Hydrocephalus on MRI Magnetic resonance imaging is actively used in neurology and neurosurgery. The method is used to visualize the brain. Layer-by-layer images fully reflect cerebral structures, allow you to identify pathological changes in any area and collect detailed information about deviations.
MRI is of great importance for the early diagnosis of brain diseases. In the images, the radiologist sees signs of life-threatening conditions, such as dropsy. Hydrocephalus of the brain on MRI manifests itself with characteristic symptoms, even at the initial stages of development. An experienced diagnostician will quickly identify the pathology, establish the form, and the clinician will select the correct treatment tactics.
What types of external hydrocephalus of the brain are there?
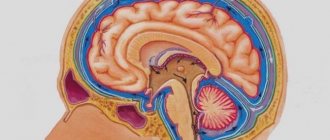
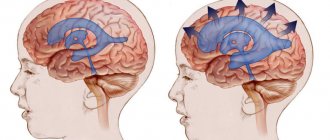
External hydrocephalus of the brain refers to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal or cerebrospinal fluid) outside the cerebral hemispheres - in the subarachnoid space. Due to the large accumulation of fluid, the subarachnoid fissures widen, which causes increased pressure on the cerebral cortex and the resulting negative consequences.
The nature and level of complexity of the disease directly depend on the specific type of dropsy. Several criteria are used for classification. The most common ones are:
- intensity of manifestation (pronounced - accumulation of a large amount of cerebrospinal fluid, causing neurological symptoms; moderate - minimal amount of fluid, no signs);
- degree of impact on brain structures (compensated - cerebrospinal fluid does not affect the brain; decompensated - there is a deterioration in the functioning of the nervous system and brain);
- causes of occurrence (replacement - more often diagnosed in older people and is accompanied by the death of brain cells; acquired - occurs due to the spread of infections and mechanical traumatic brain injuries);
- nature of the course (chronic form - a gradual increase in neurological disorders; acute form - a sharp deterioration in the patient’s well-being).
Employees of the Department of Neurosurgery of the City Clinical Hospital named after. Eramishantsev will first determine the type of external hydrocephalus and only then begin treatment. Particular attention is paid to diagnostic data and a thorough study of the symptoms of the identified disease.
Development mechanism
With external hydrocephalus, cerebrospinal fluid accumulates outside the cerebral hemispheres, in the subarachnoid spaces. Excessive amounts of cerebrospinal fluid compress the cerebral cortex. External non-occlusive hydrocephalus of the brain occurs as a result of hypersecretion or malabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid. Closed (occlusive) hydrocephalus is a form of the disease in which the exit of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles is blocked by a tumor or adhesions.
Internal hydrocephalus can be congenital or acquired. Congenital hydrocephalus develops during intrauterine exposure to the fetus, acquired hydrocephalus develops during life. Mixed hydrocephalus is a separate form of the disease in which cerebrospinal fluid accumulates both in the ventricles and under the meninges.
Make an appointment
Symptoms of external hydrocephalus
The clinical picture in each specific case will be different, and the nature of the manifestation of the disease depends on the severity of the pathological process and the state of the central nervous system. Common symptoms are frequent headaches, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, and weakness. By the way, pain is more localized in the frontoparietal region and in the area of the eyeballs. A person with dropsy experiences pain in the first half of the day, with sudden movements, coughing, sneezing, or severe physical exertion.
Symptoms may vary depending on the severity of the disease. Scientists distinguish 3 stages, and each has its own characteristics:
Mild external hydrocephalus. With a minimal amount of dropsy, the human body will try on its own to cope with such a problem as impaired circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid. In this case, you will feel a slight malaise, periodic dizziness, short-term darkening in the eyes, and a tolerable headache.
The middle stage of development of the disease. At this stage of the spread of the disease, symptoms appear intensely and are more pronounced. Due to an increase in intracranial pressure, severe headaches occur during physical activity, swelling of the optic nerve and facial tissues, increased fatigue, nervousness, depression, and surges in blood pressure.
Severe form of the disease. Signs of pathology in severe forms of external hydrocephalus are reduced to convulsive seizures, frequent fainting, a state of apathy, loss of intellectual abilities, memory loss and inability to care for oneself. Progressive dropsy can even lead to death, so there is no need to delay going to the doctor. It is better to do this at the first suspicion and a slight deterioration in health.
With chronic accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid, symptoms such as unsteady gait, paralysis of the upper and lower extremities, urinary incontinence, nighttime insomnia and daytime sleepiness, depressed mood, and a complex of psychoneurological disorders can be observed.
Symptoms and signs of hydrocephalus
External hydrocephalus is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- a disproportionately large skull in a child, divergence of sutures, enlargement of the fontanel;
- nausea and vomiting;
- intense headache;
- decreased intelligence, memory, hearing, vision;
- drowsiness;
- speech disorders.
Moderate external hydrocephalus appears gradually, and its symptoms are often mild. Only as the disease progresses does replacement hydrocephalus occur with severe consequences:
- mental disorders;
- violation of motor functions, balance;
- disturbance of mental activity.
Hydrocephalus in adults is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- intense, untreatable headache;
- vestibular disorders;
- loss of visual fields;
- paralysis of limbs;
- lack of skin sensitivity.
Internal hydrocephalus mainly affects the structures of the cerebellum: gait is disrupted, coordination of movements is lost, handwriting becomes uneven and large.
Symptoms of hydrocephalus require urgent medical attention, as this disease can cause irreversible consequences.
Why does dropsy of the brain occur?
In adult patients, acquired hydrocephalus is often encountered, which develops either due to any mechanical damage to the head, or as a result of the development of pathological processes. Why does cerebrospinal fluid accumulate outside the cerebral hemispheres? The explanation is simple: brain structures are disrupted, adhesions appear in the veins, arachnoid villi are destroyed, and as a result, the cerebrospinal fluid does not circulate as it should.
If we delve deeper into the question of the causes of such a disease as external dropsy of the brain, we can identify some factors:
- infectious diseases (tuberculosis, meningitis, encephalitis);
- post-stroke condition, development of sepsis, extensive hemorrhage;
- concussion, head or cervical spine injury;
- malignant tumors that develop in the stem region.
Frequent intoxication of the body leads to the appearance of external hydrocephalus. For example, alcohol abuse, which damages neurons and leads to tissue death. Those patients who suffer from metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis, encephalopathy, and atherosclerosis are also at risk. Another reason that deserves due attention is irreversible age-related changes that cause aging of blood vessels and brain tissue.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery
Types of hydrocephalus
Depending on the cause of development, hydrocele of the brain can be congenital or acquired. Based on the distribution of cerebrospinal fluid, pathology is classified into types:
- external;
- internal (mono-, bi-, tri- or tetraventricular);
- mixed.
Based on the mechanism of development, hydrocele of the brain occurs:
- open (communicating);
- closed (occlusal).
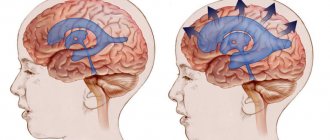
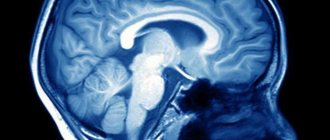
Internal triventricular occlusive hydrocephalus on MRI in the frontal and sagittal planes: the left image shows a giant cystic-solid formation, which was the cause of obstruction of the cerebrospinal fluid ducts at the level of the aqueduct of Sylvius
Diagnosis of external hydrocephalus in adult patients
Studying the symptoms and visual examination of the patient is not a sufficient condition for determining external hydrocephalus of the brain. Indirect signs, of course, are important, but you can’t do this without professional diagnostics. Today, 6 methods for detecting dropsy are used:
- Ultrasound examination (US) of the neck and head to assess the condition of blood vessels;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) helps to identify changes in soft tissues and most accurately determine the type of hydrocephalus and the stage of development of the pathology;
- computed tomography (CT) is intended to determine the degree of damage to brain tissue, the size of subarachnoid fissures, and the presence of neoplasms;
- X-rays with the introduction of a contrast agent are aimed at identifying disturbances in the outflow of venous blood and damage to the vascular bed;
- a spinal puncture is prescribed if there is a suspicion of the development of dropsy after encephalitis or meningitis and you need to find out what level of cerebrospinal fluid pressure;
- ophthalmological examination - an opportunity to determine whether the patient has swelling of the optic nerve and atrophy of the tissues of the ocular apparatus.
IMPORTANT! If the diagnosis of “chronic external hydrocephalus of the brain” is confirmed, it is advisable to carry out an additional diagnostic examination after 6 months. The intensity of further visits to the doctor depends on the data obtained and is determined individually.
How does hydrocephalus manifest?
The clinical picture of hydrocephalus depends on the age of the patient:
- Cranial sutures in children under two years of age are pliable and easily diverge under internal pressure, and the course of hydrocephalus is accompanied by progressive macrocrania - an increase in cranial size. Disproportions of the forehead with overhanging eyebrows, stagnant veins of the scalp and a bulging fontanel are observed. Hydrocephalus in infants is often accompanied by atrophy of the optic nerves, muscle hypertonicity, and strabismus.
- In children after two years of age, hydrocephalus occurs with symptoms such as frequent vomiting, morning headaches, congestion in the fundus, muscle weakness and fatigue. Possible delays in growth and development, drowsiness, sluggishness, obesity, and water-salt imbalance. In addition, there is a disorder of motor coordination and involuntary movements due to contraction of the muscles of the limbs, trunk or face.
- Hydrocephalus in adults is manifested by congestion of the optic discs, displacement of brain structures along with increased intracranial pressure, stretching of the dura mater at the base of the skull and the walls of blood vessels.
Treatment of external hydrocele in adults
Treatment methods are selected at a consultation with a neurosurgeon or neurologist after diagnosing the disease. Intervention must be timely, otherwise the risk of various neurological complications increases. It is important to take into account both the type of pathology and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
In the Department of Neurosurgery of the City Clinical Hospital named after. Eramishantsev practice only effective methods of treating external hydrocele of the brain. Methods are divided into two large groups: conservative (medicinal) and surgical (operative), each of which has its own characteristics and advantages.
CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT
Drug treatment is only relevant at a mild stage of the disease. Special medications accelerate the outflow of fluid from the brain, increase urination, relieve inflammation and swelling, strengthen blood vessels, and normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system. To combat severe headaches, your doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Common groups of medications are vascular, neurotropic, venotonics, diuretics. But in acute illness they will be ineffective. Mixed hydrocephalus is poorly corrected. In this case, conservative treatment will not get rid of the disease, but will only restore or improve the functioning of individual systems and functions of the human body. Often surgical intervention is not possible.
SURGERY
If acute external dropsy is diagnosed, in most cases drainage of the cerebral ventricles is prescribed. The main technologies are endoscopy and open surgery.
In the first case, we are talking about manipulations that are characterized by minimal trauma, a very low risk of complications, and fairly rapid postoperative recovery. Endoscopy methods allow, with minor intervention, not only to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid, but also to eliminate vein defects, hematomas, and blood clots.
Currently, open surgery is chosen only in exceptional cases. Why? It is difficult to imagine performing open surgery without craniotomy. And trepanation always means increased risks and a long postoperative recovery period.
Another way to get rid of external dropsy is bypass surgery. Doctors use a system of valves and silicone tubes to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid from the skull. The fluid is redirected to other cavities of the body, in particular to the abdominal cavity, right atrium, and superior vena cava. According to statistics, the effectiveness of this technique is 85%.
Is it possible to protect against the occurrence of external hydrocephalus of the brain? This is a very difficult question. But, if you completely give up bad habits and avoid traumatic brain injuries, there is a high probability that trouble will bypass you. Another important point is the timely and professional treatment of such serious diseases as encephalitis, polio, meningitis, as well as other infectious diseases.
Features of drug therapy
Treatment and diagnosis of hydrocephalus is the responsibility of a neurosurgeon. Drugs are used in therapy exclusively at an early stage of the disease or as an adjunct to surgery. Their purpose serves two purposes: removing excess fluid from the body and improving blood supply and nutrition of brain structures.
| Drug group | Drugs |
| Diuretics | Diacarb, Furosemide, Mannitol |
| Means for correcting potassium levels | Asparkam |
| Drugs to improve nutrition of brain tissue | Actovegin, Cavinton |
| Vasoactive drugs | Magnesium sulfate, Glivenol |
| Painkillers | Nimesil, Ketoprofen |
| Hormone replacement drugs | Prednisolone, Betamethasone |
| Barbiturates | Barbiturates |
If necessary, the doctor prescribes sedatives to eliminate the patient’s psycho-emotional stress. Additionally, it is recommended to take vitamin complexes. Specific medications, their dosage and duration of use are determined by the attending physician.
Small nodules of a pale pink hue can spread throughout the body or be localized in one area. Curettage, laser therapy, and medications are used for treatment. Read more in the article: “ointments for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum.”
Use of diuretics
Advertising:
The main drugs used for hydrocephalus are diuretics. They promote the removal of urine from the body and reduce the amount of fluid in internal organs and tissues. As a result, intracranial pressure decreases - one of the signs of the disease. In the case of cerebral hydrops, diuretics of three subgroups are used: loop, osmotic and carbonhydrase inhibitors.
Diuretics are prescribed not as the main medicine, but as a symptomatic remedy.
This means that they cannot eliminate the cause of the disease; they can only temporarily alleviate the patient’s condition. For hydrocephalus, long-term use of diuretics is prohibited. This is due to the fact that useful substances and microelements leave the body along with the fluid. Subsequently, the deficit of the latter is quite difficult to restore. In addition, when using potent medications, severe dehydration occurs, and excess cerebrospinal fluid does not always drain away as quickly.
Review of effective diuretics
Loop diuretics are considered the most fast-acting and effective. Their action is based on slowing the reabsorption of sodium ions and inhibiting chlorides. Most often, patients are prescribed Furosemide in tablets, injections for intramuscular or intravenous administration. The dosage is selected individually.
To enhance the therapeutic effect, loop diuretics must be combined with Diacarb. It is a carbonhydrase inhibitor. The regimen for taking it is also determined individually, taking into account the clinical picture, but the daily dosage cannot exceed 750 mg. Duration of use is 5 days. If this period is exceeded, the likelihood of metabolic acidosis increases.
The group of osmotic diuretics is represented by Mannitol and Triampur Compositum. The latter is a combination drug that includes a diuretic and antihypertensive component. Take it orally after meals with a sufficient amount of liquid. The maximum daily dosage is 4 tablets.
Medicines for correcting potassium levels
Treatment of hydrocephalus is impossible to imagine without the use of diuretics. However, such drugs remove from the body not only excess cerebrospinal fluid, but also many useful substances and microelements. To compensate for the deficiency of the latter, the course of treatment for hydrocephalus is always supplemented with Asparkam.
This drug is used to correct potassium and magnesium levels. It is also able to regulate metabolic processes. The drug is available in the form of tablets and solution for injection. The doctor selects its dosage individually. The course of treatment is usually at least a month. If necessary, they are repeated after a short break of 2-3 weeks.
Asparkam should be taken with caution. This drug is not recommended for patients with a history of impaired renal function, a high likelihood of edema, or metabolic acidosis of the blood. In addition, it should be taken strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor to avoid overdose. It manifests itself as bradycardia, decreased blood pressure, and respiratory paralysis.
Nootropics
Nootropics are neurometabolic stimulants. They have a beneficial effect on higher mental functions. However, it is necessary to carefully select the dosage.
One of the representatives of this group is the drug Cortexin. It has a pronounced neuroprotective, antioxidant and nootropic effect. The medication helps to normalize the ratio of amino acids that perform mediator functions of inhibitory and excitatory types of action. Reduces the level of convulsive brain activity. The duration of treatment is no more than 10 days.
Advertising:
Quite often doctors prescribe Mexidol. This is a powerful antioxidant and nootropic agent. It helps increase the body's resistance to aggressive factors and pathological conditions caused by oxygen deficiency. The drug should not be used in patients with liver/renal impairment. It is usually prescribed intravenously for 10-14 days, and then intramuscularly.
Correctors of cerebral circulation
One of the stages of drug treatment for hydrocephalus is the use of drugs to improve the nutrition of brain tissue. These are Cavinton and Actovegin. They have a dilating effect on blood vessels, increasing blood circulation and improving the supply of oxygen to tissues.
Cavinton is taken in long courses. Immediately after taking it, a moderate decrease in blood pressure may occur. It has a relaxing effect on smooth muscles, which leads to vasodilation. Cavinton also enhances the exchange of norepinephrine and serotonin in brain tissue. It is prescribed with caution due to the large number of side effects. Among them, it is necessary to highlight tachycardia, changes in ECG indicators and extrasystole.
Actovegin increases glucose consumption in cells and improves the process of oxygen utilization. This helps to activate energy processes in brain structures, affecting their functional metabolism. Treatment of hydrocephalus begins with the use of high doses of the drug, gradually reducing them.
Vasoactive drugs
Vasoactive medications are used when it is necessary to simultaneously improve blood supply to the brain, dilate blood vessels and lower intracranial pressure. They quickly relieve unpleasant symptoms such as headaches, problems with coordination of movements, etc. Magnesium sulfate is most often used in neurology. The drug acts as an antispasmodic, dilates blood vessels and has a diuretic effect. In addition, it normalizes heart rhythm.
Among other medications in this group, Nicergoline, Sermion, and Glivenol are characterized by a positive therapeutic effect. As a result of their intake, there is an improvement in blood circulation in the brain, intracranial pressure quickly normalizes, and painful symptoms are relieved. However, the use of vasoactive drugs is strictly controlled by doctors. Their use is strictly contraindicated in cases of low blood pressure, bradycardia and depressed breathing.
Medicines for headaches
Headache is a common accompaniment of hydrocephalus. It significantly worsens the quality of life of patients. For pain relief, neurologists suggest using the following drugs:
Advertising:
- Analgin
. This is an inexpensive and universal drug. Its active substances block pain impulses in the central nervous system. Tablets are usually taken 2-3 times a day. - Aspirin
. The medication has a pronounced analgesic effect. In addition, it acts as an antipyretic and relieves inflammation. - Paracetamol
. The drug belongs to the first group of drugs of choice for severe pain syndrome. It is also effective in case of high temperature. - Ibuprofen
. This is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Has a high toxicological threshold. It belongs to the first group of drugs of choice for various pains and inflammations.
The listed drugs can be replaced with analogues (Nurofen, Citramon, Pentalgin). With hydrocephalus, headaches are usually regular, so patients try to relieve them in various ways. When using analgesic medications, it is important to avoid overdose.
Glucocorticoids and barbiturates
Glucocorticosteroid drugs remove toxins from the body. In addition, for hydrocephalus they are indicated to relieve swelling of the brain. Effectively reduce the formation of cerebrospinal fluid due to its effect on the choroid plexus.
Typically, glucocorticoids are prescribed to critically ill patients as immunosuppressants.
Depending on the situation, the doctor’s choice may fall on Dexamethasone or Prednisolone. The minimum dosage per day of the latter is 20-30 mg. For long-term or palliative therapy, it is selected at the rate of 1-2 mg of the drug per kg of patient weight. Long-term use of glucocorticoids can provoke iatrogenic hypercortisolism.
Barbiturates are characterized by a sedative effect. They successfully eliminate the negative influence of external factors on the central nervous system. Phenobarbital is most often used in the treatment of hydrocephalus. Take it 30-50 mg three times a day. Phenobarbital is used as a sleeping pill and a sedative. The circulation of this drug is currently limited; it is prohibited for import into some countries (USA, UAE, Lithuania).
Treatment of hydrocephalus
In the case of congenital hydrocephalus, treatment is carried out mainly through surgery. Its goal is to eliminate the cause that impedes the outflow of fluid. Surgical treatment is also used in the presence of a tumor process in the brain, intracranial hematoma, or abscess. If the cause cannot be eliminated, then shunting is performed (a system for cerebrospinal fluid drainage is applied to another area where nothing will interfere with its absorption).
For acquired hydrocephalus, treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of its occurrence. Diuretics are prescribed as drugs to alleviate the patient's condition.
Sources:
- Bogadelnik I.V. Hydrocephalus in children / I.V. Almshouse [and others] // Child’s health. — 2011.
- Zamyshlyaev P.S. Hydrocephalic syndrome. Pathomorphology. Prevalence in the Republic of Mordovia / P.S. Zamyshlyaev [and others] // Pulse. - 2015. - T. 17. - No. 2. - P. 65-67.
Disease prevention
The list of measures that can prevent the development of pathology includes:
- pregnancy planning;
- prevention of birth injuries;
- giving up bad habits before conceiving a baby and during pregnancy;
- vaccine prevention of infectious diseases of the brain (meningitis, encephalitis);
- early perinatal diagnosis;
- regular monitoring of children at risk by a pediatrician and neurologist;
- timely completion of preventive examinations up to a year;
- providing the child with safe living conditions to prevent household traumatic brain injuries.
Parents need to closely monitor the development and condition of young children, promptly contacting doctors in case of infectious diseases, falls and injuries affecting the head and neck area.
Specialists at the SM-Doctor clinic will conduct a detailed diagnosis if hydrocephalus is suspected, plan treatment and monitor the child throughout therapy and rehabilitation.
Reasons for the development of hydrocephalus in children
Factors that can lead to the internal form of the disease are:
- anomalies and malformations of the fetus during the period of intrauterine formation, associated with infections, injuries, and the influence of bad habits of the mother;
- various birth injuries;
- prematurity and premature birth with low body weight.
The causes of acquired hydrocephalus in a child can be infectious diseases of the brain and its structures: meningitis, malignant and benign neoplasms, encephalitis. In some cases, the starting mechanism is traumatic brain injuries and bruises resulting from falls, blows, accidents and other injuries.