People over 60 years of age often experience mental disorders with confusion, with symptoms reminiscent of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. They are often accompanied by delusions, hallucinations, and paranoid manifestations without dementia. In this case, doctors suspect senile psychosis in elderly people. In psychiatry it has a synonym - senile. Relatives of this category of patients have a question: what to do in this case. We recommend contacting the Moscow clinic “Leto”. Our specialists treat mental disorders, including acute/chronic psychotic disorders. Phone number of our medical center: 8(969)060-93-93 . You can call him at any time and get a free consultation.
Senile psychosis, features and causes
The frequency of senile psychotic disorders is in the range of 12-25% of all mental illnesses in old age. The exact causative factors of the disease have not yet been established.
Psychiatrists suggest that the disease develops as a result of age-related changes, character traits and the influence of unfavorable living conditions.
More often, psychosis in an elderly person is characterized by:
- Women.
- Depressed individuals.
- Patients with a hereditary predisposition to this pathology.
- Persons with long-term chronic somatic diseases.
Causes of diseases in old age
- Genetic predisposition;
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, hypertension, hypotension, diabetes mellitus in an advanced stage;
- Abuse of sleeping pills, drops containing alcohol, alcoholic beverages, psychoactive substances;
- A sharp change in the usual way of life;
- Exacerbation of chronic somatic disease or acute inflammation.
- Alzheimer's disease.
- Aging of the body.
During the period of exacerbation of these diseases, signs appear that may be symptoms of the development of psychosis.
Risk factors for the disease are:
- Sleep disturbances;
- Surgical interventions;
- Acute vitamin deficiency;
- Diseases of the organs of hearing or vision;
- Constant state of stress;
- Social isolation, loneliness, especially depression
- Traumatic brain injuries;
- Neoplasms in the brain.
Senile psychosis, types
Doctors at our clinic use the generally accepted classification of the disease.
It includes:
- Affective reactions.
- Paraphrenia.
- States of confusion.
- Mental disorders in severe internal diseases.
Each variant has a dominant syndrome, according to which their differentiation is made.
Treatment of depression in old age
To begin with, let's make a reservation that depression is a disease that always needs to be treated. The main methods of treating depression in late age are psychopharmacotherapy (the effectiveness of treatment with modern antidepressants reaches 80%) and psychotherapy.
Since older age is characterized by the presence of additional somatic diseases, the selection of an antidepressant should be made taking into account these somatic problems.
The optimal drug for the treatment of late-life depression should have sufficient efficacy with a favorable tolerability and safety profile, and not have a negative effect on the patient’s cognitive functioning.
Expected treatment results:
- Restoring a satisfactory mood background;
- Improved sleep, allowing you to eliminate regular use of sleeping pills;
- Elimination of cognitive impairment to the age norm;
- Elimination of somatoform disorders (disorders that are of a mental nature, but cause somatic complaints).
Anti-relapse therapy: taking thymostabilizers (valproic acid, carbamazepine); taking antidepressants for at least 6 months.
How does psychosis manifest in the elderly?
Senile psychotic disorders identified by specialists at our health center are divided into several types. They can occur in isolation, with periodic attenuation and new exacerbations. Sometimes one set of symptoms is reduced to another. There are also isolated mental disorders that go into stable remission, which is an indicator of their effective cure. Let's consider the main symptom complexes.
Acute forms of senile psychoses
These are the problems our psychiatrists most often have to deal with.
Their development is caused by somatic ailments:
- Cardiovascular and respiratory failure.
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Diseases of the kidneys and liver.
Patients exhibit characteristic disorders:
Partial or complete disorientation in space and time with confusion.- Motor restlessness.
- Anxiety.
- Transient hallucinatory visions.
- Crazy statements.
The duration of symptoms is several days, less often weeks. After the end of the attack, prolonged asthenia and mild lethargy remain. The episode may be repeated.
Chronic senile depression
The severity of clinical manifestations of this form depends on the age of the patients (usually women).
The psychotic reaction consists of:
- Apato-adynamic complex.
- “Silent” depression, in which few people pay attention to the emerging symptoms. And this kind of patient is prone to suicide, which is a complete surprise to others.
- Hypochondriacal complaints with ideas of self-accusation, up to Cotard's delirium.
This senile psychosis lasts a long time - 10 or more years. Thanks to successful therapy in our clinic, it is possible to significantly mitigate its course. Intellect in this form practically does not suffer, only memory problems appear over time.
Chronic paranoid psychoses
The main manifestation of the disorder is the patient’s delusional ideas, with fear of harm from loved ones.
They believe that relatives or neighbors want:
- Bring their death closer.
- Poison.
- Kick out of the home.
- Rob.
Patients turn to various authorities for “protection”, initiate checks, etc. This kind of client retains complete social adaptation, and their nonsense is perceived by department officials as the truth until the circumstances are fully clarified.
Hallucinosis
Characteristic of old age (after 80 years).
Manifest:
- Vivid visual, tactile and auditory hallucinations.
- Severe memory impairment.
- Dermatous delirium. A person is sure that he has parasites and foreign objects on his skin that he cannot get rid of. The patient itches, brushes off non-existent objects, consults dermatologists, and constantly washes clothes and bed linen.
Hallucinatory-paranoid form
This option is characterized by:
- Delirium of damage.
- By adding hallucinations of fantastic content.
- Echo thoughts with hearing voices (schizophrenia-like course).
- False ideas.
This type of disease occurs continuously with slow progression, leading to gradual memory loss.
Senile paraphrenia
Psychotic disorder is manifested by false memories with fantasizing. Patients talk about incredible events, meetings, acquaintances that had no place in their lives. Patients often develop euphoria and delusions of grandeur. The painful episode lasts 3-4 years, then begins to gradually fade.
Contact phone number
+7 (495) 774-62-59 around the clock
Request a call
Gerontopsychiatry (geronto + Greek psyche - soul, iatreia - treatment) is a branch of psychiatry and geriatrics that studies the clinic, etiology, pathogenesis and social rehabilitation of mental illnesses of late age, including diseases specific to old age (cerebral atherosclerosis , senile and presenile dementia).
As a result of demographic changes, the number of elderly people began to increase rapidly in the last century.
This trend continues today in both developed and developing countries. This is due to the general improvement in the average standard of living, and with advances in medicine and pharmacology, and with the spread of ideas about a healthy lifestyle, and with many other significant factors.
And although Russia is now far from being in first place in terms of average life expectancy, these trends have affected it too. In general, it can be seen that the world's population is aging.
Aging problem
It goes without saying that morphological and functional changes, especially in the brain, cannot but affect the state of mental activity of an elderly person and the entire structure of his personality.
Caused by the biological factor of aging, a decrease in physical and mental performance, a decrease in productivity, a deterioration in biological and social adaptive capabilities, difficulties in adapting to new requirements and an accelerated pace of life lead to the fact that in the family and society the social significance of an elderly and old person generally decreases, his suffering prestige, his authority, his self-affirmation.
All this, in turn, affects his somatic state.
A single complex of biopsychosocial characteristics of an old person emerges.
For most people, mental disorders in old age are associated with dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, etc.
But the most pressing diseases of senile and old age are depression. These include isolated depressive episodes, recurrent (recurring) depressive disorder, and mixed anxiety-depressive disorder.
The main diagnostic criteria for such conditions are decreased mood and loss of interests and feelings of pleasure (anhedonia). In addition, there are: sleep disturbances, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, appetite disorders, suicidal thoughts, decreased libido.
Depression in old age is caused by many factors, and many manifestations of depressive disorders, such as problems with concentration and memory, superficially resemble dementia (senile dementia). In these cases they talk about “pseudo-dementia”.
Diagnostics
At the appointment, the doctor at our clinic draws attention to characteristic symptoms that indicate the client has senile psychosis.
During examination and questioning of patients, the following is revealed:
- Preservation of intelligence.
- Stability and limited symptoms.
- Duration of deviations.
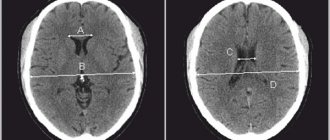
It is very important for a psychiatrist to distinguish senile psychosis from schizophrenia, manifestations of vascular pathology. For differential diagnosis, CT and MRI of the brain are used, which can reveal anatomical vascular defects and changes in brain tissue characteristic of other diseases.
Alzheimer's disease
A neurodegenerative disease first described in 1907 by German psychiatrist Alois Alzheimer.
In AD, the cognitive functions of the brain are primarily affected: gnosis (cognitive abilities), executive functions (information processing, analysis and synthesis, inference and thinking in general), memory and expressive functions (speech and practical skills).
There are types 1 and 2 Alzheimer's disease (late and early onset).
In type 2 AD, the disease begins before age 65, develops slowly at the onset of the disease, and progresses rapidly at the stage of severe dementia.
This is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder. Type 1 (after 65 years) has a less malignant course, with the exception of the terminal stage. It is considered as a complex disease.
In general, AD is characterized by a slow development of symptoms, without noticeable jumps that are typical in vascular dementia.
In the initial , or initial period, gradually increasing impairments of short-term memory are noted (mainly for current events).
Patients cope increasingly worse with professional activities; difficulties appear in performing everyday activities.
In later stages, “three A syndrome” appears - aphato-agnoso-apraxia, which is a diagnostic sign of AD.
Aphasia (speech impairment) manifests itself in difficulties in naming familiar and previously well-known objects, distortions in pronunciation, “verbal slur” or pronouncing individual syllables or parts of words. Almost always, aphasia is accompanied by aphasia (writing impairment) and alexia (reading impairment), as well as sensory aphasia (when the patient does not understand speech addressed to him.
Agnosia (misrecognition) - the patient ceases to recognize faces, outlines of objects, colors, loses orientation in a familiar environment.
And finally, apraxia is a disturbance in the performance of practical skills and actions.
Along with memory impairments, intellectual functions suffer, while individuality and personal characteristics are preserved for quite a long time.
As the disease progresses, self-care skills are gradually lost, down to the most basic ones. There is a need for constant care for the patient.
How to get to our medical center
All you have to do is call 8(969)060-93-93 . The call center manager will provide all the necessary information. From him you will learn the methods and cost of the upcoming treatment. The consultant will help you choose a room. After making an appointment, all you have to do is drive to the clinic. Our hospital is located in a convenient location. Getting to it will not be difficult, either by public transport or by your own. In cases where there are problems with the client, you can order a transfer service from us. Our staff will deliver the patient using convenient transport. All types of diagnostics and therapy are provided anonymously.
Benefits of treating older adults in a medical setting
- Qualified specialists with extensive experience;
- Proven effective techniques and high-quality care are used;
- Modern diagnostic methods that allow timely detection of pathology;
- Patients are under 24-hour supervision;
- We maintain contact with the patient’s relatives and provide them with psychological assistance;
- If necessary, we are ready to deliver the patient to our hospital or take him home free of charge.
Articles in the gerontology section:
- Dementia treatment
- Gerontology Clinic
- Gerontology hospital
- Treatment of senile insomnia
- Senility
- Gerontologist (geriatrician)
Cost of services
| CONSULTATIONS OF SPECIALISTS | |
| Initial consultation with a psychiatrist (60 min.) | 6,000 rub. |
| Repeated consultation | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist-narcologist (60 min.) | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 3,500 rub. |
| Consultation with Gromova E.V. (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| PSYCHOTHERAPY | |
| Psychotherapy (session) | 7,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (5 sessions) | 30,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (10 sessions) | 60,000 rub. |
| Group psychotherapy (3-7 people) | 3,500 rub. |
| Psychotherapy session with E.V. Gromova (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| TREATMENT IN A HOSPITAL | |
| Ward for 4 persons | 10,000 rub./day |
| Ward for 3 persons | 13,000 rub./day |
| Ward 1 bed VIP | 23,000 rub./day |
| Individual post | 5,000 rub. |
| PETE | 15,000 rub./day |
This list does not contain all prices for services provided by our clinic. The full price list can be found on the “Prices” , or by calling: 8(969)060-93-93. Initial consultation is FREE!
Treatment of senile psychoses is possible at home
To do this, you should invite a psychiatrist to your home, who will clarify the condition and give recommendations on therapy, supervision and care.
In cases of gross behavioral disturbances in the form of aggression, suicidal intentions, confusion with a danger to the life of the patient or others, hospitalization in a specialized hospital will be required. In this case, the patient can be delivered to the clinic independently or call an ambulance or special services for transporting patients to the home.
Hospitalization of patients with senile psychoses is possible both in public psychiatric clinics and in private ones.
Treatment of senile psychosis
To relieve the manifestations of psychotic disorders, mandatory medication correction is required. Medicines are selected after examination on an individual basis. The doctor must take into account the characteristics of the patient, age, character, temperament and other aspects of the personality.
Drug therapy is based on:
Neuroleptics that eliminate delusions and hallucinations.- Antidepressants that relieve depression and anxiety.
- Sedatives that relieve the patient of fears, agitation, and sleep disturbances.
The treatment complex necessarily includes the following:
- Nootropics.
- Vitamins.
- Drugs for the treatment of somatic pathology.
Against the background of pharmacotherapy, psychologists work with clients, correcting their behavior. Each of our patients is cared for and monitored. Medical staff quickly and effectively provide relief to the sick.
Treatment
Therapy for delusional manifestations in our clinic consists of the comprehensive use of medication, psychotherapeutic and rehabilitation measures.
To relieve severe symptoms, use:
- Neuroleptics.
- Tranquilizers.
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid preparations, nootropics.
- Symptomatic remedies.
Psychotherapy is carried out against the background of drug therapy. Patients with senile mental disorders require careful care. Here you can learn the rules of communication with such patients and other necessary procedures.
If your loved one has mental disorders and you don’t know what to do in this case, call us immediately. The Leto Clinic is a specialized medical institution for providing assistance to persons with neuropsychiatric pathology.
Forecast and preventive measures
A stay in the hospital of our center with timely assistance provided gives reason to talk about a positive prognosis after treatment of acute conditions. Chronic psychotic forms, unfortunately, have an unfavorable course; doctors can only achieve temporary remission. After discharge, clients, under the supervision of relatives, should follow the recommended regimen, avoid neuropsychic overload, and treat existing pathologies of internal organs. When the first signs of exacerbation appear, simply dial 8(969)060-93-93.
Mixed dementias
In 60% of cases, the origin of dementia is difficult to explain solely by Alzheimer’s disease or exclusively by vascular lesions of the brain, since in the clinical picture and during neuroimaging (for example, magnetic resonance imaging) we see a combination of primary degenerative brain lesions and disorders of a vascular nature. In this case, it is customary to talk about mixed dementia.
This is the most common form of dementia.
Pick's disease. Dementia with Lewy bodies
10-25% of dementia cases (third place after mixed dementia and Alzheimer's disease) are dementia with Lewy bodies . The development of the process is associated with the deposition of specific protein formations (Lewy bodies) in the cortex and subcortical structures of the brain.
The age of debut is 50-70 years. Characterized by visual-spatial disturbances, disturbances in attention and speech activity, memory problems and hallucinations.
In Pick's disease, the average age of onset is 57 years. In half of the cases, someone in the family suffered from similar disorders.
Personality changes are characteristic, which distinguishes this disease from Alzheimer's disease. The ability to abstraction decreases, then memory impairment and neurological symptoms gradually increase.
What are organic (irreversible) mental disorders in pensioners?
Dementia can lead to organic mental disorders of personality and behavior. Such disorders are serious, irreversible diseases and most often occur in old age.
Dementia syndrome does not occur suddenly; the progression of mental disorders occurs rather slowly, from unnoticeable manifestations to an acute deterioration of psychological health. Dementia can lead to two types of disease, total and lacunar. Total , by its name, says everything about itself - this is the final defeat of all internal systems. An elderly person suffering from total dementia will ultimately lose himself as a person, cease to understand who he is, will not be able to perceive information, and will be as helpless and inadequate as possible. Lacunar dementia has less complex consequences: partial memory loss, with the preservation of the person as an individual.
Degenerative dementia can take the form of the following organic mental diseases: senile dementia, Alzheimer's and Pick's disease.
Senile dementia. This mental disorder leads to a complete loss of intellectual capabilities. Such patients behave extremely unpleasantly; they are constantly irritated by something, grumble and suspect everyone around them. Short-term memory is impaired, so that long-lived events are remembered in every detail, and yesterday is completely forgotten. Such memory gaps can be filled with fantasies, leading to delusional obsessions. Extreme mood swings, inappropriate behavior of an elderly person, lack of any analysis and forecasting of events. The patient may pour his hot coffee on the floor and bring a mug with nothing in it to his mouth, while expecting a cold drink. There may be extreme manifestations of instincts: from complete loss of appetite to overeating with the inability to satisfy the feeling of hunger. Sexual instincts also undergo changes.
So how can you help a patient diagnosed with senile dementia? This can only be done through patient care and care. It is currently impossible to cure this disease.
Alzheimer's disease. This mental disorder progresses gradually.
It is necessary to be as attentive as possible to the loss of an elderly person’s ability to remember distant and not so distant events. The appearance of absent-mindedness, forgetfulness, confusion in matters, past and present, are the first signs of a mental disorder. There are disturbances in the sequence of events, and difficulties arise with orientation in time. The patient changes for the worse: he exhibits selfish behavior and does not tolerate objections. Prolonged depression, delusional states, and various hallucinations can also be symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. As Alzheimer's disease progresses, the symptoms of dementia become clearer and more noticeable. An elderly patient is poorly oriented in time, places, events, confuses names, may not remember his address, and cannot determine his location. Patients with this disease are unable to say how old they are and are lost in the main moments of their own lives. There may often be a loss of real sense of time: they may see and speak like a child, and be confident that their deceased loved ones are still alive and well. Household skills are lost: patients lose the ability to use household appliances, cannot dress themselves and perform simple hygiene procedures. Clear actions are replaced by chaotic wandering and collecting unnecessary things. The patient may have difficulty counting and forget letters and words. Speech changes radically. At first, vocabulary becomes scarce. Real actions in dialogue with an elderly patient can be replaced by fantasies. As the disease progresses, speech loses all meaning and consists only of simple words and fragments of phrases. In advanced stages of the disease, older people completely lose the ability to live without outside help , physical activity degrades or is completely suspended, and meaningful speech is lost.
The main problem is that the first symptoms of mental disorders and illnesses (memory abnormalities, changes in behavior and character) are not observed by a doctor. Timely treatment in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease will be most effective. In modern medicine, there are a number of drugs that can significantly alleviate this mental disorder.
Vascular dementia. The causes of this mental disorder may be pathologies in the blood vessels of the brain, leading to impairment of cognitive functions. Also, this disease develops very rapidly. The ability to adapt socially suffers greatly. The symptoms of this disease are very similar to the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease, however, they are less severe. Gaps in memory, confusion in time and space, can have clear manifestations and change throughout the day. It is necessary to distinguish between these diseases as early as possible, because the methods of treating them are radically different.
Pick's disease. Caused by damage to parts of the brain, it leads to personality disintegration. At the same time, the patient’s intellectual abilities are not lost; he is still able to count, assimilate information, and remember dates and events. Speech also does not suffer in any way, the patient uses the previously accumulated vocabulary and can speak well. So what was hit? An elderly person begins to experience anxiety, he is constantly under stress, irritability appears, and he loses the ability to predict the consequences of his actions.
Therapy and development of the disease for this mental illness depend on the identification of the affected part of the brain. There is no cure for this disease. When using pharmacological drugs, you can only slow down the process.
Parkinson's disease. Manifestations of the disease may be noticed by others when all timely treatment deadlines are missed. The disease can develop for several years without showing itself in any way. Almost everyone experiences trembling of the limbs, but if you add to this anemia for a long period, then it is better for an elderly patient to see a doctor. If you do not seek professional help, you may develop difficulties with coordination of movements, slower reactions, and motor activity becomes noticeably slower. Sudden surges in blood pressure can cause fainting and lead to severe periods of depression. Parkinson's disease usually does not affect the intellectual abilities of an elderly patient. But this can be a negative factor. Old people who observe and accept the progression of the disease, their own helplessness, and the futility of treatment can fall into severe depression. At the same time, the quality of life of the elderly patient will gradually deteriorate, but this is not the main thing. With the modern development of pharmacology, patients live quite a long time, but the main danger lies in poorly coordinated movements, which leads to falls, injuries, fractures and difficulties with swallowing food. Caring for and caring for an elderly patient must be done extremely delicately so as not to complicate depression. To ensure that your actions in caring for an elderly relative do not cause him to feel guilty, it is worth looking for opportunities to treat him in a specialized boarding house for the elderly.
Description and classification
The disease usually develops in people over 50–60 years of age and is more often diagnosed in women. Depending on the clinical characteristics, several types of senile psychosis are distinguished:
- late (or involutional) depression;
- paranoids of late age;
- senile hallucinosis.
How to prevent mental disorders in older people?
Aging involves the emergence of many diseases that cannot be protected against at a young age. However, there are methods to prevent involutional disorders. Organic personality disorders cannot be prevented, but there are methods for prevention. To maintain mental clarity for as long as possible, you need to be aware of the main causes of possible stress. Therefore it is recommended:
- Seek communication with new people, get involved in a variety of hobbies, and do physical exercise.
- Eliminate any loneliness.
- Seek support in case of loss of loved ones.
- Think about retirement in advance, look for like-minded people, think about employment or hobbies.
- Maintain a high standard of living.
The main method of preventing mental disorders is interaction with peers who have found order in life after retirement. Health groups, dance clubs, third age institutes - there are a huge number of places that will help you cope with loneliness. Grown-up children should also pay their attention to their elderly parents (in person or by telephone) and constantly provide all possible support.
The most severe stress condition is loneliness. The passage of time for an elderly lonely person is suspended. Observing the vibrant lives of other people, he realizes that he has fallen out of this rhythm. When an elderly person observes the indifference of people towards him, especially relatives, he begins to feel useless, which leads to complex emotional experiences and anxiety. This can trigger the progression of mental disorders. Oddly enough, old people living with their relatives are much more likely to feel useless and useless. How is this possible? It is not enough to just move an elderly relative into your home, you need to find time every day to listen to him, encourage him and make him feel important to the family. You can ask him for some simple help with everyday life, with children, etc., do not refuse if he offers it himself.