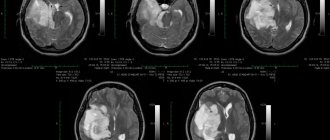
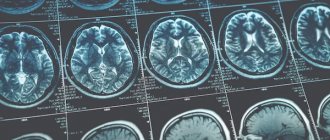
This type of brain tumor, such as astrocytoma, is the most common among neoplasms of the central nervous system and accounts for up to 50% of all tumors of the central nervous system. The favorite localization of cerebral astrocytoma is the cerebral cortex, less often - the cerebellum, brainstem and optic nerve. Specialists of the Northern Capital Medical Center help in the early diagnosis of this dangerous disease - our equipment allows us to identify the formation even before the first clinical symptoms appear.
Brain astrocytoma: what is it?
Prices for MRI of the brain What does a brain MRI show? MRI of the head MRI of the brain MRI of the pituitary gland MRI of the orbits MRI of the sinuses
Astrocytoma refers to a tumor of neuroglia in the brain. This is a special tissue that is auxiliary in the central nervous system - it helps transmit signals and supports and nourishes neurocytes. A brain tumor formed from star-shaped cells - astrocytes - is called an astrocytoma.
Diagnostics
The main method for identifying and examining patients suspected of having this type of tumor is tomography (CT or MRI). The best results are obtained when studying the brain using a contrast agent. This allows you to visualize the tumor, find out all the nuances of pathogenesis, choose the appropriate treatment method, and also determine the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy. PET diagnostics (positron emission tomography) with methionine is also widely used.
The note. The most reliable way to confirm the diagnosis and clarify the features of pathogenesis is through a biopsy (sampling of a tumor) followed by cytohistological analysis of the selected sample. Most often, the material is sent for analysis after surgical treatment.
Brain astrocytoma: causes of occurrence
Scientists have already identified the main factors that are present in most patients with astrocytoma:
- heredity burdened with cancer;
- unfavorable environmental, economic, social factors;
- traumatic brain injury;
- chronic concomitant diseases that cause intoxication of the body;
- hormonal changes in the body, such as pregnancy or menopause;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- occupational hazards (for example, radiation, oil refining or working with paint materials);
- viral infections with a high degree of oncogenicity.
The exact causes of the development of the disease have not yet been sufficiently studied, but it is easy to notice that modern people encounter most of the provoking factors quite often. It cannot be said for sure that these factors are absolute provocateurs of the development of cancer, but it has been proven that they have a detrimental effect on the body as a whole. Therefore, it is necessary to take care of your health and protect yourself from their excessive exposure, conduct timely preventive examinations, and also not delay diagnosis if complaints from the brain arise.
Life forecast
The life prognosis when diagnosed with anaplastic astrocytoma is generally unfavorable, due to the high degree of malignancy. Early benign stages often worsen into aggressive forms of cancer. After removal of anaplastic astrocytoma, there is a high probability of relapse. The most favorable prognosis for life is in the earliest stages with a low degree of malignancy. But even in this case, life expectancy is, as a rule, no more than five years. The worst prognosis for the terminal stage is that the patient will not live longer than a year.
Types of brain astrocytomas
According to the degree of malignancy, all astrocytomas of the brain are divided into 4 grades, which differ significantly in course and prognosis.
First degree of malignancy
It includes a benign tumor that has regular boundaries. Pathological cells in it divide evenly and have the same size and shape. The growth of the tumor process is slow, and the main treatment option is surgery. Brain surgery allows you to completely get rid of the tumor if it was detected at this stage. The tumor is common among children with its favorite localization in the cerebellum and brainstem.
The frequency of occurrence among all types of brain astrocytomas reaches 15%. This is the least dangerous variant of the course of the disease, however, if the location of the tumor mass is unsuccessful, even this relatively favorable variety can lead to serious symptoms - this happens if the tumor tissue presses on vital centers in the brain.
Second degree of malignancy
Such a tumor is a neoplasm that has blurred boundaries. Cells multiply more actively than in grade 1, but the growth of the tumor process still remains relatively slow. A characteristic feature of this course is the high frequency of relapses and the young age of patients (approximately 25 years).
Despite the vagueness of the formation, it is still benign, and therefore does not metastasize. But such a tumor has the danger of degenerating into a malignant neoplasm, and this can happen at any time, absolutely unpredictably. Therefore, it is necessary to perform timely surgical treatment and add chemotherapy treatment if necessary.
Third degree of malignancy
Such brain astrocytomas are characterized by higher malignancy and uncontrolled cell division. Cancer cells lose their identity and no longer resemble normal astrocytes. The tumor grows rapidly and has no clear boundaries. This variant of the course is more common among patients aged 40 years, and males are more often affected by the disease.
Treatment is significantly difficult, since metastases appear in the central nervous system quite early. Dissipation of astrocytoma may occur before clinical signs and complaints appear. It is extremely difficult to cure the disease radically at the stage of metastatic screenings, so this variant of the course is considered unfavorable.
Fourth degree of malignancy
The tumor is characterized by a more extensive pathological process and the presence of metastases in the brain and spinal cord. Cancer cells in this case multiply uncontrollably and rapidly; stopping their division is almost impossible at the present stage of development of medical science. The prognosis for patients with such astrocytoma is unfavorable.
It cannot be treated, and all therapy is supportive in nature and is aimed at possibly prolonging the patient’s life, reducing pain and reducing overall negative symptoms.
Anaplastic astrocytoma
It belongs to tumors of moderate malignancy, characterized by rapid infiltrative growth, that is, it has no clear boundaries. This prevents radical surgical removal of the astrocytoma.
This tumor is diagnosed more often in men in the age group from 35 to 50 years. It is localized more often in the cerebral hemispheres and is clinically manifested by focal symptoms. As the tumor grows, hypertension syndrome and increased intracranial pressure occur.
Symptoms of brain astrocytoma
The first clinical manifestations of the disease include a headache of a local or widespread nature, which gradually ceases to be relieved by taking painkillers. The nature of such pain can be either bursting and aching, or sudden and acute, which is associated with a sharp disruption of blood flow due to compression of the blood vessels by the tumor. Seizures are common, which is why it is important to seek medical help for children and adults who experience sudden seizures, even if they have only had one seizure. This serves as an absolute indication for a person to contact a specialized medical institution to see a neurologist or epileptologist for the purpose of further diagnosis and instrumental methods to confirm the diagnosis.
In addition to cramps and headaches, changes in the psycho-emotional background, fatigue, irritability, and impaired ability to concentrate and remember are often observed. Patients may experience nausea and vomiting of central origin, which does not bring relief. There are complaints of visual impairment on the opposite side from the formation of the tumor process, the gait becomes unstable and shaky. Such symptoms develop due to the growth of a tumor that compresses the brain, resulting in increased intracranial pressure. In some cases, a perversion of taste preferences, a desire to eat inedible objects, or a change in taste sensations may develop.
Symptoms will vary depending on the location of the astrocytoma. Therefore, a competent specialist, with the correct interpretation of the clinical picture, can determine the localization of the tumor process even before performing instrumental research methods, although, of course, their implementation remains absolutely necessary for this disease. So:
- a lesion of the frontal lobe will be characterized by a disturbance in the sphere of the emotional and psychological components, the patient’s criticism decreases, there is an unreasonably elevated mood, half of the body on the opposite side of the lesion may be immobilized;
- with the development of a tumor in the temporal lobe, symptoms such as impaired memory and speech, poor coordination of movements will be observed, very often the first symptom is convulsive episodes and auditory disorders;
- astrocytoma of the brain in the parietal lobe is accompanied by a decrease in tactile and pain sensitivity from the trunk and limbs, agnosia (impaired perception of surrounding objects), the inability to perform simple manual manipulations and a violation of written speech;
- When a tumor affects the cerebellum, the patient cannot properly coordinate his movements and, most often, is unable to maintain balance. There is pronounced unsteadiness of gait, the person cannot move without support;
- the pathological process in the occipital lobe includes visual hallucinations and decreased vision on the opposite side of the lesion.
Treatment using the CyberKnife system
For a group of brain tumors, which are combined into the “astrocytoma” , radiosurgical treatment on CyberKnife has an extremely selective use. Typically, an astrocytoma (a type of glioma , a glial tumor ) is diagnosed after the tumor has grown into adjacent brain structures and caused neurological symptoms due to disruption of normal brain function.
Non-surgical treatment of astrocytoma - CyberKnife. The area highlighted in red corresponds to the tumor volume into which a high dose of radiation will be delivered
In this case, the tumor volume already exceeds the maximum recommended for treatment with CyberKnife. This is why treatment of all types of astrocytoma ( pilocytic astrocytoma , fibrillary astrocytoma , anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma ) usually begins with surgical removal of as much of the tumor and damaged brain tissue as possible, followed by irradiation of the tumor bed.
If the volume of the tumor bed (the place of contact between the preserved brain tissue and the tissue removed as a result of neurosurgical operation does not exceed the recommended values, then radiosurgical treatment of this area is performed using CyberKnife.
However, if the tumor is inoperable due to the patient’s condition, its deep location near critical areas, or its location in functionally important parts of the brain, the patient may be prescribed a combination of treatment, including radiation therapy using a linear accelerator and radiosurgery using a CyberKnife.
Diagnosis of brain astrocytoma
Symptoms of brain astrocytoma are nonspecific, so timely diagnosis is sometimes difficult. The examination plan is prescribed by a clinical physician - a neurologist or neurosurgeon. At the Medical Center “Medicine of the Northern Capital”, experienced radiology doctors can recommend diagnostic procedures that must be performed before visiting a specialized specialist - in this case, patients come to the attending physician with ready-made instrumental examinations. The clinician must carefully collect anamnestic data, identify family history, occupational hazards and other risk factors listed above. Pays attention to complaints, their intensity and duration, all this helps to identify the reason why a person decided to go to a specialized medical institution. For diagnosis, laboratory research methods are used, such as a general blood and urine test, a biochemical blood test and an analysis for tumor markers.
After a conversation with the patient, the following instrumental research methods may be prescribed:
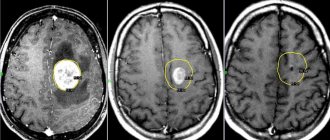
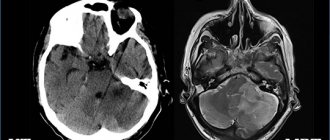
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This study is a modern diagnostic method that is highly informative and is usually used when a tumor is suspected. With astrocytoma, areas of altered brain tissue will be visible on the tomogram. The tumor can compress nearby brain structures, thereby causing their deformation or compression. To improve the effect and more accurately determine the extent of the tumor process, contrasting with drugs from the lanthanide group (gadolinium) is used, which makes it possible to differentiate glial tumors from each other. The more “malignant” the process, the more contrast agent is absorbed. If we consider the 1st degree of malignancy, then on the tomogram the tumor will appear as a round formation with regular boundaries and a clear contour. Further degrees of severity of the tumor process do not have clear boundaries, and this is manifested in the image by an increase in edema, loss of homogeneity of the tumor, in the later stages, multiple zones of necrosis and an increase in the number of hemorrhages.
- Computed tomography (CT). This research method has the same advantages as MRI, but due to its structural features it is the subject of choice for people suffering from claustrophobia. Ideal for tumor growth in the skull bones.
- Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck (USDG BCA). Dopplerography allows you to assess the condition of blood vessels and exclude pathology of the vascular bed, and identify the severity of the disease.
- A biopsy is a mandatory component of the study, as it can reveal the heterogeneity of cellular structures and confirm the diagnosis of brain astrocytoma. The biopsy is performed in an open operating room, that is, in addition to the instruments intended for puncture, there are instruments for surgical intervention. If microscopic examination of the biopsy material confirms the presence of cancer cells, surgical intervention aimed at excision of the tumor is possible.
- Cerebrospinal fluid examination. When studying the component of the cerebrospinal fluid, an increase in the amount of protein catches the eye, b-lipoproteins appear, which should not be normal, and the total number of cells that have different composition and shape also increases. Such diagnostics are performed only in specialized medical institutions.
- Electroencephalography (EEG) has a characteristic clinical feature. At first, nerve impulses travel slowly, then there is a sharp increase in amplitude and their alternation, which makes it possible to suspect a focus of pathological activity that affects the reticular formation. The electroencephalogram of such patients consists of unevenly spaced notches with different frequencies of oscillatory movements;
- If necessary, neurologists can additionally prescribe an examination by an ophthalmologist, an otorhinolaryngologist, and certainly a neurosurgeon and an anesthesiologist. The anesthesiologist, depending on gender, age, weight and the presence of concomitant diseases, must select the correct anesthesia that would be useful during the operation.
Clinical manifestations
Fibrillary astrocytoma of the brain is characterized by benignity and slow growth, so symptoms appear gradually. Much depends on the location of the tumor and the stage of the pathological process. Early symptoms are not typical for fibrillary astrocytoma. Clinical signs begin to appear as the disease progresses. Most often, patients experience the following negative symptoms:
- dizziness and headaches;
- nausea, vomiting and other dyspeptic symptoms not associated with poisoning;
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- mental disorders of the epileptic type.
Note. Local signs of fibrillary astrocytoma of the brain include: visual pathologies, impaired coordination, hearing impairment, problems with speech, memory, and others. In this case, the symptoms depend on the location of the tumor.
If unfavorable symptoms are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor to determine its nature.
Treatment of astrocytoma
Treatment depends on the degree of malignancy of the pathological process, the characteristics of its localization and size.
Surgical intervention is prescribed to patients to excise the astrocytoma, while nearby healthy tissue is removed at the same time. This is important because the minimum number of cancer cells is enough for a relapse to occur. When removing a tumor of low differentiation and high degree of malignancy, chemotherapy or radiation therapy is added to the operation. However, operations for malignant neoplasms are more supportive in nature; as a rule, the infiltration of surrounding brain tissue is so strong that the distribution of healthy and damaged tissue is simply impossible, especially at a late stage the tumor gives metastases.
Chemo-radiation therapy is a drug or radiotherapy treatment aimed at suppressing the growth of cancer cells and destroying them. Damage to healthy tissues is often observed.
Types and stages
There is treatment for anaplastic astrocytoma, but it is determined solely on the basis of diagnostic data and the course of the disease. Today, there are four stages of disease development, which form further forecasts:
- Stage 1 of the disease - it is a benign tumor that grows quite slowly. At this stage, treatment will be more effective and the prognosis will be positive;
- Anaplastic astrocytoma of the 2nd degree of malignancy - the neoplasm slowly increases, signs of degeneration from benign to malignant appear. The boundaries of such a tumor are at a certain distance from the tissues that surround it;
- Grade 3 anaplastic astrocytoma is a malignant formation, and aggressive growth forms here. It should immediately be noted that this pathology is extremely difficult to irradiate;
- Astrocytoma grade 4 - the formation is called glioblastoma, and is considered the most dangerous. Treatment at this stage is extremely rarely favorable. This type of astrocytoma most often actively develops in adults after forty years.