Possible symptoms of a concussion
- Brief confusion or loss of consciousness. With a strong blow, the moment of injury disappears from memory.
- Dizziness even at rest, and when turning, bending or other changes in body position, the symptom intensifies.
- Severe headache, nausea and vomiting.
- Double vision, inability to concentrate on one point.
- Increased sensitivity to light and sounds.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Reaction inhibition - the victim gives an answer to the question after some time.
- Pale skin, weakness, sweating.
Important! A concussion is not always accompanied by visible head injuries, so the absence of wounds does not exclude brain injury.
Types of traumatic brain injuries
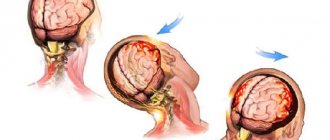
Injuries caused by a head impact are called TBI for short. There are several types of damage.
Concussion (CHM)
With a strong impact on a hard surface, the gray matter is displaced and after a second returns to its original position. This is how a double displacement of the brain occurs.
FMS is reported equally often in adults and children. This is the most common head injury. It accounts for 70% of all registered TBIs. Symptoms that may indicate a concussion:
- feeling of weakness;
- short-term (up to 15 minutes) loss of consciousness;
- vomiting, feeling of nausea;
- headache;
- inability to remember how the injury occurred;
- dizziness;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- blurred vision;
- Pain in the eyes.
SMG can happen even after a blow to the jaw. Then pain when chewing and talking is added to the symptoms.
Body temperature and blood pressure are restored in a short time after injury. But unpleasant consequences in the form of nausea and dizziness make themselves felt for a long time. The matter is aggravated by problems with falling asleep, up to complete insomnia.
If there is a suspicion of a concussion, a doctor's examination is required. If the symptoms of injury are minor, the patient is allowed treatment at home. It is allowed to use folk remedies, such as head massage and a special linen patch. In some cases, hospital treatment is recommended.
Brain compression
The main risk is damage to the stem formations in the cerebellum area. This area of the brain is responsible for breathing and regulates blood circulation.
Therefore, it is extremely important to examine the patient and conduct an MRI. If the presence of internal hematomas is determined, they are urgently removed. Hemorrhages increase pressure on the brain and aggravate the patient’s condition.
Brain contusion
A common injury among boxers. It also develops after a beating, a fight, or a strong blow to the head. As a result:
- cranial vault injury;
- damage to brain tissue;
- necrosis of affected areas.
The presence of a brain contusion can be judged by the following signs:
- loss of consciousness (always);
- disorientation in space;
- feeling dazed;
- memory impairment;
- cephalgia;
- bouts of vomiting;
- disruptions in heart function and breathing;
- neurological symptoms (Kernig's syndrome, nystagmus);
- throbbing pain in the occipital region.
If the injury results in a fracture of the skull bones, it may look like a dent in the back of the head. Remember, if there are fragments that get into the brain matter, life support functions will be affected. Roughly speaking, a person can die or go into a vegetative state.
There are three degrees of severity for brain contusion. A mild degree occurs in children. High activity combined with carelessness leads to damage. Moderate and severe damage most often occurs in adulthood. More often these are fights and traffic accidents.
As therapy, neurologists prescribe:
- neuroprotectors;
- antioxidants;
- drugs that strengthen blood vessels.
Axonal damage
Severe injury causing contusion. After this, brain activity stops. The man falls into a coma. The injury is not treated, but only supported by the vital functions of the body. Making predictions regarding recovery is extremely difficult. The individual characteristics of the organism play a decisive role.
First aid for concussion
- If one or more symptoms are present, immediately call an ambulance or take the victim to a doctor.
- Treat a wound on the head if it appears as a result of an impact.
- For an hour or until the doctor arrives, it is important not to fall asleep, but to remain at rest.
- If you lose consciousness, lay the person on his side, bend his knees, and put his hands under his head.
- If symptoms of a concussion do not immediately appear, it is recommended to rest and not begin vigorous activity.
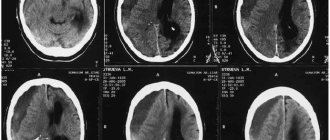
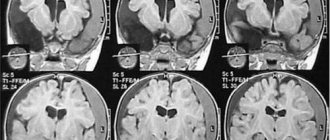
Diagnosis of head injury due to concussion and contusion
As before, at the initial stage of diagnosis for traumatic brain injury, the first diagnostic method is radiography of the skull bones.
To study the location and extent of damage to brain tissue, MRI of the brain is best. In case of a concussion, the patient does not need to undergo a diagnostic MRI procedure of the brain. Carrying out a lumbar puncture (LP) for diagnostic purposes makes it possible to most accurately, compared with other methods, recognize subarachnoid hemorrhage and the degree of its severity, identify reactions of the meninges to TBI, and detect inflammatory complications of TBI and spinal injuries.
X-ray of the skull bones in case of a concussion or bruise of the brain.
The most typical signs and symptoms of traumatic brain injury occurring in the acute period after injury (a blow to the head, a fall, a car accident, etc.):
- scalp damage
- abrasions and swelling
- skull fracture
- nosebleeds and nasal discharge
- neck muscles are tense
- loss of consciousness
Signs and symptoms of traumatic brain injury (concussion, brain contusion).
Based on the results of a neurological examination, a diagnosis can already be made. If the diagnosis is preliminary and requires clarification, the patient will be given additional instrumental or laboratory diagnostic appointments.
Possible additional instrumental or laboratory diagnostic appointments to clarify the diagnosis of traumatic brain injury:
- REG, USDG of neck and brain vessels, EchoEG
- X-ray of the skull bones, cervical spine with functional tests
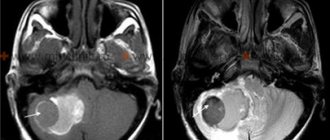
- MRI of the brain
- MRI angiography of cerebral vessels
- MRI of the cervical spine, etc.
- Lumbar puncture (LP) to analyze the composition of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain (MRI) is performed when diagnosing a patient with a traumatic brain injury (bruise, compression of the brain, etc.).
Recommendations for the treatment of concussions
If hospitalization is not required, with the permission of a doctor, a mild concussion can be treated at home:
- Bed rest and rest are required, no work. Long sleep is very important.
- You cannot read, watch TV, play computer games or use gadgets.
- Under no circumstances should you play sports.
- You are allowed to listen to music, but not through headphones.
- You can use herbal sedative drops or herbal infusions.
- In your diet, you should give preference to dairy and plant products, limit salt intake - to prevent increased pressure, including intracranial pressure.
If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner and all recommendations are followed, recovery will occur quickly and without complications.
Treatment
For severe TBIs, surgery is usually performed. The procedure may consist of primary surgical treatment. But sometimes, you have to do craniotomy, pump out fluid, remove hematomas, restore (assemble) the skull. After surgery, it is treated with medications.
If the victim is vomiting, it is stopped with an injection of Metoclopramide or Etamzilate. Pain is relieved with analgin. If there is no vomiting, they give a tablet (no more than 2 per dose), otherwise it is administered by injection.
In order to normalize blood circulation and metabolic processes in the brain, Etamzilat and Piracetam are prescribed. The standard dose is 2 tablets (varies depending on the patient’s age).
In addition, based on the nature of the injury and its clinical manifestations, he may prescribe:
| A drug | Therapeutic effect |
| Eufilin | Neutralizes cerebral edema. Prohibited for people with low blood pressure. |
| Askorutin | Strengthens the vascular system. |
| Cefatoxime, Amoxicillin | Prescribed for rupture of the meninges. The first symptoms are discharge of cerebrospinal fluid from the nose and ears. The drugs prevent complications such as meningitis. |
Even if the patient is at home, it is important to follow the following recommendations:
- avoid sudden movements;
- stay in the shade, do not overheat;
- ensure silence;
- get plenty of rest and sleep.
What parents need to know
In medical practice, an abnormal change in the shape of the head, followed by a violation of the correct outline and possible destruction of the bone, is called a deformation of the skull.
The pathology can be congenital or acquired. Often, a deformation of the skull is formed in a child in the womb and is detected during pregnancy using ultrasound examination of the fetus.
Parents or a pediatrician can notice head deformation in a newborn during a routine examination. At the same time, it is important to carry out special diagnostic measures, and not to determine the degree of deformation “by eye”. This will help to establish the causes of the development of pathology and correctly select effective treatment.
Head deformation in children is a very serious cause for concern for most parents. However, in many cases, these experiences are in vain, since the deformities disappear in the first month of life, without the use of any special treatment methods.
If the deformity persists 2–3 weeks after birth or is just beginning to form, as well as for prevention purposes, repositioning therapy is used. Its essence is to minimize the contact of the deformed area of the head with the surface, thanks to the correct change in the position of the child’s body.
- Always put your baby to sleep on his back! This reduces the risk of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome.
- After the child has fallen asleep, turn the child's head so that it does not lie on the deformed area, without changing the position of the body.
- Place your baby's head on different ends of the crib alternately. We also recommend changing the position of the bed itself in the room.
- While awake, it is necessary to change the position of toys and light sources so that the objects that the child pays attention to make him turn his head.
- Do not place your baby to fall asleep on a pillow or other soft surface.
- Place the baby on his tummy more often, but at the same time, do not leave him for a second because he may suffocate by burying his nose in a blanket or pillow.
- When breastfeeding, the mother should ensure that the baby's head does not lie on the flattened area.
As a rule, positioning treatment does not completely correct the deformity, but it is quite possible to improve the shape of the head by carefully following the recommendations.
By the end of the 3rd month of life, bone thickness increases and repositioning therapy loses its effectiveness. If the deformity persists at the age of 3 months, it is necessary to use additional treatment methods.
The biomechanical basis of orthopedic treatment is the controlled growth of the skull in the shape specified by the helmet. The helmet provides room for head growth in flattened areas and discourages growth in protruding areas. Using the potential of skull enlargement due to brain growth, we achieve the desired head shape.
The best age to start orthopedic treatment is 4 - 6 months. The sooner you start, the faster and more successful the treatment will be. For example, if treatment is started at 4 months of age, over the next 4 months the child will gain 25 mm in head circumference, which will be enough to fill the empty spaces in the helmet. In contrast, if treatment is started at the age of 16 months, the head circumference will increase by only 10 mm in 8 months, where the treatment potential may stop. Therefore, we recommend starting treatment between 4 and 6 months of age, but no later than 12 to 14 months.
Uncontrolled development of skull deformation can lead to serious complications and be extremely dangerous to the child’s health.