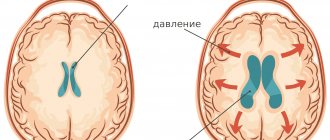
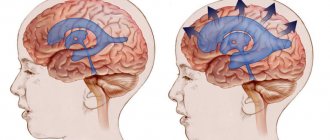
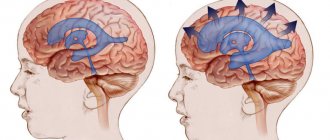
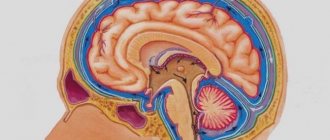
Hydrocephalus in adults can be an independent disease or a manifestation of pathology of other organs and systems. In patients with hydrocephalus, the process of excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cerebrospinal fluid spaces, caused by disturbances in its production, circulation or absorption, is actively progressing. It is manifested by an enlargement of the ventricles of the brain, a decrease in the density of the brain matter due to its saturation with cerebrospinal fluid and a narrowing of the subarachnoid spaces. At the Yusupov Hospital, neurologists treat hydrocephalus with the most effective drugs that have a minimal range of side effects. Patients are examined using modern research methods performed by experienced specialists from the neurology clinic.
Symptoms
Mixed atrophic hydrocephalus of the brain is an acquired form of the disease. The pathology is characterized by enlargement of the cerebral ventricles and subarachnoid space in conditions of progressive brain atrophy.
Based on the rate of progression of the disease, the following are distinguished:
- acute hydrocephalus (no more than 3 days pass from the first symptoms of the disease to severe decompensation);
- subacute progressive hydrocephalus (develops within a month from the onset of the disease);
- chronic hydrocephalus (forms within 3 weeks to 6 months).
Based on the level of cerebrospinal fluid pressure, hypertensive, normotensive and hypotensive replacement hydrocephalus are distinguished. Mixed asymmetric hydrocephalus is characterized by an enlargement of one of the ventricles of the brain. Mixed hydrocephalus of a replacement nature occurs against the background of traumatic brain injury, arterial hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis, instability of the cervical vertebrae, and alcoholism.
A distinctive feature of mixed hydrocephalus is the replacement of the vacated brain space with cerebrospinal fluid. Minor mixed hydrocephalus contributes to a decrease in cerebral blood flow. This leads to inhibition of neurological functions. If replacement hydrocephalus is accompanied by an increase in the volume of the cerebral ventricles, then a decrease in intracranial pressure is detected in patients, in other cases it will be increased.
Moderate mixed asymmetric hydrocephalus of the brain may be asymptomatic for a long period of time. Signs of ventricular asymmetry are determined during the examination of patients. Patients with replacement hydrocephalus complain of severe headache in the morning after waking up, caused by a long-lasting horizontal position of the body, nausea, and vomiting. They experience increased blood pressure, increased heart rate, and arrhythmia. The following signs of the disease are also determined:
- insomnia and sleep quality disturbances;
- drowsiness and lethargy;
- increased fatigue;
- irritability;
- decreased hearing and visual acuity;
- unsteadiness of gait, loss of coordination of movements.
In the later stages of the disease, symptoms of dementia appear: absent-mindedness, memory loss, impaired short-term memory, and inability to think logically. A severe complication of replacement hydrocephalus is epileptic syndrome. The patient develops dementia and may fall into a coma.
General information
The medical term “hydrocephalus” refers to a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs in the brain.
On this topic
How is shunting performed for cerebral hydrocephalus?
- Natalia Sergeevna Pershina
- March 26, 2021
Normally, it freely penetrates into and out of the brain, ensuring normal brain activity. But when exposed to certain factors, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted and it begins to accumulate in the cavities of the brain.
With a mixed type of hydrocephalus, the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid occurs inside and outside the brain, as well as in its ventricles and subarachnoid space. Since the development of this disease affects almost all parts of the brain, the pathology progresses very quickly and is accompanied by a pronounced symptomatic picture.
The main point in the treatment of mixed hydrocephalus is timely diagnosis of the disease. Since only in the initial stages of its development it is possible not only to cure the pathology, but also to prevent the occurrence of serious complications.
Diagnostics
At the Yusupov Hospital, computer and magnetic resonance therapy are performed immediately after the patient’s admission to the neurology clinic. To assess the stage of hydrocephalus and determine indications for surgical intervention, doctors calculate ventriculo-cranial coefficients, which show the degree of expansion of the ventricular system. Computed tomography makes it possible to clarify the presence and extent of ischemic brain damage in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage.
To predict the outcome of surgical treatment of replacement hydrocephalus, all patients undergo a tap-test. Its essence is that by removing at least 40 ml of cerebrospinal fluid during lumbar puncture in patients suffering from chronic hydrocephalus, their health status improves for a short time. If the test is positive, it is more likely that the patient will recover after surgery.
At the Yusupov Hospital, neurologists conduct a comprehensive examination of patients with replacement hydrocephalus. It includes ultrasound examination of the brain, craniography (x-ray of the skull), and fundus ophthalmoscopy. Patients are consulted by an ophthalmologist, cardiologist, and neurosurgeon.
If mixed replacement hydrocephalus occurs in a moderate form with minimal symptoms, patients are examined every 6 months for timely detection of negative dynamics of the disease. If there are pronounced signs of increased intracranial pressure, treatment is started immediately. In the case of severe replacement hydrocephalus, at a meeting of the expert council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category, tactics for managing the patient with hydrocephalus are developed.
Types of disease
Depending on the cause of the disease and the pathological processes occurring in the brain, hydrocephalus is divided into:
- occlusal;
- hypersecretory;
- communicating.
Today, mixed type hydrocephalus is classified as a general pathological process in the brain, in which atrophy of its tissues is observed with a subsequent decrease in their volume. Due to the presence of such processes, the consequences of the development of mixed hydrocephalus can be very different.
In adults, this pathology is observed extremely rarely, but is diagnosed in almost every newborn child.
In most cases, it goes away on its own, without posing any threat to the health and life of the little patient. But in the presence of certain factors affecting the child’s body, hydrocephalus progresses, provoking the death of brain tissue.
Depending on the course of the disease, it is also divided into acute and chronic forms. However, there is another type of hydrocephalus, in which there is a combination of acute and chronic stages of the disease. According to scientists, this type of hydrocephalus is the most dangerous. But the only reassurance is that it occurs in only 1% of patients suffering from this pathology.
Consequences
Lack of therapy when mixed hydrocephalus of the brain is detected leads to the development of a number of complications. Among them are:
- Impaired quality of hearing and vision. In severe cases, their complete loss may occur.
- Dementia.
- Memory loss.
- Violation of certain brain functions.
- Death.
With the mixed form of hydrocephalus, the general condition gradually deteriorates. Symptoms become more pronounced. After a few months, the patient may begin to lose certain self-care skills. There is also a violation of memory and attention. It becomes difficult for a person to answer questions, even the simplest ones, and to correctly express his thoughts. That is why symptoms that arise should not be ignored, especially in children.
Childhood hydrocephalus causes physical, psycho-emotional and mental development. It is possible to cure the pathology, but only in the early stages of its development. But it is impossible to completely eliminate the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain.
Hydrocephalus is not a rare disease that poses a danger to the life of children and adults. There are many reasons for its appearance, as well as symptoms. Treatment should be carried out in the early stages, since only complex and timely therapy will help avoid consequences, including death, and significantly improve the condition.
Causes
The main reason for the development of mixed hydrocephalus is excessive production of cerebrospinal fluid and disruption of its movement. In newborn children, these processes are easily provoked by various infections that affected them during the period of intrauterine development.
In addition, in infants, the development of this pathology can occur against the background of congenital obstruction of the excretory canaliculi, due to which cerebrospinal fluid easily penetrates into the brain, but cannot be removed from it.
But in infants, hydrocephalus can be not only congenital, but also acquired. In the latter case, an important role is played by birth injuries, neurosurgical interventions, infections of the meninges, cancer, and bleeding in the skull.
On this topic
7 facts about mild hydrocephalus of the brain
- Natalia Sergeevna Pershina
- March 26, 2021
The development of mixed hydrocephalus in an adult is also often provoked by infections. And most often these are viruses and bacteria. An important role is played by intoxication of the body and resulting brain injuries. All these conditions can also cause blockage of the excretory ducts and the formation of cerebral dropsy.
Mixed replacement hydrocephalus is quite often observed in older people. And the reason for this is:
- concussions ;
- inadequate treatment of hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- uncontrolled use of certain drugs that lead to weakening of muscle tone in the cervical region;
- alcohol abuse .
This pathology can also be a consequence of diseases such as meningitis, pneumonia, etc. And, according to doctors, there are many reasons for the development of mixed hydrocephalus. But all of them have not yet been identified, since literally every year when examining a patient, several new causes of the development of hydrocephalus are discovered in both adults and children.
And in order to cure this disease, it is necessary to accurately determine the root cause and eliminate it. Without this, the therapy will not produce any results. And in order to accurately determine the factor that provoked the occurrence of dropsy in the brain, the patient needs to undergo a comprehensive examination.
Treatment
When mixed hydrocephalus is established at an early stage of its development, drug treatment is used. Drugs are used to reduce intracranial pressure. Diuretics are also prescribed.
All medications should be prescribed only by the attending physician, who will determine the duration of use and dosage in accordance with the stage of development of the disease.
When mixed hydrocephalus is diagnosed, other treatment methods are also used. The course of therapy may include special therapeutic massage, physiotherapeutic treatment methods, such as UHF or electrophoresis.
Surgical intervention
Depending on the severity of the pathology, surgical intervention may be prescribed. Today, bypass surgery, drainage installation and endoscopy are used. Bypass surgery involves the installation of special shunts that will facilitate the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. But the procedure is traumatic and can cause infection of the membranes of the brain. It is used in rare cases when other methods cannot be used.
Drainage is used for high intracranial pressure. Endoscopic surgery is aimed at creating holes in the ventricles of the brain. It is considered the most gentle way to eliminate large amounts of fluid in the skull. The method of performing the operation is selected by the attending physician.
Treatment of atrophic hydrocephalus
Conservative therapy for moderate mixed hydrocephalus of the brain is aimed at reducing intracranial pressure. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe diuretics to patients that reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid (diacarb, mannitol, mannitol and diacarb in combination with lasix or furosemide), drugs that improve brain trophism (cavinton, pantogam, actovegin, cerebrolysin), vitamin and mineral complexes. With the progression of hydrocephalus symptoms, the only treatment method to improve the quality of life of patients is surgery. If there is a formation that impedes the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid (tumor, intracranial hematoma), it is removed, and the adhesions are separated during surgery.
To create additional outflow pathways for mixed non-occlusive hydrocephalus, neurosurgeons perform shunt operations:
- cystoperitoneal shunting;
- ventriculoperitoneal shunt;
- lumboperitoneal shunt;
- external ventricular drainage.
Shunts are replaced as needed, as they can become clogged, rejected, and become small. An alternative treatment for obstructive hydrocephalus in selected patients is endoscopic ventriculostomy of the third ventricle. The operation is performed using a neuroendoscope equipped with a miniature television camera.
To restore neurological functions, rehabilitation specialists at the Yusupov Hospital use innovative techniques of massage and physical therapy. Selective acupressure massage of the arms and legs, torso, scalp and face, paravertebral points, back and pelvis increases muscle tone. Therapeutic physical culture is aimed at regulating muscle tone, developing normal reflex motor activity, improving blood circulation and metabolism, and increasing the body's reactivity.
Patients undergo a course of acupuncture and manual therapy. They help reduce muscle spasms, improve blood flow, and temporarily relieve pain. Psychologists work with patients who have developed cognitive impairment. Psychotherapists help them restore self-care skills and carry out social adaptation.
Make an appointment with a neurologist by calling the Yusupov Hospital. Timely treatment of moderate mixed hydrocephalus of the brain can stop the progression of the disease. After surgery, patients can return to their normal lifestyle.
Methods
In addition, hydrocephalus is eliminated by the following methods:
- Palliative intervention. It is carried out through puncture if hydrocephalus is characterized as open.
- Radical surgery. To eliminate excess fluid, special shunts are installed in the spinal canals. Internal drainage allows you to remove cerebrospinal fluid into an adjacent organ or system.
Most often, operations to eliminate hydrocephalus go well and allow you to get rid of the problem. If dropsy is caused by a tumor in the brain, surgical removal can prolong the patient's life by several years.
What is mixed hydrocephalus
This term is used in medicine to define a human condition when fluid (CSF) accumulates in the brain. Its quantity may vary.
Hydrocephalus is a disease in which, for certain reasons, cerebrospinal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid, penetrating into the organ, does not exit and begins to accumulate.
There are many forms of the disease. But the most complex and difficult to treat is mixed. It is characterized by a violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid both outside and inside the organ.
Mixed hydrocephalus is accompanied by pronounced symptoms, since the pathological process affects all parts of the brain, causing a disruption in their functioning.
The success of treatment depends on the timeliness of diagnosis, since in the early stages of the development of pathology there is a chance to completely cure it. Also, timely therapy can eliminate a number of dangerous diseases.
Causes
Mixed hydrocephalus of the brain develops for several reasons. Previously it was believed that the disease was specific to children. And today, pathology is most often diagnosed in newborns in the first six months of life or during intrauterine development.
Mixed hydrocephalus in children occurs as a result of birth trauma or infectious lesions during intrauterine development. Also among the reasons are:
- Violation of fetal development.
- Heredity.
- Poisoning of the fetus during gestation.
But mixed hydrocephalus is also diagnosed in adults. It has the following development factors:
- Alcohol poisoning.
- Overdose of drugs.
- Trauma to the skull and infectious lesions of the nervous system.
- Thinning of bone tissue as a result of calcium deficiency or various diseases.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Hypertension.
The disease in children causes not only mental, but also intellectual development. In adults, the pathology may not manifest itself for a long time, but over time it causes a deterioration in the quality of life.
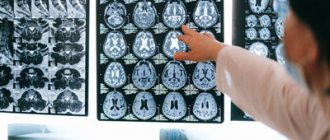
Signs of hydrocephalus in adults according to MRI
Manifestations of pathology in photographs can be direct or indirect. The first are associated with the expansion of the cerebral ventricles (III, IV and lateral (in the initial period - in the area of the anterior horns and body)), aqueduct and/or subarachnoid space (convexital, in the area of the basal cisterns, Sylvian fissures, etc.). Indirect signs on MRI scans:
- interventricular index over 0.5;
- periventricular edema with intense dropsy;
- downward displacement of the hypothalamus;
- local protrusion of the roof of the lateral ventricles, etc.
Additionally, tomograms determine the cause of cerebral hydrocele—the underlying disease.
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus at the MART clinic
When diagnosing hydrocephalus, the etiology and form of the disease are clarified. A neurologist will need anamnestic information about the nature of intrauterine development, childbirth, and the neonatal period in order to identify prematurity, hypoxia-ischemia, infection inside the womb and in infancy. In addition, it is necessary to determine intracranial pressure and its changes.
Based on the data obtained, a decision is made on the need and possibility of surgical intervention.
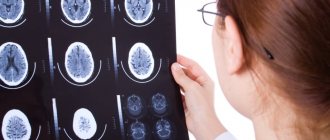
The most effective research method for diagnosing hydrocephalus is magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. MRI allows you to assess the size of the ventricles and cavities of the brain, its maturity, internal structure, as well as get an idea of the presence, extent and distribution of brain parenchyma, and identify malformations in the structure of the brain and its blood vessels.
Computed tomography is inferior to magnetic resonance imaging in image resolution and information content.
MRI images show non-communicating hydrocephalus. There is an expansion of the frontal and temporal horn in the lateral ventricles. There is no evidence of enlargement of the third and fourth ventricles.
At the MART medical center, research is carried out for you using modern equipment from leading foreign companies, including an expert-class magnetic resonance imaging scanner.