MRI of cerebral vessels is a diagnostic procedure that allows you to assess the condition of the vessels of the head. There are no harmful factors such as radiation during MRI. The procedure is intended to identify various diseases, which will be discussed further. You will also find out what an MRI of cerebral vessels shows and when it is prescribed.
The accuracy of MRI is due to the fact that the tomograph works with signals from hydrogen nuclei (protons). While a person is in the magnetic field of the device, the protons of his body emit electromagnetic waves. With their help, the device builds an image of internal organs on a computer screen.
In addition to standard MRI, which is used when a tumor, multiple sclerosis and other brain pathologies are suspected, a type of method is used to examine the blood vessels of the brain. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) shows the arteries, magnetic resonance venography (MRV) shows the veins. From the outside it seems that there is no difference in these studies. In fact, these are separate procedures in different operating modes of the tomograph.
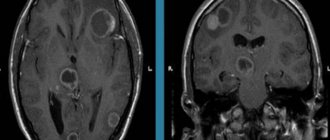
Image of the vessels of the head during MRI
Cerebrovascular diseases
Headache is often overlooked. Patients believe that such pain, if it is not too intense, can be ignored. People live with “ordinary” headaches for years, and during this time pathological processes occur in their brain. MRI makes it possible to distinguish migraine from, for example, an aneurysm, and psychosomatic headache from tumors and impaired blood supply to the brain.
What diseases are detected using MRI of cerebral vessels?
Most often, cerebral vessels suffer due to three pathologies: atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, which can lead to the development of serious complications.
Stroke
A stroke is an acute circulatory disorder in the brain, a very dangerous condition that can lead to serious health consequences. MRI is often used to diagnose strokes as a high-tech method that allows one to obtain accurate images of the pathology.
Stroke is divided into several types depending on the cause:
- Ischemic. It occurs when an area of the brain stops receiving blood due to blockage of a vessel by a blood clot or cholesterol plaque. The brain matter dies, not receiving oxygen through the bloodstream. Heart failure, diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis can contribute to the occurrence of the disease.
- Hemorrhagic. Occurs due to hemorrhage into the brain tissue from a damaged vessel. A risk factor for this type of stroke is hypertension.
Timely diagnosis of stroke is very important. Timely measures taken to identify and assess the consequences of a stroke help to begin early rehabilitation and restore damaged functions.
In the event of a stroke, MRI gives a clear and detailed picture of the course of the disease, the location and extent of brain damage.
Atherosclerosis
This disease develops to one degree or another in almost every adult, but the severity of the disease and the speed of its development are strictly individual. When the disease occurs, cholesterol and fats are deposited in the artery wall and a plaque forms. The following options for the development of the disease are possible:
- the plaque narrows the lumen of the vessel, the brain does not have enough blood;
- expansion of the artery walls (aneurysm) is formed;
- the vessel wall ruptures with subsequent bleeding;
- a blood clot forms at the site of the plaque, further interfering with the movement of blood;
- the contents of the plaque and/or the thrombus breaks off and clogs the vessel.
The following diseases contribute to the emergence and rapid progression of atherosclerosis:
- High blood pressure (arterial hypertension, hypertension) damages the vessel wall, which becomes less elastic and cannot cope with the load. Fats are deposited in it more easily and atherosclerosis develops. Due to high pressure, thin or severely damaged vessels, such as vessels with an aneurysm, rupture.
- Diabetes mellitus type 2. Excess glucose also damages the vessel wall. People with type 2 diabetes mellitus develop atherosclerosis and hypertension more quickly. Often one person has a combination of atherosclerosis, hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. They reinforce each other and increase the risk of stroke.
- Heart diseases (heart rhythm disturbances, myocardial infarction, heart defects).
Conditions that are less common: autoimmune diseases (vasculitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, type 1 diabetes, etc.), infectious diseases, sepsis, traumatic brain injuries.
Cerebral small vessel disease
A new diagnostic method sometimes opens up a whole world of diseases about which not much was known before. MRI technology helps study a group of diseases of small vessels in the brain, those with a diameter of less than 2 mm.
Small vessel disease of the brain is dangerous for cognitive decline and/or stroke. About a quarter of ischemic strokes occur due to capillary damage. There are many causes of damage to small vessels and they are still being studied.
Some older people may develop cerebral amyloid angiopathy. It affects approximately 20% of people 61-70 years old; The older the age, the more often it is detected. A special protein called amyloid is deposited in the brain vessels, gradually the blood supply to the brain is disrupted and neurons die.
Aneurysm
An aneurysm is a pathological enlargement of an artery, which occurs on average in 2-3 people out of 100. The disease occurs more often in women, as well as in the age group over 30 years. Aneurysms can be congenital, but over time, the vessel wall is also deformed by atherosclerosis, blood pressure, trauma, and an infectious process, which aggravates the course of the disease.
A vessel affected by an aneurysm may burst. Most often, the gap occurs between the ages of 20-40 years. Before this, a person may suffer from headaches similar to a migraine attack. MRI is indispensable for early diagnosis of the disease. Modern tomographs are capable of visualizing even the slightest pathological lesions in the brain with great accuracy.
Risk factors for the formation of aneurysms include smoking, high blood pressure, the use of hormone replacement therapy during the postmenopausal period, and if there are people in the family with aneurysms and other diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Angioma (vascular malformation)
A benign tumor consisting of overgrown and intertwined veins and arteries of the brain. The formation does not pose a threat to life, but as it grows, it can compress the structures of the brain, resulting in headaches and disrupting the normal functioning of the areas of the brain near which the pathology is located.
Based on size, malformations are divided into:
- Capillary. They consist of tiny vessels and usually do not cause symptoms.
- Venous. Includes larger veins and arteries. May cause specific symptoms.
- Tricky. The vessels intertwine so closely that they form entire cavities in which blood accumulates. Such a tumor can grow quite strongly and put pressure on the brain tissue.
The causes of angiomas have not been fully studied. Often the disease is congenital or occurs in early childhood. A small percentage of angiomas occur after infectious diseases.
MRI of the brain vessels will accurately show not only the location, size and shape of the tumor, but also the degree of compression of the surrounding tissues. Thanks to magnetic resonance imaging, the attending physician will be able to develop an effective plan for subsequent therapy.
Causes of vascular genesis
Vascular genesis has a lot of different causes. Including demyelinating diseases, gliosis, aresorptive and basal forms of hydrocephalus, as well as various degenerative changes in the brain. Demyelination of the brain is a pathology in which the conductivity of the sheaths of central and peripheral nerve fibers is damaged and impaired.
Demyelinating diseases are characterized by the formation of round or oval lesions. The most common include multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica and leukoencephalopathy.
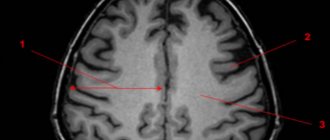
Foci of demyelination are diagnosed using magnetic resonance imaging, which can detect small focal changes in the white matter up to 3 mm.
Brain gliosis is a condition in which healthy nerve cells are destroyed and subsequently replaced by glial elements.
This is not a separate disease, but serious disturbances in the functioning of nerve impulses. Failures occur due to the proliferation of foci of white matter gliosis.
Gliosis has several varieties, which are classified according to the cause of formation and the zone of localization:
- anisomorphic - chaotic foci;
- subependymal - formed under the inner lining of the cerebral ventricles;
- fibrous - predominate over cellular glia;
- marginal - located in the intrathecal medullary zone;
- supratentorial - single focal changes, characteristic of old age, in most cases not dangerous to health;
- diffuse - multiple foci;
- vasogenic lesions - formed from vascular problems;
- isomorphic - have an exact sequence;
- subcortical - subcortical foci.
How to do an MRI of cerebral vessels
After the patient enters the radiologist's office, the doctor asks several questions about bothersome symptoms and contraindications for the procedure. The patient is asked to remove all metal objects and lie down on the tomograph bed. Normal operation of the tomograph is accompanied by noise, knocking and other loud sounds; this should not be alarmed. In our medical center, each patient is given headphones that play pleasant, calm music during the examination.
Preparation for MRI of the head and blood vessels
The patient is given a special button in his hand, which can be pressed during the procedure to inform the doctor about a sudden deterioration in health.
MRI of cerebral vessels - indications and contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral vessels is used in the presence of a wide range of symptoms that may indicate vascular pathology and circulatory disorders.
- headaches of varying duration and severity;
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- seizures similar to epileptic;
- unsteady gait, loss of coordination;
- changes in sensation of temperature, touch;
- deterioration of attention, memory;
- difficulties with understanding speech and pronouncing words;
- traumatic brain injuries.
If one or more of the symptoms described above occurs, you should consult a doctor and undergo an MRI scan to make sure there are no cerebral vascular pathologies.
Despite its safety, MRI still has a number of contraindications, in the presence of which the procedure is impossible.
- The tomograph is not designed for body weight more than 130 kg or chest (hips, abdomen) girth more than 150 cm.
- The magnetic field of the tomograph can disrupt the functioning of a pacemaker, neurostimulator, or cochlear implant - the presence of these devices is an absolute contraindication for the study.
- Magnetic metal (shards, shot, metal shavings) inside the body can shift under the influence of a magnetic field and damage surrounding tissue.
- MRI is not done in the 1st trimester of pregnancy and in children under 5 years of age.
Prostheses made of non-ferromagnetic materials allow MRI to be performed if the following conditions are met:
- there are documents for the prosthesis;
- more than 3 months have passed since installation;
- the prosthesis is not installed in the scanning area.
There are MRI-compatible pacemakers and other electronic implants. If there are any medical devices in the patient’s body, it is necessary to study the product passport for the possibility of conducting magnetic resonance imaging.
Symptoms of the disease
The main signs indicating the presence of vascular origin:
- arrhythmia - a pronounced disturbance of the pulse even at rest (jumps from 60 to 90 beats/min);
- spontaneous episodes of increased or regular high blood pressure;
- unmotivated weakness in the limbs;
- cephalalgia of various types, dizziness;
- impairment of speech, memory, vision or attention, depends on the nature of the impairment;
- increased fatigue.
Based on pain sensations, it is easy to distinguish between general and focal signs, which means a more accurate diagnosis.
Contrast MRI of cerebral vessels
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) creates images based on signals from hydrogen atoms, which are abundant in blood and other fluids. The image on the monitor screen is very clear, so a contrast agent is rarely required. When performing computed tomography, unlike MRI, contrast is used much more often.
In MRI diagnostics, substances based on gadolinium are used. A contrast agent is injected into a vein, changing the magnetic properties of the tissue for a short time, and is excreted through the kidneys. It was possible to create gadolinium compounds that rarely cause unwanted and allergic reactions. There is no evidence that they cause neurological problems after contact with the human body. However, they are used with caution in severe kidney disease.
Before a contrast study, be sure to tell your doctor about:
- pregnancy (confirmed or probable);
- breastfeeding;
- kidney diseases;
- previous allergic reactions to any medications.
Contrast makes it easier to decipher images, as it shows the condition of the vessels in more detail.
Gadolinium-based contrast agent
Besides MRI, how to check the vessels of the head?
To study the veins and arteries of the brain, ultrasound research methods are also used, which are easily tolerated, have no contraindications and do not require special training.
The simplest study - Doppler ultrasound (USDG) shows in which main arteries and veins of the head the blood flow is impaired. The main method of ultrasound diagnosis of a wide variety of cerebral vascular diseases is duplex scanning. It detects blood supply disorders when there are no symptoms yet. Transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCUSDG or TCDG) additionally evaluates blood flow in large intracranial vessels.
Comparison of images obtained using: ultrasound (left), MRI (center), CT (right)
Ultrasound examination is safe, but does not provide a three-dimensional picture and is significantly inferior to MRI in terms of information content.
Computed tomography (CT) is also used to study blood vessels - this is an X-ray scan. Multislice CT is a more advanced type of examination and is capable of recreating three-dimensional images on a computer screen. The disadvantage of this method is the radiation exposure to the body.
MRI or CT scan of cerebral vessels?
MRI and CT have their advantages in different situations. People who have electronic devices (pacemaker) or objects made of magnetic metals in their body are allowed only CT scanning.
An MRI scan takes tens of minutes and requires you to lie still. A CT scan takes less time, but this procedure uses X-rays. CT scans should not be done too often. The procedure is contraindicated for pregnant women at any stage. MRI is performed as many times as necessary; it is contraindicated only in the 1st trimester of pregnancy.
MRI of cerebral vessels is a safe procedure that will provide a detailed picture of the disease. At the medical office, you can undergo an MRI scan by appointment on any convenient day and time.
Treatment: folk and traditional
Only a specialist can decide how to treat problems associated with vascular origin. Self-medication is completely excluded.
Therapeutic therapy is selected based on the medical history and diagnosis. Traditional treatment includes the use of medications and physical therapy. If necessary, for example, removal of plaques, surgical intervention is possible.
Folk remedies are used as an auxiliary treatment. We offer recipes to improve blood circulation.
Recipe with pine cones
Collect 10 cones, rinse with warm water, chop. The resulting mixture must be poured into 0.5 liters of vodka and left for 14 days. It is enough to add 1 tsp once a day. pine tincture in tea. The course of admission is 7 days with a break of a month.