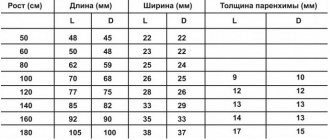
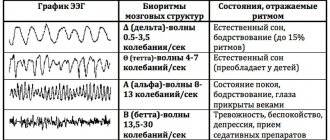
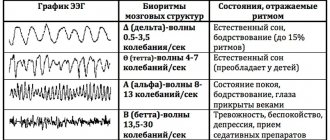
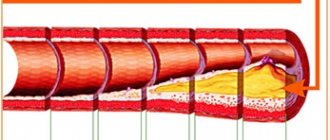
The brain is a complex and poorly understood human organ that is difficult to diagnose. However, the brain is the control center responsible for the operation of all systems in the body. Therefore, any pathological processes in it affect the physical and mental health of a person.
MRI is one of the methods for studying the brain to determine negative conditions in it. Diagnostics is prescribed for adults and children and is a safe examination method.
What it is
The method refers to a non-invasive examination using radio waves and a magnetic field. During the scanning process, the doctor receives an image showing parts of the brain. Diagnosis is carried out without radiography. The study reveals disturbances in the functioning of the nervous and vascular systems, aneurysms, and tumors.
Also, based on the results of the examination, the level of activity of the cerebral cortex is determined. When using a contrast agent, tissues are better visualized, which helps to more accurately identify pathologies.
Safety of magnetic resonance imaging in humans
Numerous clinical studies confirm the safety of this type of diagnosis.
The experimental results indicate that the level of radiation from the magnetic field of the device is identical to the parameters emitted by household appliances and modern gadgets.
There were no cases of negative impact of the examination on human health or manifestations of negative consequences as a result of the procedure. Therefore, MRI is one of the safest diagnostic methods.
Advantages of the method
Advantages of brain tomography:
- the patient does not experience pain during diagnosis;
- During the examination, no foreign substances are introduced into the human body;
- no ionizing radiation;
- clear images help to accurately recognize pathology and prescribe treatment;
- as prescribed by a specialist, an examination of the head and cervical/upper spine is carried out to assess the functional activity of the brain - based on the results, a safe method of surgical intervention is prescribed;
- areas of the brain hidden by the bones of the skull are examined - other methods do not diagnose these areas;
- MRI helps to obtain a complete picture of the brain and vascular system even without the use of a contrast agent;
- tumors and other pathologies are detected in the early stages of development.
Make an appointment now!
Is it possible to perform an MRI of the brain during pregnancy?
Yes, you can. The exception is the first trimester, but for serious indications, tomography can still be performed.
But the use of a contrast agent is prohibited during this period, since there are no official and long-term studies on the effect of drugs on the fetus. The teratogenic effect has not been proven, which was revealed in small experiments.
If it turns out that a woman had an MRI and then found out that she was pregnant, then she can safely carry the pregnancy to term. When using contrast in this case, consultation with a geneticist is indicated.
Why is an examination prescribed?
MRI diagnostics helps to recognize pathological changes in the soft tissues of the lining of the brain, inflammatory reactions, and disorders of the central nervous system. Also, with the help of an examination, the conditions of the parts of the head are studied: the visual and occipital lobes, the pituitary gland, the cerebellum, areas of thinking and memory, and the ventricles of the brain.
Before the procedure, the patient undergoes tests, the results of which determine the type of diagnosis. For example, tests showed that the patient had an excess level of the hormone prolactin. The doctor writes a referral for examination of the cerebellum.
Examination of the brain in a magnetic field helps determine the presence of:
- Multiple sclerosis - lesions of the myelin sheath of nerve fibers. The diagnosis determines the stage of the disease, the level of damage, after which the doctor prescribes therapy.
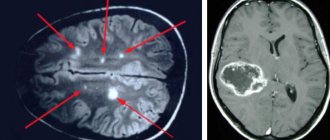
- Benign and malignant tumors. Brain scanning is used to identify the affected area, monitor the development of the tumor, as well as the treatment process.
- Disorders in the cerebral cortex - Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease. MRI determines the density of white and gray matter, the presence of pathologies in the subcortex and cortex of the head.
- Ischemic strokes, heart attacks. The images determine the area and density of ischemic lesions, the presence of cortical necrosis, the appearance of edema, and the stage of development of the disease.
- Brain injuries are damage to blood vessels and tissues due to trauma. Diagnostics reveals the first signs of VSD.
- Mental disorders of endogenous and exogenous types. The method helps to identify hereditary pathologies, changes after traumatic brain injury, viral infection, and poisoning with toxic substances. MRI diagnostics determines schizophrenia.
For children, head tomography is prescribed for the following pathologies:
- head injury, concussion after injury, intrauterine infectious processes;
- hypoxia, ischemia and other disruptions in brain development;
- epileptic seizures, cerebral hemorrhage;
- the first stages of multiple sclerosis;
- dangerous diseases such as pituitary adenoma, brain tumors, cysts and suspicions of them;
- a sharp deterioration in vision and hearing, malfunction of the inner ear;
- high intracranial pressure.
Diagnostics helps to study the state of the brain and its parts, identify the causes of headaches in children, and prevent the development of autism.
Differences between MRI and CT scan of the brain
Magnetic resonance imaging of the head differs from other diagnostic methods in the following:
- the examination is performed in 3-4 projections, which provides more information for identifying diseases and choosing treatment methods;
- pathologies are detected in the early stages of development - ischemic changes are detected 2-3 hours after a stroke;
- even minimal changes in the brain that cause multiple sclerosis are determined;
- parts of the brain that are not diagnosed by computed tomography (CT) are studied - the brain stem, the cerebellum.
When is a diagnosis prescribed?
A brain examination is prescribed for the following ailments:
- developmental anomalies and diseases of cerebral vessels;
- head injuries and bruises, cerebral hemorrhages;
- sharp deterioration of vision and hearing;
- tumor development;
- infectious reactions in the central nervous system - meningitis, HIV infections, abscesses;
- pituitary adenoma, epilepsy;
- pathologies of the base of the skull;
- multiple sclerosis, sinusitis, neurodegenerative diseases;
- aneurysms, thrombosis and other anomalies in the vessels of the head.
Diagnosis is also carried out after surgery. Prescribed for frequent migraines and fainting, tinnitus, sudden deterioration of memory and attention, impaired coordination of movements, and mental disorders.
When is an MRI with contrast needed?
Indications:
- Presumable neoplasm of a benign nature in the structures of the pituitary gland, which is not visualized with a standard MR procedure.
When prescribing an MRI with contrast, the degree to which multiple sclerosis is activated is determined.- The presence of cancerous or benign tumors in the brain and spinal cord, visualization of their boundaries.
- Contrast MRI will allow us to give an opinion on the state of brain structures in the postoperative period. During the scanning period, the doctor looks for the presence or absence of relapse of the pathology.
- Metastases to the spinal cord and brain. MRI, which uses a contrast component, will help find areas of metastasis.
- Diseases of the blood vessels supplying the brain. This may be a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, aneurysm, vasculitis or malformation.
Contraindications
Head tomography is not prescribed if the patient has absolute contraindications, but is allowed at the discretion of the doctor in case of relative contraindications. Diagnostics is prohibited if the following conditions exist:
- the patient has prosthetic heart valves, pacemakers or neurostimulators;
- presence of insulin pumps, inner and middle ear prostheses, cochlear implant;
- the patient has an Ilizarov apparatus;
- the presence of metal implants, ferromagnetic particles, fragments in the body.
Relative indications include:
- tremor, the patient’s inability to hold his breath for a long time during examination;
- presence of dental braces, dentures, stents, vena cava filters;
- heart failure, clip instead of gallbladder;
- pregnancy;
- claustrophobia;
- severe pain while standing still;
- coronary artery bypass grafting.
Relative contraindications:
- condition after operations: stenting of cardiac vessels (no more than 5 stents), coronary artery bypass grafting, microsurgical removal of the gallbladder (MRI is possible 1.5 months after surgery);
- MR angiography of the brain (after a hemorrhage) is carried out after 1.5-2 months, with large volumes of hemorrhage - much later (after complete resorption);
- condition after a puncture biopsy of the breast (the examination can be done after 6 months), after a biopsy of the prostate gland (in this case, an MRI is performed after 1-1.5 months), however, on the recommendation of the attending physician, the examination can be carried out earlier;
- condition after sectoral resection of the mammary gland (MR imaging is recommended to be performed no earlier than after 1-1.5 years);
- condition after radiation therapy of the mammary glands (MRI is performed after 1.5-2 years);
- metal braces, with the exception of sapphire braces and retainers (for MRI of the head
,
cervical spine
and
temporomandibular joints
); - the presence of a non-magnetic metal joint prosthesis localized in the area under study (when performing MRI of joints
); - MRI of the mammary glands
is not performed during radiation and chemotherapy.
Preparatory stage
The doctor, based on the test results, determines whether to perform a tomography with or without the introduction of a contrast agent. If the first option is chosen, then the patient does not take food or liquid 5 hours before the diagnosis. Before the procedure, you must remove all jewelry and accessories, watches and objects with metal elements.
During a consultation with a doctor, the patient reports the presence of chronic diseases, allergies to medications, claustrophobia, and pregnancy.
When preparing a child for a head tomography, it is not recommended to give him anything to drink or eat 3 hours before the diagnosis. If an MRI is performed with the administration of contrast, the examination is performed on an empty stomach. Before the procedure, the child should be shown to an allergist to check for an allergic reaction to the injected substance.
Comparison of the main contraindications by type of radiation diagnostics
| Type of contraindication | MRI | CT | Ultrasound | PAT |
| Pregnancy | Except the first trimester | It is forbidden | Acceptable | It is forbidden |
| Body mass | Standard up to 130 kg, on a special support up to 201 kg | Standard up to 130 kg, on a special support up to 201 kg | Doesn't matter | Standard up to 130 kg, on a special support up to 201 kg |
| Early postoperative period | Acceptable | Sometimes preferable, depends on the fabric | Doesn't matter | Not effective |
| Inflammatory process | Acceptable | Acceptable | Acceptable | Undesirable - risk of false positive results |
| Allergy to contrast occurs | Rarely | Often | No | Rarely, for iodine containing contrast - often |
| Implants, pacemaker | Let's lie. implants are tested for compatibility with 1.5 Tesla MRI | Acceptable | Acceptable | Acceptable |
| False claustrophobia | Acceptable during preparation | Rarely | Not found | Rarely |
| True claustrophobia | Acceptable with sedation | Rarely | Not found | Rarely |
| Cachexia (extreme wasting) | Acceptable during preparation | Acceptable during preparation | Acceptable | Acceptable during preparation |
| Hyperkinesis | Acceptable with sedation | Acceptable with sedation | Acceptable | Acceptable with sedation |
| Kidney failure | Preferably | Extremely careful | Acceptable | Extremely careful |
| Small children | Preferably with sedation | Extremely careful | Preferably | Extremely careful |
In all cases of doubts or questions about contraindications for MRI, you can call our polite, qualified administrators and get preliminary advice on your concerns and sign up for a doctor’s consultation and/or MRI diagnostics. You can also order a call at a convenient time or through the feedback form. Our phone.
Top of page
- The article uses materials from the national manual “Fundamentals of Radiation Diagnostics and Therapy” edited by prof. S.K.Ternova , GEOTAR-Media, 2013.
Medical editor of the article, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor MISCHENKO Andrey Vladimirovich
Diagnostic features
If a brain tomography is performed with the introduction of a contrast agent, the examination takes 1-1.5 hours.
Stages:
- the patient removes objects and clothing with metal elements;
- lies on the tomograph table on his back;
- the doctor administers a contrast agent intravenously;
- if there is tremors or inability to lie still, the patient takes sedatives;
- legs and arms are secured with belts, bolsters are placed under the neck;
- the table is pushed into the tomograph capsule - the doctor monitors the procedure from a special room with equipment;
- during the diagnosis, the patient hears slight noises of the tomograph operating - the procedure is safe and painless, a slight sensation is felt in the area of the injection of the substance;
- head diagnostics lasts 15 minutes - the patient is recommended to remain in a stationary position to obtain accurate scan results.
Preparing for an MRI with contrast
Preparation largely depends on which organs and systems will be examined.
The bladder is better visible when full, so you should refrain from urinating an hour before the test, and drink 2 glasses of water 20 minutes before the test.
If the gastrointestinal tract is examined, it is recommended to follow a low-carbohydrate diet for several days and exclude foods that contribute to excess gas formation: brown bread, legumes, milk, raw vegetables and fruits. The last full meal should be 6-8 hours before the procedure, but a light snack is allowed.
MRI of the head, neck, and joints does not require special preparation.
Clothing is preferable to a loose fit, without metal parts.
It is better to leave hairpins, piercings, jewelry, and watches at home.
Features of examination of children
Brain tomography in children is carried out under the drug n8a8p00ko70z0o-7m9, -6v5 Propofol is administered. Anesthesia helps keep the child still during diagnosis. Children over 5 years old are given a sedative and given psychological adjustment and support before the tomography.
During the examination, the baby is shown cartoons and toys. Some clinics use open tomographs, when only the child's head is placed in the capsule, and the parents stand nearby and hold his hand.
Before diagnosis, it is recommended to take the child to the toilet, remove electronic items and jewelry with metal inserts from clothes and body. Next, the child is dressed in special clothes, “introduced” to the tomograph and allowed to listen to how it works. This helps to calm the baby before the procedure and obtain his consent to the examination.
Side effects
After tomography, the patient may experience nausea, dizziness, vomiting, weakness, and disorientation in space. This is a normal reaction. It occurs in people with increased sensitivity, when there are metal objects on the patient’s body, and when the rules for preparing for an MRI are not followed. Unpleasant sensations go away on their own. However, if side effects do not disappear for a long time, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
If the rules are followed, the procedure takes place without pain or side effects. The images help doctors accurately determine the cause of the disease and prescribe effective treatment.