that the disease is associated with a mutation of certain genes.
It was possible to identify some factors that may increase the risk of tumor development. These include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- previous traumatic brain injury;
- other brain tumors, especially astrocytomas;
- neurofibromatosis;
- exposure to ionizing radiation;
- cytomegalovirus, herpes IV and other viral infection.
Symptoms of glioblastoma
At the initial stage of the disease, there are practically no symptoms, so it is difficult to diagnose it in the early period. Pronounced signs are observed when the tumor has already grown significantly and puts pressure on the brain. The first manifestations of glioblastoma are common dizziness and memory impairment. In some cases, the fingertips become permanently numb.
As the disease progresses, cerebral and neurological manifestations develop.
The development of cerebral symptoms is associated with increased intracranial pressure and progression of intoxication. These are the following manifestations:
- Severe headaches that become more intense when the person lies down.
- Constant feeling of dizziness.
- Nausea that has nothing to do with eating; vomiting, after which there is no relief.
- Constant weakness, drowsiness, severe fatigue.
- Deterioration of mental abilities, lethargy.
- Depression , apathy , irritability.
The manifestation of neurological symptoms depends on the location of the tumor. The following signs may be observed:
- Cramps.
- Impaired vision, hearing, speech, smell.
- Decreased sensitivity or paralysis of the limbs.
- Auditory and tactile hallucinations
- Movement coordination disorder.
- Respiratory depression.
Since neurological symptoms are similar to those of a stroke , this may be the reason for an incorrect diagnosis.
Unfortunately, in the later stages, when these symptoms appear, it is no longer possible to cure the patient. Doctors can only prolong his life.
Symptoms of oligodendroglioma also depend on its location. In all types of oligodendroglioma, intracranial pressure increases. Other symptoms similar to the manifestations of glioblastoma described above also develop.
Treatment of glioblastoma of the brain
Treatment of glioblastoma is selected individually, depending on the stage of carcinogenesis and the general condition of the patient. How long they live after removal of glioblastoma will directly depend on how far into the disease the surgery to remove the tumor was performed. In the initial stages, when the tumor is still small, it is possible to remove glioblastoma using new methods. These endoscopic techniques are minimally invasive and allow excision of the affected tissue without craniotomy. Microsurgery is performed using intraoperative fluorescent navigation. Before surgery, the patient is injected with a solution that stains the neoplasia tissue, which allows better visualization of the tumor. In this case, the removal of glioblastoma of the brain takes place with minimal trauma, the consequences of the surgical intervention quickly heal, which reduces the rehabilitation time.
Craniotomy (open brain surgery by opening the skull) is often performed because, as a rule, the tumor reaches a large size by the time of diagnosis, so it can only be removed by trephination or resection of the skull.
Due to the spread of the tumor, the unclearness of its boundaries and proximity to vital areas, it is not always possible to completely remove the tumor. In this case, surgery to remove glioblastoma will be considered palliative treatment. This will reduce intracranial pressure, significantly reduce negative manifestations and increase life expectancy. The consequences of surgery to remove glioblastoma will depend on how much pathological tissue is removed. The best result is when the tumor is completely removed.
Important. For this type of brain cancer, surgical treatment can reduce negative symptoms and increase life expectancy by a year or more.
Treatment of glioblastoma of the brain in Russia is characterized by high standards that are not inferior to similar therapy in Western clinics. The advantage of domestic cancer centers is the lower cost of treatment and the availability of insurance programs. Treatment of glioblastoma is always complex. The operation is supplemented with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Before surgery, these methods help stabilize tumor growth and reduce its size, and after surgery, kill or significantly weaken the remaining cancer cells.
It is important to note that in advanced stages of glioblastoma, surgery is often not possible. In this case, treatment of inoperable glioblastoma is carried out using radiotherapy (which becomes the main method of treatment) supported by the administration of cytostatic drugs. However, as practice has shown, glioblastoma cells exhibit high resistance to ionizing radiation.
To eliminate unfavorable symptoms, symptomatic treatment is prescribed:
- analgesics;
- anti-inflammatory;
- narcotic painkillers;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- sedatives;
- antinausea, antiemetic drugs and others.
Tests and diagnostics
Development can be detected in the early stages if a person regularly attends preventive examinations and examinations. In this case, you can take timely measures at the first sign of a threat. It is very important to visit a neurologist and neurologist who can identify the disease.
If there is a suspicion of glioblastoma, a medical history, examination, and laboratory tests are performed.
Next, the doctor prescribes appropriate examinations. The patient may be prescribed the following examinations:
- computed tomography - makes it possible to obtain a high-quality image of the structures of the central nervous system;
- magnetic resonance imaging – using an intense magnetic field, you can obtain a clear image of the structures of the central nervous system;
- functional MRI – allows you to obtain broader information about the tumor, blood flow, tissues;
- biopsy - in the process of selecting material, taking biomaterial;
- MR spectroscopy – allows you to obtain information about metabolism in the brain;
- lumbar puncture - a sample of cerebrospinal fluid is taken;
- PET, SPECT - these studies make it possible to determine the functional activity of brain tissue;
- electroencephalography – carried out to study brain activity.
How and why glioblastoma develops
The brain's gray matter cells, or neurons, are highly specialized cells that cannot reproduce. Malignant tumors develop not from neurons, but from neuroglial cells. Neuroglia are auxiliary tissue of the central nervous system that ensures the functioning of neurons, supplies nutrients and protects them.
Neuroglial cells actively function, divide and can acquire oncological characteristics. Neoplasms from astrocytes, a type of glial cell, under certain conditions transform into malignant glioblastomas. The exact diagnosis is “glioblastoma multiforme,” which indicates the presence of several types of cells, but astrocytes still form its basis.
If left untreated, the tumor mass rapidly increases in size, compressing the surrounding nerve tissue. At the same time, new blood vessels are formed (angiogenesis occurs) - the neoplasm needs nutrients and “material” for such growth. Frail young blood vessels are often damaged, which threatens intense bleeding and necrosis of areas of the brain. Another danger is the spread of cancer to healthy areas of the brain. The boundary between the cancer lesion and normal tissue cannot be reliably established.
The only and exact reason for the development of this type of cancer, unfortunately, has not been established. Therefore, there are no means to prevent the disease. However, doctors note a number of patterns in the development of glioblastoma:
- More often diagnosed in men
- Typical for mature age - over 50 years old
- More common among whites and Hispanics
- Develops under the influence of ionizing radiation and chemicals (polyvinyl chloride)
- Associated with genetic factors - the presence of a similar type of cancer or neurofibromatosis in family members
The assumption about the influence of mobile communications on the development of tumors from neuroglia was tested in clinical studies and, fortunately, was not confirmed.
Treatment with folk remedies
In the case of glioblastoma, traditional methods can only be additional treatments aimed at reducing the severity of symptoms. If you replace the traditional treatment regimen with folk remedies, a quick death is inevitable.
- Radish compress – grate the radish and add salt. When the juice begins to stand out, rub the mixture on your head and wrap it with a towel. The course lasts three weeks.
- Soda solution - dissolve 3 g of soda in 100 g of water and drink this solution. Gradually increase the amount of soda to 5 g.
- Chamomile tea - it is prepared from dried chamomile flowers (15 g of raw material per glass of boiling water). Drink instead of tea.
Prevention
The most effective method of prevention is regular attendance at preventive examinations, which make it possible to identify problems at an early stage. It is especially important to undergo annual examinations for people over 45 years of age, because with age the likelihood of this dangerous disease increases.
To reduce the risk of developing this disease, you must follow the recommendations regarding a healthy lifestyle:
- Get a full night's rest - healthy sleep and its sufficient duration are important.
- Spend time outdoors – you need to walk as much as possible every day.
- Avoid stress and emotional turmoil.
- Give up bad habits - do not smoke, do not consume excessive amounts of alcohol.
- Do not abuse spending time with various gadgets.
- Eat right - lots of vegetables, fruits and grains, be sure to have legumes, high-quality proteins, and unsaturated fats. Harmful foods - fast food, smoked meats, soda, confectionery, etc. - must be excluded.
Prognosis and possible prevention
The prognosis depends on a large number of factors, which also include general health, the patient’s age group, the size and location of the tumor, and the response to treatment. The final result will be known only after completing the full course of complex therapy. Glioblastoma multiforme is characterized by unfavorable prognosis; people die when it develops.
If the tumor is amenable to surgical treatment, then the prognosis after surgery is better. Because the exact causes are unknown, there is no way to prevent the disease. Prevention consists of constant examinations.
Medicine all over the world, including neurosurgery, is constantly evolving. More recently, it was not even possible to remove the tumor. In this regard, there remains the possibility of developing effective and more reliable methods of therapy that will significantly increase the life expectancy of patients even with the 4th degree of the disease.
Adelina Pavlova
Diet for glioblastoma
Diet for cancer
- Efficacy: no data
- Duration: until recovery or lifelong
- Groceries cost: 2500 - 4800 per week
With this disease, the patient needs to eat more fat and less carbohydrates. This diet is called a ketogenic diet. Its essence is that the tumor receives less energy for its growth. People are allowed to consume more protein and fatty foods than on a regular diet.
But for now, scientists are studying the mechanism of action of such a diet in malignant brain tumors.
At the same time, it is important to consume foods that will help cleanse the body, strengthen the immune system , improve blood counts and give the body additional strength.
But in general, the following nutritional rules are relevant for oncology:
- Do not make too drastic changes in your usual diet.
- Make adjustments to your diet gradually.
- Monitor how the body reacts to certain foods.
- Do not eat food that you absolutely do not like.
- Do not practice low-calorie diets.
- Try to eat food that does not contain artificial additives and preservatives.
- Be sure to include vegetables, fruits, dairy, legumes, vegetable fats, grains, seafood, green tea, and nuts in your diet.
But in general, it is important that the diet is healthy and does not contain harmful foods and dishes.
Treatment of glioblastoma with Avastin
This drug was developed by geneticists. It contains antibodies to the proliferation factor, which is produced by the endothelium of tumor-forming vessels. This factor is a protein component secreted by glioblastoma.
Thanks to it, a vascular network is formed, which guarantees nutrition to the pathogenic focus. The more vessels there are, the faster the tumor progresses. Avastin blocks the formation of the vascular network, preventing the progression of the cancer focus. You need to know that: • Avastin is used in recurrent forms of glioblastoma; • to this day the drug does not belong to the category of drugs prescribed primarily for relapses; • The medicine can be prescribed alone or in combination with another medicine called Irinotecan.
Forecast
Survival and life expectancy in this disease directly depend on the type of glioblastoma, its location, and the general condition of the patient.
If proper treatment is not given, only about 10% of people survive more than three months after diagnosis.
With the most aggressive form of the disease - glioblastoma multiforme - even with a competent approach to therapy, a person rarely lives more than one year. However, the likelihood of a favorable prognosis largely depends on the completeness of tumor resection and on some tumor biomarkers.
Complete recovery, provided proper treatment, is possible only with grade 1 or 2 glioblastoma. Treatment will require a very large number of different procedures, and the likelihood of relapse with a fatal outcome will remain.
Glioblastoma grade 4 is most often inoperable. To increase life expectancy, doctors prescribe drug therapy and special procedures. Patients with this pathology are most frightened by the question of how they die from glioblastoma of the brain. Having learned about the diagnosis, a person is frightened by the thought of dying from this malignant disease in severe pain. In such a situation, doctors prescribe painkillers and other medications to alleviate the person’s condition.
Diagnostics
The success and consequences of treatment for brain cancer largely depend on at what stage of carcinogenesis the tumor is detected. The earlier glioblastoma is detected, the better the treatment. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance (MRI) imaging using contrast remains the gold standard in head examination. Recently, PET – positron emission tomography – has been widely used. The most accurate diagnosis and all its features can be determined by cytohistological analysis of the selected material (biopsy). These are the main diagnostic measures; in addition to them, the following can be carried out:
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- angiography of head vessels;
- molecular tests;
- immunohistochemical tests;
- histological typing;
- genetic analysis of genes.
List of sources
- A.P. Romodanov, N.M. Mosiychuk. Neurosurgery. - Kyiv: Vyshcha School, 1990. - P. 16. - 105 p.
- Zemskaya A.G. Glioblastoma multiforme of the brain. - L: Medicine, 1976.-S. 192.
- Pishel Y.V. Glioblastomas of the brain. (Pathomorphology, clinical picture, diagnostics, comparative assessment of treatment methods): Abstract of thesis. dis. . Dr. med. Sci. - Kharkov, 1971. P. 32.
- Savchenko A.Yu. Brain gliomas. Omsk: Publishing house. Omsk State Pedagogical University, 1997. - P. 312.
- Fadeev B.P., Zhabina PM Combined treatment of glial and metastatic brain tumors // Bulletin of Surgery named after. I.I. Grenova. - 2005. - No. 1. — P. 80-82.
Consequences and prognosis
Life expectancy is predicted individually, depending on the patient’s age, type of tumor, nature of the course, intensity of progression, localization, degree of influence on surrounding brain structures, Karnofsky index (the general condition of the patient on a 100-point scale, where 100% indicates normal health, 10% - on the state shortly before death).
The stage (degree) of glioblastoma plays a decisive role in predicting how long the patient can live. With an aggressive course of glioblastoma that has affected the brain, the duration of the period, how long they live with it after surgery, is determined individually. Statistics show that on average this figure is 14-36 months.
In recent weeks, patients diagnosed with a stage 4 tumor that is not amenable to therapy usually live in specialized hospitals, where they are under round-the-clock medical supervision. For inoperable forms of cancer of the fourth stage, the patient is recommended maintenance therapy, which includes intravenous administration of painkillers and sedatives.
To defeat glioblastoma, which is considered one of the most aggressive tumors of all that form in the tissues of the central nervous system, you must adhere to the recommendations of your doctor. Often, surgical treatment, chemotherapy and radiation significantly increase the patient's life expectancy.