What is the pineal gland?
The content of the article
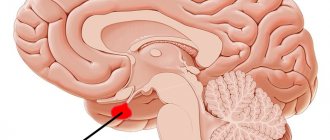
The pineal gland is a small organ located in the brain. It is similar in size to a grain of rice (5 to 8 mm) and its name comes from its cone-like shape.
Pineal gland
Despite its location, the pineal gland is not covered by the blood-brain barrier and its rich blood supply is similar to that of the kidneys. It is noteworthy that her complete education takes place between the ages of 1 and 2 years. After this time, the organ stops developing. Its mass increases only after puberty.
The pineal gland consists of several groups of cells divided into so-called lobules. Connective tissue septa separate individual lobules from each other.
The pineal gland consists of:
- Pinacocytes, or pineal gland cells, contain pleomorphic cell nuclei consisting of smaller nuclei;
- Glial cells with a network of glial fibrils - these cells, together with nerve cells, form the nervous system and constitute a layer of insulating cells;
- Nerve cells with nerve fibers - nerve fibers come from neighboring parts of the brain;
- Brain sand - this part consists of round and slightly yellow cells. In addition, it contains calcium phosphates and carbonates.
In ancient times, philosophers emphasized that the pineal gland is the place where the soul influences the body. It is often called the most mysterious organ of the human body, because it is it that has the greatest influence on the human psyche.
This single, odd element of the brain, located exactly in its center, is very often called the “third eye.”
Methods for surgical removal of tumors
Unfortunately, a cyst on the pineal gland, independent of echinococcal infection, is difficult to treat therapeutically. Therefore, in extreme cases, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention: if the cyst grows rapidly, affects the cardiovascular system, and provokes hydrocephalus.
- Endoscopy. Through a special tube inserted into the cranial cavity, a drainage is installed into the cyst to drain fluid. The capsule of the cystic formation is emptied and falls off.
- Shunting. It involves draining fluid from the neoplasm into a cavity where the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid is not dangerous to human health. For example, through a special catheter - from the skull into the abdominal cavity.
- Trepanation of the skull. The operation is highly traumatic, but also highly effective. After opening the skull, the cyst is completely removed from the body of the pineal process. If it is not possible to separate the cystic formation, the surgeon may remove the pineal gland completely.
After the cyst is eliminated, its contents are sent for histological examination to ensure that it is benign.
Important! You cannot refuse therapeutic measures; sometimes supportive therapy is enough to curb the growth of the cyst.
Sometimes surgical intervention is contraindicated, despite the threatening size of the capsule and its negative impact on the epiphysis of the brain. For example, in people with low blood clotting, pregnant women, elderly patients. Then doctors recommend conservative treatment. But usually it does not help reduce the size of the cystic formation, but eliminates the signs of the disease: headache, nausea, blurred vision.
What are the functions of the pineal gland?
The pineal gland is an endocrine gland. This means that the hormones it produces enter the bloodstream. Thus, the gland regulates the functioning of certain tissues and organs.
Located at the back of the diencephalon, the gland connects to the telencephalon, which is responsible for most mental processes.
The main task of the pineal gland is primarily the production of melatonin. This hormone has many functions in the central nervous system, the most important of which is responsible for the circadian cycle. When exposed to light, melatonin synthesis is suppressed, and when we are in the dark, melatonin synthesis increases - this affects the rhythm of sleep and wakefulness.
Melatonin production
In addition, the pineal gland is responsible for the release of growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, which is responsible for regulating the thyroid gland, and adrenocorticotropic hormone, which regulates the adrenal cortex.
In addition, the pineal gland is responsible for the release of sex hormones that regulate the maturation process.
The most important functions of the pineal gland include:
- regulation of blood pressure;
- coordination of the central nervous system;
- regulation of the human circadian system through the production and secretion of melatonin and serotonin;
- informing the body about the need to go to bed, causing a feeling of drowsiness;
- informing the body about its readiness to engage in everyday activities;
- release of certain groups of growth hormones; TSH; ACTH;
- influence on the level of melanin (skin pigment) through melatonin;
- responsibility for autumn and winter depressions;
- maintaining the body's ability to fight cancer cells;
- strengthening the immune system;
- influence on metabolic changes;
- strengthening bones (decreased pineal hormone levels significantly weaken bones);
- slowing down the aging process by regulating sleep.
The pineal gland also produces substances that are largely responsible for the feeling of euphoria. Scientists believe that it is also responsible for hallucinatory states. But most importantly, the hormones secreted by the pineal gland give a person joy and a sense of satisfaction, and also reduce depressive mood, which is a very important element of everyday life.
What threatens a cyst in the gland?
An epiphysis cyst (pinealoma) is not classified as oncology. The cells of the formation have a normal morphology, and the cyst itself does not grow in the brain tissue and does not metastasize to the body.
According to the international classification of diseases (ICD 10), the neoplasm has the code: D35.4.
The consequences for life and health strongly depend on the etiology of cyst formation, as well as on the individual dynamics of the development of formation.
Among the main ones we can mention:
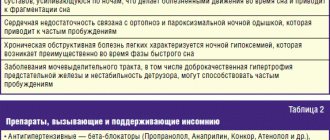
- disruptions in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- chronic headaches, including migraines;
- neurological disorders of skeletal muscles, partial paralysis;
- change in any sensitivity (tactile, temperature);
- epileptic seizures;
- sleep disorders;
- mental disorders - depression, neuroses, obsessive disorders;
- in childhood, deviations in psychosomatic development may begin.
The degree of danger varies greatly from case to case.
Pineal hormones
Pineal hormones have a very strong influence and regulate the lifestyle of every person. An analysis of the functions of the individual hormones secreted by this gland in everyday life provides convincing support for the assertion that the pineal gland is the place where the soul interacts with the body, and the body with the soul. What hormones does this “secret” gland secrete?
The two most important hormones produced directly by the pineal gland are:
- Serotonin
– this hormone is released throughout the day. First of all, it has a calming effect, but too low its level causes depression, anger and even aggression. Serotonin additionally provides a signal to prepare for sleep. - Melatonin
– produced by the pineal gland at night. It makes people feel sleepy. But the light that reaches melatonin definitely lowers its levels. So, this is the information that you need to get up after the night. - DMT (dimethyltryptamine)
– this hormone is produced by the cells of the pineal gland. It is a type of psychedelic psychoactive substance. May cause hallucinations and strong visual effects.
By producing these hormones, the pineal gland is entirely responsible for regulating each person's circadian system. The effect of the hormones of this gland is most strongly felt when changing time zones (the famous “jet lag syndrome”). Their deficiency additionally causes appetite or metabolic disorders.
Jet lag syndrome
The pineal gland not only produces its own hormones, but also participates in the production of others. These include:
- Vasopressin
– stimulates growth levels. It also regulates the density of urine. The largest amount of this hormone is produced during sleep. Vasopressin also stimulates the production of cortisol, and the pineal gland secretes this hormone from the pituitary gland. - Somatropin
is the name of growth hormone. The pineal gland is involved in its production, and the highest levels of this hormone occur during puberty. - Thyroid hormones
- the small pineal gland secretes melatonin and also regulates the thyroid gland by stimulating thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). - Gonadotropins
- these hormones stimulate the activity of the human gonads (ovaries and testes). The pineal gland plays a very important role in the process of puberty and supports the functioning of these organs, - ACTH
, also known as the stress hormone, the pineal gland is involved in the production of this hormone. As a result of its action, more cortisol is released, and the pineal gland regulates this process. Thanks to these actions, the body properly prepares for awakening.
Diagnostic measures
If at least a few of the manifestations described above persist for a long time, then you should consult a doctor immediately with this set of symptoms.
Due to the vagueness of the symptoms, an initial clinical examination by a neurologist is unlikely to yield anything definite. The main and main diagnosis here is the magnetic resonance imaging method for examining the brain.
Sometimes a patient undergoes an MRI for prevention, and quite by chance, a cystic transformation of the pineal gland is discovered at an early stage, when symptoms are still far away.
It is a great success to discover a cyst when its size is still very far from critical.
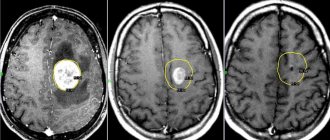
If a pineal cyst is detected on MRI, it is recommended to do a separate MRI of this particular part of the brain. A separate study will provide a much higher resolution picture. It will be possible to evaluate the structure of the neoplasm, its density, cavity size, and contents.
In most cases, diagnosis is limited to MRI of the pineal gland, and sometimes general MRI of the central nervous system.
But sometimes additional research is carried out:
- radiography of cerebral vessels (angiography) - identifying pathologies of the blood supply to the brain;
- Ultrasound of cerebral vessels - similar research purposes;
- ventriculography is a subtype of radiography, where the contrast of the cavities is obtained in the image (the quality of the cerebrospinal fluid flow can be assessed);
- electroencephalogram - the object of study is electromagnetic impulses passing along the membranes of neurons; such a diagnostic procedure is relevant for a large cyst.
Any blood tests in this case turn out to be uninformative. This is the norm for such diseases.
Biopsy
The last resort in diagnosis is a biopsy. When, along with a cyst, a tumor of the central nervous system is suspected of an oncological nature, or when the pathology is provoked by meningitis or encephalitis.
There are three types of biopsy: open, stereotactic, puncture:
- An open biopsy is the most traumatic; it is performed under general anesthesia in an operating room, and after it the patient is forced to spend a long recovery period. — During an open biopsy, a hole is made in the skull, biomaterial is taken through this trepanation window, then the window is closed with a special plate or the patient’s own bone. — When we are talking only about an epiphysis cyst, such a biopsy is not done.
- Stereotactic. — A small hole is drilled in a predetermined area through which a needle with an LED and a microcamera is inserted. “Plus, the invasion is carried out based on the MRI image, which is transmitted in real time. — The doctor can visually completely control the entire process.
- Puncture. — The hole in the skull becomes even more miniature, where a hollow needle is inserted to collect biomaterial for further study of the cerebrospinal fluid.
The last two types of biopsy do not require subsequent hospital recovery. Only gentle recommendations. And after a week the patient is able to return to the normal rhythm of life.
Melatonin, the most important hormone produced by the pineal gland
Melatonin, synthesized by the pineal gland, acts as a “signpost” to our biological clock. The cycle in which it is secreted by the pineal gland affects sleep at night. Its proper release is very important for health. However, with today's lifestyle, this rhythm is very easy to disrupt.
So-called “night breaks” or night shifts lead to a decrease in the release of this hormone from the pineal gland. Not only does this lead to later problems falling asleep, but it can also increase your risk of diabetes, prostate and breast cancer.
As we age, the activity of the pineal gland decreases, which can lead to problems falling asleep in older people. Therefore, for insomnia, medications containing melatonin are recommended. However, it should be remembered that medications with melatonin should be used only after prior consultation with an endocrinologist.
Prevention
To prevent the development of this disease, there are only general recommendations:
- prevention of cerebrovascular diseases
- reducing the risk of stroke
- reducing the risk of head trauma during childbirth
- excluding contact of a pregnant woman with patients with infectious diseases or bacteria carriers
- reduce the likelihood of fetal hypoxia in a pregnant woman (excluding the use of cigarettes, alcoholic beverages, and drugs)
- reducing the risk of traumatic brain injury
- maintaining personal hygiene and maintaining a healthy lifestyle
A very common disease is asymptomatic and does not have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. However, you should remember the possible risks of an epiphysis cyst and be able to recognize its presence in time.
Pineal gland diseases
The main disease that can affect the pineal gland is a tumor of the pineal gland. When tumors (or cysts) appear, most often, but not always, the activity of this organ is completely suppressed.
The most common symptoms of a pineal tumor are:
- dizziness and headaches;
- vomiting, nausea;
- impaired vision and balance;
- loss of consciousness.
Dizziness
In young people, tumors on the pineal gland can cause premature puberty.
Magnetic resonance imaging is performed to detect changes in the pineal gland. And surgery is required to remove them.
Reasons for the development of epiphysis cysts
A pineal cyst is a benign neoplasm that can occur in one of the lobes of the pineal gland or on its surface. It is a cavity with watery contents.
It is assumed that the disease develops for two reasons:
- Clogging of the lumen through which the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid enriched with melatonin occurs. In turn, the lumen is clogged due to:
- High viscosity liquor.
- Too much secretion produced.
- Brain injuries.
- Surgical intervention and the appearance of scars on the epiphysis.
- Brain damage by echinococcus. Echinococci (a type of parasite, worms) enter the pineal gland through the bloodstream. In this case, many echinococcal capsules are formed - in them the parasite is protected from immune attacks of the body. Subsequently, the cyst capsules are filled with waste products of the parasite and increase in size. Echinococcosis can affect not only the pineal gland, but also other parts of the brain and human organs.
Considering that the pineal gland is a poorly studied organ of the brain, there may be other reasons why a pineal cyst appears. There is a hypothesis that blockade of the pineal gland canal occurs in people who are genetically predisposed to the disease or have a congenital brain pathology.
Pineal cyst
A pineal cyst is quite often diagnosed as a disease.
A pineal cyst is a very benign tumor lesion that does not spread to other organs. This cyst is filled with inflammatory cells (leukocytes, lymphocytes and macrophages). Usually surrounded by delicate epithelium. It is difficult to identify clear reasons for its formation. Most often it occurs in young people when the pineal gland undergoes many transformations. This causes some changes in the organ.
A pineal cyst is asymptomatic, but when it puts too much pressure on the brain structures, the following symptoms may appear:
- long-term migraines (up to 72 hours);
- problems with proper vision, squint;
- sleep disturbance;
- disturbances of wakefulness.
Prolonged migraine
This disease is very often detected only by computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, carried out in the diagnosis of other diseases. Treatment for pineal cysts mainly involves eliminating symptoms and pain. This condition should be regularly monitored by a doctor. Very often the cyst resolves or significantly decreases in size, but if the lesion grows, surgical intervention is required.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional medicine recipes can be used to treat pineal cysts only after consulting a doctor. Benign neoplasms are treated:
- Tincture based on hemlock. To prepare the medicine, the flowering caps of the plant or dry seeds are used. The raw materials are filled with vegetable oil and infused for three weeks. The resulting solution is filtered through gauze. The medicine must be dripped into the nose, two drops, twice a day. The course of treatment is long, up to two months.
- Tincture based on Caucasian dioscorea. Dry raw materials are infused with vodka. Used to improve cerebral circulation and normalize blood pressure.
- Rosemary decoction. A tablespoon of dry herb is brewed with a glass of boiling water. The solution is drunk in four doses, before meals. You can only take freshly prepared medicine. Rosemary decoction can be drunk until the symptoms of the disease pass.
- Burdock juice. The juice squeezed from the leaves of the plant is infused for five days in a cold place. Morning and evening every day you should drink two tablespoons of the medicine on an empty stomach. The treatment is long - two sessions of 20 days each with a break of a month.
- Herbal infusions. To improve brain function, a general strengthening complex is taken. You can prepare a decoction from a mixture of herbs, flowers, fruits: linden, rose hips, elderberry, calendula, viburnum.
Attention! If, after taking the medicine, unpleasant symptoms do not disappear, but, on the contrary, intensify, you must stop home treatment and consult a doctor again.
Calcification of the pineal gland
Calcification of the pineal gland means the appearance of calcifications on the pineal gland. The pineal gland is quite a strong magnet for fluoride and other harmful elements such as phosphorus and mercury. Excess fluorine and phosphorus disrupts the mineral balance of the body.
Over time, a rather hard limestone crust forms around the gland, which in some sense limits the normal functioning of the organ. The more fluoride deposits there are on the pineal gland, the more severe the calcification.
Symptoms of calcification include:
- severe nausea, vomiting;
- frequent headaches;
- problems with raising the eyeballs.
People with pineal calcification tend to be pessimistic.
Proper diet plays a huge role in cleansing the pineal gland. You need to eat plenty of vegetables and fruits, avoid alcohol and smoking, and avoid fluoride.
Eating plenty of vegetables and fruits
This type of calcification can cause many diseases such as dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and multiple sclerosis.
Magnetic resonance imaging of epiphysis calcifications
The etiological factors of excess calcium deposition in the pineal gland tissue have not been reliably established. To identify calcifications, MRI is not necessary, since dense structures are shown by CT. Computed tomography is accompanied by radiation exposure of tissue, so indications for the method are strictly limited. When using radiation diagnostic methods in order to reduce radiation exposure, it is enough to do a targeted examination with a limitation of the area of exposure.
Calcification forms at the site of hemispheric defects. Pathological changes develop at the sites of impaired blood supply, inflammatory, and infectious lesions. At the beginning of the development of nosology, the normal dimensions of the epiphysis on MRI change, and areas of altered density appear. To detect defects at the beginning of formation, it is rational to do tomography with high-field devices with the ability to identify pathological foci with a diameter of 1 mm.
Types of pineal gland calcification
The prevalence of physiological calcifications is observed in people after 50 years of age. Areas of increased calcium accumulation are localized in the cerebellum, choroid plexus, falx, epiphysis, and arachnoid granulation. Calcification of the nerve ganglia in young people under thirty years of age is a sign of pathological processes.
Dystrophic calcification occurs against the background of chronic infections and long-term persistence of epidural hematoma. There are practical facts of the appearance of calcifications after chemotherapy, radiation exposure, leukoencephalopathy, microangiopathy, and degenerative diseases in the elderly.
Congenital calcification in children is formed due to neurofibromatosis, basal cell nevus syndrome.
Giant cell astrocytomas and areas of sclerosis also often undergo calcification.
Vascular calcifications appear with atherosclerosis, malformations, and aneurysms. Typical localization is the middle, anterior cerebral artery.
Congenital infections with calcium deposition in the pineal gland - rubella, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex, HIV, tuberculosis, cysticercosis, sarcoidosis.
Tumors with calcification:
- Meningiomas;
- Craniopharyngiomas;
- Ependymomas;
- Astrocytomas;
- Oligodendrogliomas;
- Glioblastoma.
Metastatic foci of brain damage provoke calcification of the pineal gland.
The accumulation of lime rarely leads to disruption of cerebral functionality. Atherosclerotic plaques limit the patency of the vessel, which causes the development of hypoxia and stroke.
Calcifications can contribute to hormonal imbalances. Hypoxic conditions disrupt the functionality of the basal ganglia, hypothalamus, and pituitary gland. Progression of the condition leads to hypothyroidism, damage to thyroid function.
Prevention of pineal gland diseases
There is currently no proven way to protect yourself from a possible pineal tumor. However, this does not mean that we cannot take steps to help the pineal gland function properly. First of all, you should start with a routine - you can’t sit for a long time at night. Adjusting your routine will help you get the right concentration of melatonin, which will help you fall asleep normally.
Additionally, as with any other organ, it is important to follow a proper diet and avoid all types of toxins, including alcohol.
Another important point in the prevention of pineal gland diseases is taking special medications with magnesium and vitamins. All this should be prescribed by an endocrinologist.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
When is treatment required?
A small cyst of the pineal gland (diameter of the neoplasm up to 4 mm) is almost guaranteed not to threaten the patient’s life. Very small, no more than 2 mm, with a considerable degree of probability it can resolve on its own. Severe symptoms begin only when the cyst passes the threshold diameter of 5 mm.
If an MRI accidentally reveals a small formation of the epiphysis, and the patient does not experience any symptoms, then the person is recommended to be observed by a neurologist and periodically, once every couple of years, have an MRI of the brain. This is common practice.
The question of the clear need for therapy arises in the following circumstances:
- tumor size is 10 mm or more;
- during monitoring, active growth of the cyst is observed;
- persistent severe symptoms are recorded for a long time;
- the cyst-like restructuring began to lead to deformation of nearby tissues.
Pathological transformation of tissue is considered one of the most negative processes in this diagnosis.
Young patients (under 12 years of age) should be observed in a special manner. Since a large progressive cyst can become a factor in delayed mental and physical development.
Drug treatment
If the situation is not critical, then the first stage involves drug treatment of a pineal gland cyst in the brain.
This therapy includes the following methods:
- Diuretics. - Excessive fluid loss will reduce the amount of cerebrospinal fluid, reduce the pressure inside the spinal canal and possibly reduce the volume of the cyst contents. — Powerful diuretics: Torasemide, Diuver, Ethacrynic acid. - Medium strength diuretics: Dichlorothiazide, Spironolactone, Mannitol. — Natural homemade diuretics include chamomile decoction, natural coffee, and hawthorn decoction.
- Antiepileptics (anticonvulsants). - For example, Carbamazepine, tranquilizers (Diazepam, Clonazepam). - Prescribed if seizures of the epileptic type occur.
- Antidepressants and sedatives: - Amitriptyline; — Afobazole; — Zopiclone (Somnol). May be needed to normalize the patient’s psychological state.
- Analgesics. “But this is problematic, because for headaches of this etiology, NSAIDs hardly help, and problems may arise with the prescription of narcotic analgesics.
In any case, drug treatment will not eliminate the cyst. This is a treatment that is used for mild, mild symptoms.
If the symptoms are such that there are prolonged, persistent headaches and epileptic seizures, then surgical therapy is necessary.
Surgical intervention
Removing a pineal cyst comes down to three options:
- open brain surgery;
- endoscopic surgery;
- using a gamma knife.
Surgical removal, as medical practice shows, reliably removes the tumor with minimal risk of relapse.
Endoscopy
An epiphysis cyst in a child is a double problem. Not only is the risk related to developmental disorders greater, but surgery on the central nervous system at such a young age is also more dangerous compared to adult patients.
Endoscopy is a good option due to its minimal invasiveness and minimal trauma.
- An endoscope with a miniature video camera and microsurgical instruments is inserted through a small hole made in the skull.
- The cyst is excised, the contents are drained, and the collapsed walls later resolve on their own.
Bypass surgery
Bypass surgery is an order of magnitude more complex operation than endoscopic removal.
The bottom line is that through a small trepanation hole in the skull, silicone tubes are inserted into the cavity of the cyst, which will have to divert the flow of cerebrospinal fluid through subcutaneous tunnels to where its presence is safe. For example, into the abdominal cavity or into the cavity of the right atrium.
Shunting is indicated when there are significant problems with the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, and the volume of liquid contents of the cavity reaches critical levels.
Craniotomy
In modern medicine, in the case of pinealoma, craniotomy is almost never performed.
This must be a very difficult, exceptional case, when numerous other surgical methods are pointless.
Of particular interest is gamma knife treatment (Lexella gamma knife).
- The point is that, using an external device, a beam of ionizing radiation is concentrated onto the cyst area.
- A stereotactic frame is fixed on the patient's head under local anesthesia, which is necessary to keep the patient's head motionless during irradiation.
- The irradiation process is absolutely painless. During the procedure, the patient is in a closed chamber, but doctors maintain audio and video communication with him.
- Irradiation time takes from 10 minutes to several hours, depending on the severity and location of the tumor. Once radiation is completed, the patient can leave the hospital.
This “operation” is performed primarily when physical invasion of the central nervous system is unacceptable.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine methods and treatment with folk remedies for this pathology are quite vague.
In Internet sources you can find references to Chinese acupuncture, Tibetan medicine, and special herbal decoctions.
However, due to difficulties in determining the mechanisms of the disease, it is impossible to say that this or that traditional therapy is effective. If only because, unlike such typical diseases as a sore throat or a cold, in folk healing they knew nothing about the pineal gland or, in general, about neoplasms in the brain.
Some recommend regular consumption of green tea (at least 2 cups per day). Others recommend traditional detoxification recipes (lemon juice with vegetable oils), because they believe that cysts arise due to chronic “pollution” of the body.
General principles of therapy
Drug therapy for cystic formations has practically no results. The only possible treatment is surgical removal of the fluid cavity. But, most forms are small in size and remain in a “dormant” state for many years. In this case, no methods of therapy are used; a wait-and-see regimen is chosen and the patient is regularly examined.
Formations that are accompanied by symptoms of hydrocephalus, complicated by bleeding and rupture, compressing the brain and rapidly increasing in size must be removed. Only a neurosurgeon decides which method of surgical treatment to use.
If the patient has a disorder of consciousness (coma or stupor), he is urgently referred to external ventricular drainage. This method allows you to reduce compression of the brain by the cyst and intracranial pressure. If the cyst ruptures or hemorrhages, surgery is performed. The patient undergoes craniotomy and the formation is excised.
In the absence of complications and disturbances of consciousness, the operation is performed planned and endoscopically. The advantage is the patient’s quick recovery period and low trauma. With endoscopic access, a milling hole is made in the skull, through which fluid is sucked out from the cavity. In order to avoid subsequent accumulation of fluid, several holes are made in the cavity (connected to the cerebrospinal fluid space) or cystoperiotoneal shunting is performed (a special shunt is installed).
The postoperative period involves rehabilitation therapy, including exercise therapy, reflexology and massage. The patient is prescribed drugs to improve blood supply to the brain, absorbents and decongestants.